|
Wherry Albion
A wherry is a type of boat that was traditionally used for carrying cargo or passengers on rivers and canals in England, and is particularly associated with the River Thames and the River Cam. They were also used on the Broadland rivers of Norfolk and Suffolk. Regional usage in Great Britain London passenger wherries evolved into the Thames skiff, a gentleman's rowing boat. Wherries were clinker-built with long overhanging bows so that patrons could step ashore dryshod before landing stages were built along the river. It is the long angled bow that distinguishes the wherry and skiff from the gig and cutter which have steeper bows following the rise of the Royal Navy, and the building of landing stages. The use of wherries on the River Cam in Cambridge was common and is described by Daniel Defoe in his journey through England. The use of wherries on the River Cam preceded the popularity of punting by Cambridge University students. By the late 18th century, a name was give ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wherry01
A wherry is a type of boat that was traditionally used for carrying cargo or passengers on rivers and canals in England, and is particularly associated with the River Thames and the River Cam. They were also used on the Broadland rivers of Norfolk and Suffolk. Regional usage in Great Britain London passenger wherries evolved into the Thames skiff, a gentleman's rowing boat. Wherries were clinker-built with long overhanging bows so that patrons could step ashore dryshod before landing stages were built along the river. It is the long angled bow that distinguishes the wherry and skiff from the gig and cutter which have steeper bows following the rise of the Royal Navy, and the building of landing stages. The use of wherries on the River Cam in Cambridge was common and is described by Daniel Defoe in his journey through England. The use of wherries on the River Cam preceded the popularity of punting by Cambridge University students. By the late 18th century, a name was given ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge became an important trading centre during the Roman and Viking ages, and there is archaeological evidence of settlement in the area as early as the Bronze Age. The first town charters were granted in the 12th century, although modern city status was not officially conferred until 1951. The city is most famous as the home of the University of Cambridge, which was founded in 1209 and consistently ranks among the best universities in the world. The buildings of the university include King's College Chapel, Cavendish Laboratory, and the Cambridge University Library, one of the largest legal deposit libraries in the world. The city's skyline is dominated by several college buildings, along with the spire of the Our Lady and the English Martyrs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Act Of Parliament
Acts of Parliament, sometimes referred to as primary legislation, are texts of law passed by the Legislature, legislative body of a jurisdiction (often a parliament or council). In most countries with a parliamentary system of government, acts of parliament begin as a Bill (law), bill, which the legislature votes on. Depending on the structure of government, this text may then be subject to assent or approval from the Executive (government), executive branch. Bills A draft act of parliament is known as a Bill (proposed law), bill. In other words, a bill is a proposed law that needs to be discussed in the parliament before it can become a law. In territories with a Westminster system, most bills that have any possibility of becoming law are introduced into parliament by the government. This will usually happen following the publication of a "white paper", setting out the issues and the way in which the proposed new law is intended to deal with them. A bill may also be introduced in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elizabethan Era
The Elizabethan era is the epoch in the Tudor period of the history of England during the reign of Queen Elizabeth I (1558–1603). Historians often depict it as the golden age in English history. The symbol of Britannia (a female personification of Great Britain) was first used in 1572, and often thereafter, to mark the Elizabethan age as a renaissance that inspired national pride through classical ideals, international expansion, and naval triumph over Spain. This "golden age" represented the apogee of the English Renaissance and saw the flowering of poetry, music and literature. The era is most famous for its theatre, as William Shakespeare and many others composed plays that broke free of England's past style of theatre. It was an age of exploration and expansion abroad, while back at home, the Protestant Reformation became more acceptable to the people, most certainly after the Spanish Armada was repelled. It was also the end of the period when England was a separate r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watermen
A waterman is a river worker who transfers passengers across and along city centre rivers and estuaries in the United Kingdom and its colonies. Most notable are those on the River Thames and River Medway in England, but other rivers such as the River Tyne and River Dee, Wales, also had their watermen who formed guilds in medieval times. Waterman can also be a person who navigates a boat carrying passengers. These boats were often rowing boat or boats with sails. Over the years watermen acquired additional skills such as local pilotage, mooring vessels at berths, jetties, buoys, and docks, and acting as helmsman aboard large vessel. Watermen in the United Kingdom: 1197 to 1859 Watermen or wherrymen were an essential part of early London. Using a small boat called a wherry or skiff they would ferry passengers along and across the river. With bad rural roads and narrow congested city streets, the Thames was the most convenient highway in the region. Until the mid-18th century Londo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for two millennia. The City of London, its ancient core and financial centre, was founded by the Romans as '' Londinium'' and retains its medieval boundaries.See also: Independent city § National capitals The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has for centuries hosted the national government and parliament. Since the 19th century, the name "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between the counties of Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent, and Hertfordshire, which largely comprises Greater London, governed by the Greater London Authority.The Greater London Authority consists of the Mayor of London and the London Assembly. The London Mayor is distinguished fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tideway
The Tideway is a part of the River Thames in England which is subject to tides. This stretch of water is downstream from Teddington Lock. The Tideway comprises the upper Thames Estuary including the Pool of London. Tidal activity Depending on the time of year, the river tide rises and falls twice a day by up to 7 m (24 ft). Because the tide goes against the outflow of fresh water from the Thames Basin, it takes longer to subside (6–9 hours) than it does to flow in (4–5 hours). London Bridge is used as the basis for published tide tables giving the times of high tide. High tide reaches Putney about 30 minutes later. Low-lying banks of London are naturally vulnerable to flooding by storm surges. The threat has increased due to a slow but continuous rise in high water level, caused by the extremely slow 'tilting' of Britain (up in the north and down in the south) due to post-glacial rebound and the gradual rise in sea levels due to climate change. The city and sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Ezekiel
The Book of Ezekiel is the third of the Latter Prophets in the Tanakh and one of the major prophetic books, following Isaiah and Jeremiah. According to the book itself, it records six visions of the prophet Ezekiel, exiled in Babylon, during the 22 years from 593 to 571 BCE, although it is the product of a long and complex history and does not necessarily preserve the very words of the prophet. The visions, and the book, are structured around three themes: (1) Judgment on Israel (chapters 1–24); (2) Judgment on the nations (chapters 25–32); and (3) Future blessings for Israel (chapters 33–48). Its themes include the concepts of the presence of God, purity, Israel as a divine community, and individual responsibility to God. Its later influence has included the development of mystical and apocalyptic traditions in Second Temple and Judaism and Christianity. Structure Ezekiel has the broad three-fold structure found in a number of the prophetic books: oracles of wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coverdale Bible
The Coverdale Bible, compiled by Myles Coverdale and published in 1535, was the first complete Modern English translation of the Bible (not just the Old Testament or New Testament), and the first complete printed translation into English (cf. Wycliffe's Bible in manuscript). The later editions (folio and quarto) published in 1537 were the first complete Bibles printed in England. The 1537 folio edition carried the royal licence and was therefore the first officially approved Bible translation in English. The Psalter from the Coverdale Bible was included in the Great Bible of 1540 and the Anglican ''Book of Common Prayer'' beginning in 1662, and in all editions of the U.S. Episcopal Church ''Book of Common Prayer'' until 1979. History The place of publication of the 1535 edition was long disputed. The printer was assumed to be either Froschover in Zürich or Cervicornus and Soter (in Cologne or Marburg). Since the discovery of Guido Latré, in 1997, the printer has been identif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Galloway News
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyne & Wear Archives & Museums
Tyne & Wear Archives & Museums (TWAM) is a regional group of United Kingdom national museums and the county archives service located across the Tyne and Wear area of north-east England. They have been administered by a joint board of local authorities since the abolition of the Tyne and Wear Metropolitan County Council in 1986. They receive financial support from the five local authorities they operate within and since 2012, Arts Council England. The service is one of those specified in the Designation Scheme administered by Arts Council England. In the past, the service received additional financial support from the Department for Culture, Media and Sport. Since 2021, the director has been Keith Merrin. Museums Tyne & Wear Archives & Museums are responsible for managing the 9 museums and galleries below and the county archives. They also share use of the Regional Museums Store at Beamish Museum. Archives Tyne and Wear Archives are based within the Discovery Museum. Galler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norfolk Wherry
The Norfolk wherry is a type of boat used on The Broads in Norfolk and Suffolk, England. Three main types were developed over its life, all featuring the distinctive gaff rig with a single, high-peaked sail and the mast stepped well forward. Development of the wherry Wherries were sail and oar craft dating back to at least 1604. These were small craft, in 1727 being of 8 tons net tonnage. They were still sail and oar boats, fitted with hoops and canvas tilts for the comfort of their passengers. They would have provided a service carrying passengers and small perishable cargoes. Alongside these early wherries were the bigger keels, which were transom-sterned clinker-built barges with a square sail on a mast stepped amidships of about by and able to carry 30 tons of goods. The keel had been built since the Middle Ages and the design probably went back to the Viking invasion. After 1800, the Norfolk Keel (or 'keel wherry') disappeared, partly because a wherry could be saile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



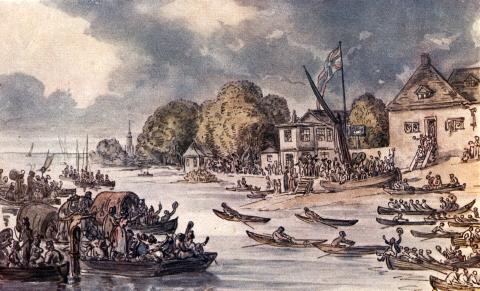


.png)
