|
Wetarese
Wetarese is an Austronesian language of Wetar, an island in the south Maluku, Indonesia, and of the nearby islands Liran and Atauro, the latter island separate from the mainland of East Timor, north of Dili. Background The four identified principal varieties of Wetarese on Wetar – Aputai, Iliʼuun, Parai and Tugun – are distinct enough that some may consider them to be different languages. Half of Wetarese speakers live on the island of Atauro in East Timor, where three closely related dialects (presumably of Iliuun) are spoken: 'Rahesuk' (''Rasua'') in the center, 'Resuk' (''Hresuk'') in the southeast, and 'Adabe' (''Raklungu'') in the southwest. ''Dadua'' in the extreme north is a subdialect of Rahesuk, and has been reported to be intelligible with the Iliuun of Liran Island. About half the Dadua population has moved to Timor, on the coast of Manatuto district, where it has undergone influence from Galoli. Wetarese is closely related to Galoli, spoken on the nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
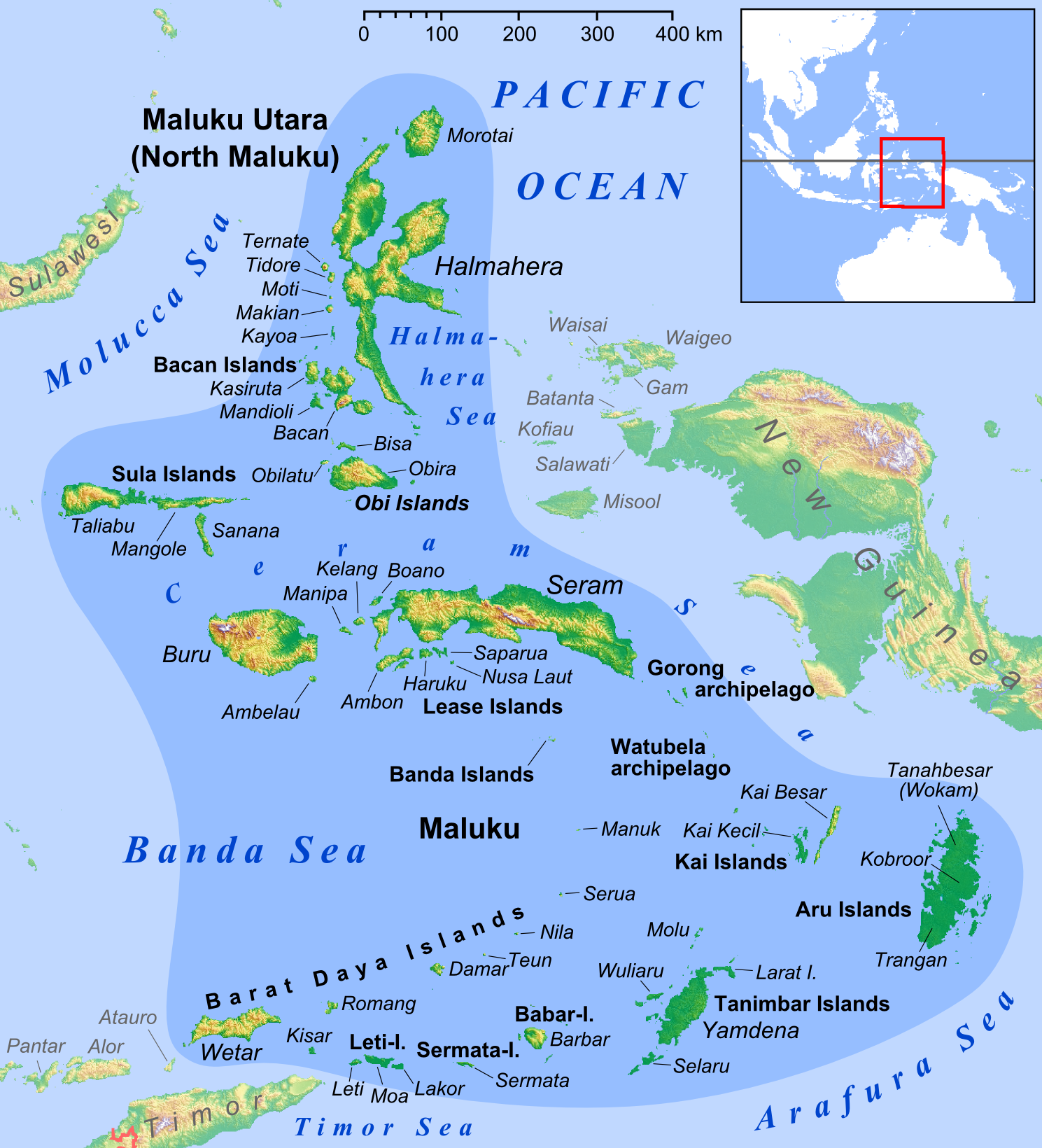
Liran
Liran ( id, Pulau Liran, ) is a small island off the southwest coast of Wetar Island, Indonesia. Administratively it is part of West Wetar District (''Kecamatan Wetar Barat'') within the Southwest Maluku Regency (''Kabupaten Maluku Barat Daya''). The East Timorese island Atauro is 12 km to the southwest. Liran is the westernmost of the Barat Daya Islands in the province of Maluku (Indonesian province), Maluku. It covers an area of 39.14 km2 (including minor offshore islands) and had 841 inhabitants in 2019.Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2021. Liran is surrounded by coral reefs. It has a small population, who speak Wetarese. They primarily live in the small village Ustutun on the east coast of the island, which also serves as the administrative centre for the West Wetar District. There is also a list of lighthouses in Indonesia, lighthouse. References External linksSatellite photo of Liran, off the coast of Wetar Barat Daya Islands Islands of the Maluku Islands {{ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
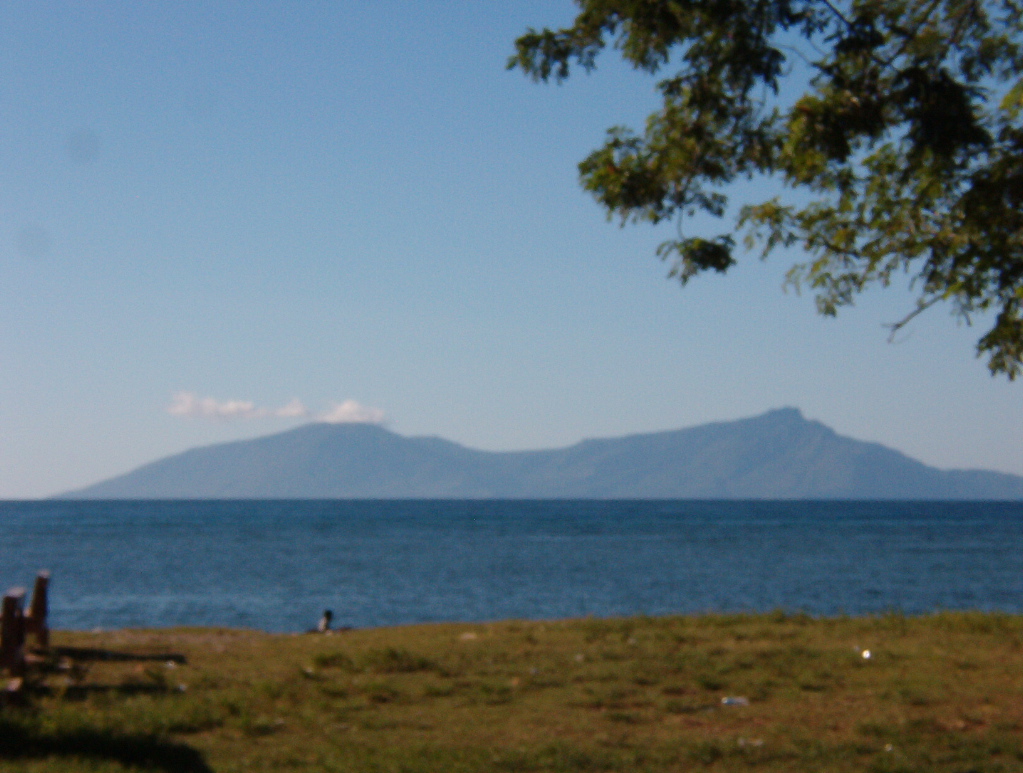
Wetar
Wetar is a tropical island which belongs to the Indonesian province of Maluku and is the largest island of the Maluku Barat Daya Islands (literally ''Southwest Islands'') of the Maluku Islands. It lies east of the Lesser Sunda Islands, which include nearby Alor and Timor, but it is politically part of the Maluku Islands. To the south, across the Wetar Strait, lies the island of Timor; at its closest it is 50 km away. To the west, across the Ombai Strait, lies the island of Alor. To the southwest is the very small island of Liran, which is also part of Wetar district (''kecamatan'') and, further southwest, the small East Timorese island of Atauro. To the north is the Banda Sea and to the east lie Romang and Damar Islands, while to the southeast lie the other principal islands of the Barat Daya Islands. Including Liran, Wetar has an area of 2,651.9 km2, and had a population of 7,916 at the 2010 Census. Wetar is one of the 92 officially listed outlying islands of Indo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetar Island
Wetar is a tropical island which belongs to the Indonesian province of Maluku and is the largest island of the Maluku Barat Daya Islands (literally ''Southwest Islands'') of the Maluku Islands. It lies east of the Lesser Sunda Islands, which include nearby Alor and Timor, but it is politically part of the Maluku Islands. To the south, across the Wetar Strait, lies the island of Timor; at its closest it is 50 km away. To the west, across the Ombai Strait, lies the island of Alor. To the southwest is the very small island of Liran, which is also part of Wetar district (''kecamatan'') and, further southwest, the small East Timorese island of Atauro. To the north is the Banda Sea and to the east lie Romang and Damar Islands, while to the southeast lie the other principal islands of the Barat Daya Islands. Including Liran, Wetar has an area of 2,651.9 km2, and had a population of 7,916 at the 2010 Census. Wetar is one of the 92 officially listed outlying islands of Indo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galoli Language
The Galoli, or Galolen, are a people of East Timor with a population of about 50,000, primarily along the northern coast of the district of Manatuto. To the west lies the Mambai people. There is an old colony on the southern coast of Wetar island, the Talo, who speak the Talur dialect. Their language, also known as Galoli, is one of the Timor–Babar group of Austronesian languages. It is one of the national languages designated by the constitution of East Timor. Because the area was used as a trading center for different cultures, there are many foreign loan words in the vocabulary, principally from Moluccan and Malay languages. Although it is not spoken by as many people as other national languages, it was adopted by the Roman Catholic Church in the district of Manatuto and thus has become fixed in grammars and dictionaries. ''Dadu'a'' is erroneously listed in some sources as a dialect of Galoli (e.gGlottolog, but actually represents a transplanted population of the Atauro di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atauro Island
Atauro ( pt, Ilha de Ataúro, Tetum and Indonesian: ''Pulau Atauro'' or ''Ata'uro''), also known as Kambing Island ( id, Pulau Kambing), is an island and municipality ( pt, Município Ataúro, links=no, tet, Munisípiu Atauro, links=no or ) of East Timor. Atauro is a small oceanic island situated north of Dili, on the extinct Wetar segment of the volcanic Inner Banda Arc, between the Indonesian islands of Alor and Wetar. The nearest island is the Indonesian island of Liran, to the northeast. At the 2015 census, it had 9,274 inhabitants. Atauro was one of the administrative posts (formerly subdistricts) of Dili Municipality until it became a separate municipality with effect from 1 January 2022. Etymology ''Atauro'' means 'goat' in the local language, and the island is also known as ''Kambing Island'' (''Pulau Kambing'') by the Indonesians (''Kambing'' means 'goat' in Indonesian). The island was so named because of the large number of goats kept there. Geography At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timoric Languages
The Timoric languages are a group of Austronesian languages (belonging to the Central–Eastern subgroup) spoken on the islands of Timor, neighboring Wetar, and (depending on the classification) Southwest Maluku to the east. Within the group, the languages with the most speakers are Uab Meto of West Timor, Indonesia and Tetum of East Timor, each with about half a million speakers, though in addition Tetum is an official language and a lingua franca among non-Tetum East Timorese. Languages Hull (1998) & van Engelenhoven (2009) Geoffrey Hull (1998) proposes a Timoric group as follows: *Timoric A ("Extra-Ramelaic", Fabronic; whatever is not Ramelaic) **West: Dawan (Uab Meto)– Amarasi, Helong, Roti ( Bilba, Dengka, Lole, Ringgou, Dela-Oenale, Termanu, Tii) **Central: Tetun, Bekais, Habu **North: Wetar, Galoli **East: Kairui, Waimaha, Midiki, Naueti *Timoric B ("Ramelaic", near the Ramelau range) **West: Kemak, Tukudede **Central: Mambai **East (Idalaka): Id ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atauro
Atauro ( pt, Ilha de Ataúro, Tetum and Indonesian: ''Pulau Atauro'' or ''Ata'uro''), also known as Kambing Island ( id, Pulau Kambing), is an island and municipality ( pt, Município Ataúro, links=no, tet, Munisípiu Atauro, links=no or ) of East Timor. Atauro is a small oceanic island situated north of Dili, on the extinct Wetar segment of the volcanic Inner Banda Arc, between the Indonesian islands of Alor and Wetar. The nearest island is the Indonesian island of Liran, to the northeast. At the 2015 census, it had 9,274 inhabitants. Atauro was one of the administrative posts (formerly subdistricts) of Dili Municipality until it became a separate municipality with effect from 1 January 2022. Etymology ''Atauro'' means 'goat' in the local language, and the island is also known as ''Kambing Island'' (''Pulau Kambing'') by the Indonesians (''Kambing'' means 'goat' in Indonesian). The island was so named because of the large number of goats kept there. Geography At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Consonant
In phonetics, a nasal, also called a nasal occlusive or nasal stop in contrast with an oral stop or nasalized consonant, is an occlusive consonant produced with a lowered velum, allowing air to escape freely through the nose. The vast majority of consonants are oral consonants. Examples of nasals in English are , and , in words such as ''nose'', ''bring'' and ''mouth''. Nasal occlusives are nearly universal in human languages. There are also other kinds of nasal consonants in some languages. Definition Nearly all nasal consonants are nasal occlusives, in which air escapes through the nose but not through the mouth, as it is blocked (occluded) by the lips or tongue. The oral cavity still acts as a resonance chamber for the sound. Rarely, non-occlusive consonants may be nasalized. Most nasals are voiced, and in fact, the nasal sounds and are among the most common sounds cross-linguistically. Voiceless nasals occur in a few languages such as Burmese, Welsh, Icelandic and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tap Consonant
In phonetics, a flap or tap is a type of consonantal sound, which is produced with a single contraction of the muscles so that one articulator (such as the tongue) is thrown against another. Contrast with stops and trills The main difference between a tap or flap and a stop is that in a tap/flap there is no buildup of air pressure behind the place of articulation and consequently no release burst. Otherwise a tap/flap is similar to a brief stop. Taps and flaps also contrast with trills, where the airstream causes the articulator to vibrate. Trills may be realized as a single contact, like a tap or flap, but are variable, whereas a tap/flap is limited to a single contact. When a trill is brief and made with a single contact it is sometimes erroneously described as an (allophonic) tap/flap, but a true tap or flap is an active articulation whereas a trill is a passive articulation. That is, for a tap or flap the tongue makes an active gesture to contact the target place of articul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trill Consonant
In phonetics, a trill is a consonantal sound produced by vibrations between the active articulator and passive articulator. Standard Spanish as in , for example, is an alveolar trill. A trill is made by the articulator being held in place and the airstream causing it to vibrate. Usually a trill vibrates for 2–3 contacts, but may be up to 5, or even more if geminate. However, trills may also be produced with only one contact. While single-contact trills are similar to taps and flaps, a tap or flap differs from a trill in that it is made by a muscular contraction rather than airstream. Phonemic trills Trill consonants included in the International Phonetic Alphabet: * – Voiced alveolar trill * – Voiceless alveolar trill * – Voiced bilabial trill * – Voiceless bilabial trill * – Voiced retroflex trill * – Voiced uvular trill * – Voiceless uvular trill * – voiced epiglottal trill * – voiceless epiglottal trill In addition, * – velopharyngeal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Consonant
A lateral is a consonant in which the airstream proceeds along one or both of the sides of the tongue, but it is blocked by the tongue from going through the middle of the mouth. An example of a lateral consonant is the English ''L'', as in ''Larry''. Lateral consonants contrast with central consonants, in which the airstream flows through the center of the mouth. For the most common laterals, the tip of the tongue makes contact with the upper teeth (see dental consonant) or the upper gum (see alveolar consonant), but there are many other possible places for laterals to be made. The most common laterals are approximant Approximants are speech sounds that involve the articulators approaching each other but not narrowly enough nor with enough articulatory precision to create turbulent airflow. Therefore, approximants fall between fricatives, which do produce a ...s and belong to the class of liquid consonant, liquids, but lateral fricative consonant, fricatives and affricate co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Timor
East Timor (), also known as Timor-Leste (), officially the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is an island country in Southeast Asia. It comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor, the exclave of Oecusse on the island's north-western half, and the minor islands of Atauro and Jaco. Australia is the country's southern neighbour, separated by the Timor Sea. The country's size is . Dili is its capital and largest city. East Timor came under Portuguese influence in the sixteenth century, remaining a Portuguese colony until 1975. Internal conflict preceded a unilateral declaration of independence and an Indonesian invasion and annexation. Resistance continued throughout Indonesian rule, and in 1999 a United Nations–sponsored act of self-determination led to Indonesia relinquishing control of the territory. On 20 May 2002, as ''Timor-Leste'', it became the first new sovereign state of the 21st century. The national government runs on a semi-presidential system, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |