|
Western Finland
Western Finland ( fi, Länsi-Suomen lääni, sv, Västra Finlands län) was a province of Finland from 1997 to 2009. It bordered the provinces of Oulu, Eastern Finland and Southern Finland. It also bordered the Gulf of Bothnia towards Åland. Tampere was the largest city of the province. History On September 1, 1997 the Province of Turku and Pori, the Province of Vaasa, the Province of Central Finland, the northern parts of the Province of Häme and the western parts of the Mikkeli Province were joined to form the then new Province of Western Finland. All the provinces of Finland were abolished on January 1, 2010. Administration The State Provincial Office was a joint regional administrative authority of seven ministries. The State Provincial Office served at five localities; the main office was placed in Turku, and regional service offices were located in Jyväskylä, Tampere, Vaasa, and Pori. Approximately 350 persons worked at the State Provincial Office. The agenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jyväskylä
Jyväskylä () is a city and municipality in Finland in the western part of the Finnish Lakeland. It is located about 150 km north-east from Tampere, the third largest city in Finland; and about 270 km north from Helsinki, the capital of Finland. The Jyväskylä sub-region includes Jyväskylä, Hankasalmi, Laukaa, Petäjävesi, Toivakka, and Uurainen. Other border municipalities of Jyväskylä are Joutsa, Jämsä and Luhanka. Jyväskylä is the largest city in the region of Central Finland and in the Finnish Lakeland; as of , Jyväskylä had a population of . The city has been one of the fastest-growing cities in Finland during the 20th century, when in 1940, there were only 8,000 inhabitants in Jyväskylä. Elias Lönnrot, the compiler of the Finnish national epic, the '' Kalevala'', gave the city the nickname " Athens of Finland". This nickname refers to the major role of Jyväskylä as an educational centre. The works of the notable Finnish architect, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, 2 United Nations General Assembly observers#Present non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (2 states, both in associated state, free association with New Zealand). Compi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Häme Province
The Province of Häme ( fi, Hämeen lääni, sv, Tavastehus län) was a province of Finland from 1831 to 1997. In 1997 the southern parts with Kanta-Häme, Päijät-Häme was merged with the province of Uusimaa and Kymi into the new Province of Southern Finland. The northern part with Pirkanmaa was merged with the provinces of Vaasa, Central Finland, Turku and Pori into the new Province of Western Finland. The province corresponds roughly to the current regions of Kanta-Häme, Päijät-Häme and Pirkanmaa. Maps Municipalities in 1997 (cities in bold) * Asikkala * Forssa * Hattula * Hauho * Hausjärvi * Hollola * Humppila * Hämeenkoski * Hämeenkyrö * Hämeenlinna * Ikaalinen * Janakkala * Jokioinen * Juupajoki * Kalvola * Kangasala * Kihniö * Kuhmalahti * Kuorevesi * Kuru * Kylmäkoski * Kärkölä * Lahti * Lammi * Lempäälä * Loppi * Luopioinen * Längelmäki * Mouhijärvi * Mänttä * Nastola * Nokia * Orivesi * Padasjoki * Parkano * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akaa
Akaa ( sv, Ackas) is a town and a municipality in Pirkanmaa, Finland. It was created on January 1, 2007 when the town of Toijala and the municipality of Viiala were united into a single town. The municipality of Kylmäkoski was consolidated with Akaa on 1 January 2011. The convert has a population of () and covers an area of of which is water. The population density is . Geography Akaa's neighboring municipalities are Hämeenlinna, Lempäälä, Urjala, Valkeakoski and Vesilahti. The city of Tampere, the capital of the Pirkanmaa region, is located north of Akaa. Akaa, as well as the town of Toijala and the former municipality of Viiala are situated by the lake Vanajavesi, which is the most central watercourse in the Tavastia Proper region as well as in the southern parts of the Pirkanmaa region. Demographics In 2020, 16.5% of the population of Akaa was under the age of 15, 59.3% were aged 15 to 64, and 24.2% were over the age of 65. The average age was 44.6, over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipalities Of Finland
The municipalities ( fi, kunta; sv, kommun) represent the local level of administration in Finland and act as the fundamental, self-governing administrative units of the country. The entire country is incorporated into municipalities and legally, all municipalities are equal, although certain municipalities are called cities or towns ( fi, kaupunki; sv, stad). Municipalities have the right to levy a flat percentual income tax, which is between 16 and 22 percent, and they provide two thirds of public services. Municipalities control many community services, such as schools, health care and the water supply, and local streets. They do not maintain highways, set laws or keep police forces, which are responsibilities of the central government. Government Municipalities have council-manager government: they are governed by an elected council (, ), which is legally autonomous and answers only to the voters. The size of the council is proportional to the population, the extremes bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finland Proper (historical Province)
Southwest Finland or Finland Proper ( fi, Varsinais-Suomi; sv, Egentliga Finland; la, Ducatus Finlandiae Meridionalis) is a historical province in southwestern Finland, administered by its historic capital of Turku ( sv, Åbo). It borders Satakunta, Tavastia, and Uusimaa. It is also bounded by the Baltic sea facing Åland. There was also a modern region by the name Finland Proper. Southwest Finnish dialects are spoken in Southwest Finland. Administration Southwest Finland was within the boundaries of the administrative province of Turku and Pori from 1917 to 1997 and that of Western Finland from 1997 to 2009, when the provinces of Finland were abolished. History The province, which had been a part of Sweden from the 13th century, separated when Finland was ceded to the Russian Empire in 1809. The provinces have no administrative function today but live on as a historical legacy in both countries. Originally "Finland" referred only to this region but later replaced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Finland
Central Finland ( fi, Keski-Suomi; sv, Mellersta Finland) is a region ( / ) in Finland. It borders the regions of Päijät-Häme, Pirkanmaa, South Ostrobothnia, Central Ostrobothnia, North Ostrobothnia, North Savo, and South Savo. The city of Jyväskylä is the regional centre and by far the largest city in the area. The largest lake in the very water-based region is Lake Päijänne (1,080 km2). Other large lakes are Lake Keitele (490 km2), Lake Konnevesi (190 km2) and Lake Kivijärvi (150 km2). The highest point in the region is Kiiskilänmäki in the municipality of Multia, which reaches an altitude of 269 meters above sea level. Kuokanjoki, Finland's shortest river and one of the world's shortest rivers is in the region. Central Finland has been one of the slowly growing regions in terms of population, but the growth has been based on the Jyväskylä sub-region's position as a significant growth center, and most of the region's municipalities are declining in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Ostrobothnia
Central Ostrobothnia ( fi, Keski-Pohjanmaa; sv, Mellersta Österbotten) is a region in Finland. It borders the regions of Ostrobothnia, North Ostrobothnia, Central Finland and South Ostrobothnia. Historical provinces Municipalities The region of Central Ostrobothnia is made up of eight municipalities, of which two have city status (marked in bold). Kaustinen sub-region: * Halsua (1,250) * Kaustinen (4,266) * Lestijärvi (842) * Perho (2,923) *Toholampi (3,480) * Veteli (3,396) Kokkola sub-region: * Kannus (5,733) *Kokkola (46,714) Politics Results of the 2019 Finnish parliamentary election in Central Ostrobothnia: * Centre Party 31.09% * Finns Party 19.60% * Social Democratic Party 16.06% * National Coalition Party 7.42% * Christian Democrats 7.29% * Swedish People's Party 6.26% * Green League The Green League (VIHR, fi, Vihreä liitto , sv, Gröna förbundet), shortened to the Greens ( fi, Vihreät, sv, De Gröna), is a green poli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satakunta (region)
Satakunta (in both Finnish and Swedish, ) is a region ( / ) of Finland, part of the former Western Finland Province. It borders the regions of Southwest Finland, Pirkanmaa, South Ostrobothnia and Ostrobothnia. The capital city of the region is Pori. The name of the region literally means Hundred. The historical province of the same name was a larger area within Finland, covering modern Satakunta as well as much of Pirkanmaa. Municipalities The region of Satakunta is made up of 16 municipalities, of which 7 have city status (marked in bold). Northern Satakunta sub-region: * Jämijärvi **Population: * Kankaanpää **Population: * Karvia **Population: * Siikainen (''Siikais'') **Population: Pori sub-region: * Harjavalta **Population: * Huittinen (''Vittis'') **Population: * Kokemäki (''Kumo'') **Population: * Merikarvia (''Sastmola'') **Population: * Nakkila **Population: * Pomarkku (''Påmark'') **Population: * Pori (''Björneborg'') **Population: * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
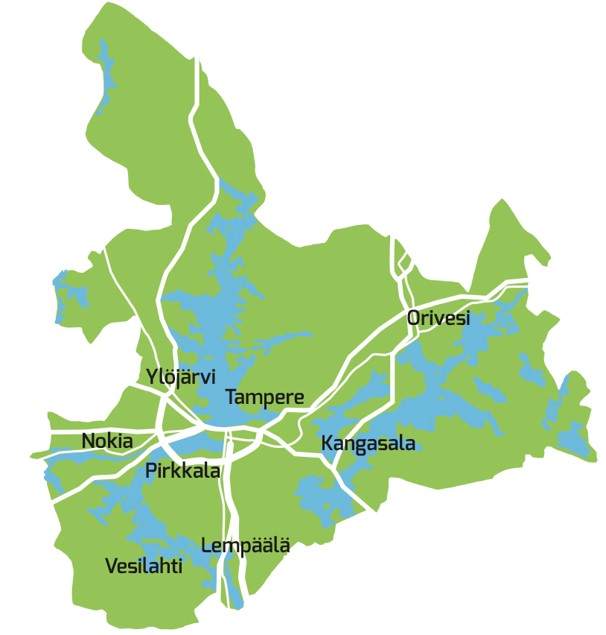
Pirkanmaa
Pirkanmaa (; sv, Birkaland; la, Birkaria, link=no), also known as ''Tampere Region'' in government documents, is a region of Finland. It borders the regions of Satakunta, South Ostrobothnia, Central Finland, Päijät-Häme, Kanta-Häme and Southwest Finland. Most of the water area in the Kokemäki River watershed is located in the Pirkanmaa region, although Lake Vanajavesi is partly in the Kanta-Häme region. The region got its name from Pirkkala, which in the Middle Ages comprised most of present-day Pirkanmaa. Tampere is the regional center and capital of Pirkanmaa, and at the same time the largest city in the region. The total population of Pirkanmaa was 529,100 on 30 June 2022, which makes it the second largest among Finland's regions after Uusimaa. The population density is well over twice the Finnish average, and most of its population is largely concentrated in the Tampere sub-region. Economy The Gross domestic product (GDP) of the region was 18.3 billion � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostrobothnia (region)
Ostrobothnia ( sv, Österbotten; fi, Pohjanmaa) is a region in western Finland. It borders the regions of Central Ostrobothnia, South Ostrobothnia, and Satakunta. It is one of four regions considered modern-day Ostrobothnia, hence also referred to as Coastal Ostrobothnia to avoid confusion. Ostrobothnia is one of two Finnish regions with a Swedish-speaking majority (the other being the constitutionally monolingual province of Åland); Swedish-speakers make up 51.2% of the total population. The region contains thirteen bilingual municipalities and one that is exclusively Finnish-speaking. The capital of Vaasa is predominantly inhabited by Finnish speakers, whereas smaller towns and rural areas are generally dominated by the Swedish language. The three municipalities with the largest number of Swedish speakers are Korsholm, Jakobstad and Pedersöre. Geographically, Ostrobothnia has little topographical relief, because it is mostly former seafloor brought to surface by pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Ostrobothnia
South Ostrobothnia ( fi, Etelä-Pohjanmaa; sv, Södra Österbotten) is one of the 19 regions of Finland. It borders the regions of Ostrobothnia, Central Ostrobothnia, Central Finland, Pirkanmaa, and Satakunta. Among the Finnish regions, South Ostrobothnia is the ninth largest in terms of population. Seinäjoki is the regional centre and by far the largest city in the area. As a cultural area, South Ostrobothnia is larger than its current regional borders and includes the region of Ostrobothnia as well. Historical provinces Municipalities The region of South Ostrobothnia is made up of 18 municipalities, of which eight have city status (marked in bold). Järviseutu sub-region: * Alajärvi (10,277) * Evijärvi (2,686) * Lappajärvi (3,394) * Vimpeli (3,212) Kuusiokunnat sub-region: * Alavus (12,354) * Kuortane (3,870) * Soini (2,367) * Ähtäri (6,394) Seinäjoki sub-region: * Ilmajoki (12,165) * Isokyrö () * Kauhava (17,206) * Kurikka (21,734) * Lapua (14, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |