|
Western Corridor Recycled Water Project
The Western Corridor Recycled Water Scheme, a recycled water project, is located in the South East region of Queensland in Australia. The scheme is managed by Seqwater and forms a key part of the SEQ Water Grid constructed by the Queensland Government in response to population growth, climate change and severe drought. The 2.5 billion project is reported as the largest recycled water project in Australia. As of 2019, the scheme has been constructed and its performance has been validated. It remains in care and maintenance mode, and will commence operation after SEQ Water Grid dam levels reach 60%. Location and features The Western Corridor is the area from Brisbane's south west suburbs towards the city of Ipswich. For many years the corridor has experienced significant population growth with the development of the suburb of Springfield and the resultant extension of the Centenary Highway and the upgrade to the Ipswich Motorway. The scheme involved the construction of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recycled Water
Water reclamation (also called wastewater reuse, water reuse or water recycling) is the process of converting municipal wastewater (sewage) or industrial wastewater into water that can be reused for a variety of purposes. Types of reuse include: urban reuse, agricultural reuse (irrigation), environmental reuse, industrial reuse, planned potable reuse, de facto wastewater reuse (unplanned potable reuse). For example, reuse may include irrigation of gardens and agricultural fields or replenishing surface water and groundwater (i.e., groundwater recharge). Reused water may also be directed toward fulfilling certain needs in residences (e.g. toilet flushing), businesses, and industry, and could even be treated to reach drinking water standards. The injection of reclaimed water into the water supply distribution system is known as direct potable reuse, however, drinking reclaimed water is not a typical practice. Treated municipal wastewater reuse for irrigation is a long-established pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ipswich Motorway
The Ipswich Motorway (M7) is a major road that connects Brisbane and Ipswich in South East Queensland, Australia. It commences at the junction of Ipswich Road and Granard Road and proceeds through to the M2 Logan Motorway interchange. It is then signed M2 until the junction of the Warrego Highway and the Cunningham Highway It initially passes through the suburbs of Rocklea, Oxley and Darra in south west Brisbane before reaching the eastern suburbs of Ipswich such as Redbank Plains, Goodna and Riverview. The Motorway is directly connected to the M5 Centenary Motorway at Darra and the M2 Logan Motorway at Gailes. In 2008, it was estimated that 80,000 cars use the road daily. In late 2010, this figure had risen to close to 100,000 vehicles per day. In 2002, the morning peak traffic volume was greatest between 7:00 am and 8:00 am. By 2008, the morning peak traffic volume peaked between the hours of 5:00 am and 6:00 am. The motorway was formed from the original Ipswich Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarong Power Station
The Tarong Power Station is a coal fired power station located on a site in Tarong in the South Burnett Region near the town of Nanango, in Queensland, Australia. The station has a maximum generating capacity of 1,400 megawatts, generated from four turbines. Coal is supplied via a conveyor from Meandu Mine, which is away and is also owned by Stanwell. Construction and design The location near Nanango was the preference of the premier of the day, Joh Bjelke-Petersen, out of a total of three possible locations that were considered. It was decided to build a new power station at Tarong in 1978, with work beginning in the following year. Initially it was expecting to be operating by October 1985 but this date was brought forward by 17 months to cover the expected growth in demand. 1 Unit was commissioned in May 1984, with 2 Unit following exactly 12 months later. 3 Unit was commissioned in February 1986, and finally 4 Unit was commissioned just 9 months later in Novemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Government
The Australian Government, also known as the Commonwealth Government, is the national government of Australia, a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy. Like other Westminster-style systems of government, the Australian Government is made up of three branches: the executive (the prime minister, the ministers, and government departments), the legislative (the Parliament of Australia), and the judicial. The legislative branch, the federal Parliament, is made up of two chambers: the House of Representatives (lower house) and Senate (upper house). The House of Representatives has 151 members, each representing an individual electoral district of about 165,000 people. The Senate has 76 members: twelve from each of the six states and two each from Australia's internal territories, the Australian Capital Territory and Northern Territory. The Australian monarch, currently King Charles III, is represented by the governor-general. The Australian Government in its exec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veolia Water
Veolia Water (formerly Vivendi Water, originally Compagnie Générale des Eaux) is the water division of the French company Veolia Environnement and the world's largest supplier of water services. In 2009, the group posted revenues of €12.56 billion. Of this, 72.9% of turnover comes from Europe; 7.4% from the Americas, 8.5% from Africa, Middle East and India, and 11.2% from the Asia-Pacific region. History The Compagnie Générale des Eaux (CGE) was created in 1853. In 1889, its first research laboratory was established at 52, rue d’Anjou in Paris, France. Veolia Water’s headquarters are still located at this site. 1918 saw the creation of the SADE (Société Auxiliaire des Distributions d'Eau), specialising in water networks and the delivery of drinking water. In 1953, construction began on a CGE water treatment facility at Clay Lane, near London; by 2001, it was the world’s largest ultrafiltration plant, supplying water to 750,000 people in the city. Veolia Water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Courier-Mail
''The Courier-Mail'' is an Australian newspaper published in Brisbane. Owned by News Corp Australia, it is published daily from Monday to Saturday in tabloid format. Its editorial offices are located at Bowen Hills, in Brisbane's inner northern suburbs, and it is printed at Murarrie, in Brisbane's eastern suburbs. It is available for purchase throughout Queensland, most regions of Northern New South Wales and parts of the Northern Territory. History The history of ''The Courier-Mail'' is through four mastheads. The ''Moreton Bay Courier'' later became '' The Courier'', then the '' Brisbane Courier'' and, since a merger with the Daily Mail in 1933, ''The Courier-Mail''. The ''Moreton Bay Courier'' was established as a weekly paper in June 1846. Issue frequency increased steadily to bi-weekly in January 1858, tri-weekly in December 1859, then daily under the editorship of Theophilus Parsons Pugh from 14 May 1861. The recognised founder and first editor was Arthur Sidney Lyo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pipeline Transport
Pipeline transport is the long-distance transportation of a liquid or gas through a system of pipes—a pipeline—typically to a market area for consumption. The latest data from 2014 gives a total of slightly less than of pipeline in 120 countries of the world. The United States had 65%, Russia had 8%, and Canada had 3%, thus 76% of all pipeline were in these three countries. ''Pipeline and Gas Journals worldwide survey figures indicate that of pipelines are planned and under construction. Of these, represent projects in the planning and design phase; reflect pipelines in various stages of construction. Liquids and gases are transported in pipelines, and any chemically stable substance can be sent through a pipeline. Pipelines exist for the transport of crude and refined petroleum, fuels – such as oil, natural gas and biofuels – and other fluids including sewage, slurry, water, beer, hot water or steam for shorter distances. Pipelines are useful for transporting water fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
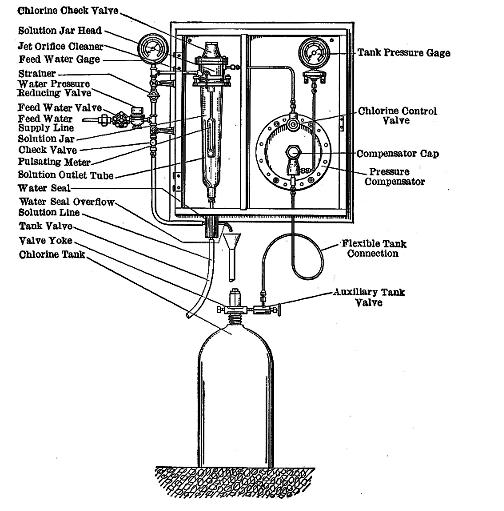
Water Chlorination
Water chlorination is the process of adding chlorine or chlorine compounds such as sodium hypochlorite to water. This method is used to kill bacteria, viruses and other microbes in water. In particular, chlorination is used to prevent the spread of waterborne diseases such as cholera, dysentery, and typhoid. History In a paper published in 1894, it was formally proposed to add chlorine to water to render it "germ-free". Two other authorities endorsed this proposal and published it in many other papers in 1895. Early attempts at implementing water chlorination at a water treatment plant were made in 1893 in Hamburg, Germany. In 1897 the town of Maidstone, England was the first to have its entire water supply treated with chlorine. Permanent water chlorination began in 1905, when a faulty slow sand filter and a contaminated water supply caused a serious typhoid fever epidemic in Lincoln, England. Alexander Cruickshank Houston used chlorination of the water to stop the epidem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
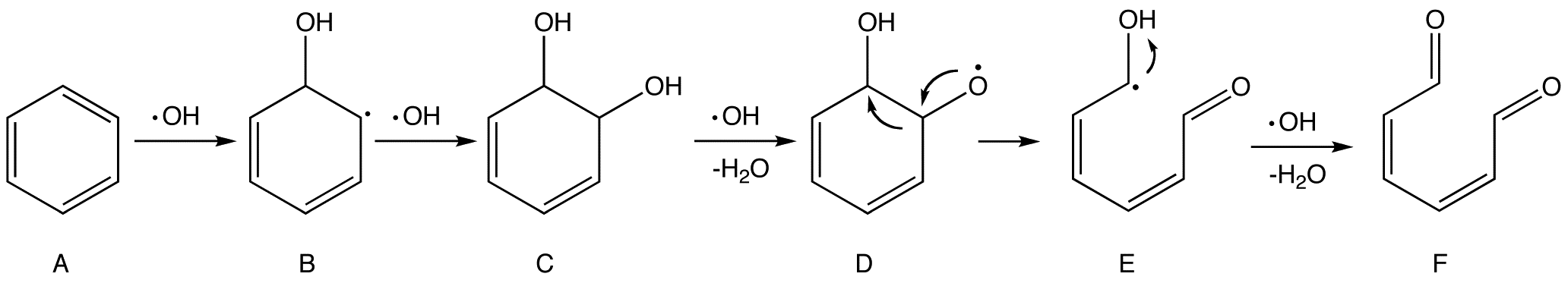
Advanced Oxidation Process
Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs), in a broad sense, are a set of chemical treatment procedures designed to remove organic (and sometimes inorganic) materials in water and wastewater by oxidation through reactions with hydroxyl radicals (·OH). In real-world applications of wastewater treatment, however, this term usually refers more specifically to a subset of such chemical processes that employ ozone (O3), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and/or UV light. One such type of process is called in situ chemical oxidation. Description AOPs rely on in-situ production of highly reactive hydroxyl radicals (·OH). These reactive species are the strongest oxidants that can be applied in water and can oxidize virtually any compound present in the water matrix, often at a diffusion-controlled reaction speed. Consequently, ·OH reacts unselectively once formed and contaminants will be quickly and efficiently fragmented and converted into small inorganic molecules. Hydroxyl radicals are produced wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
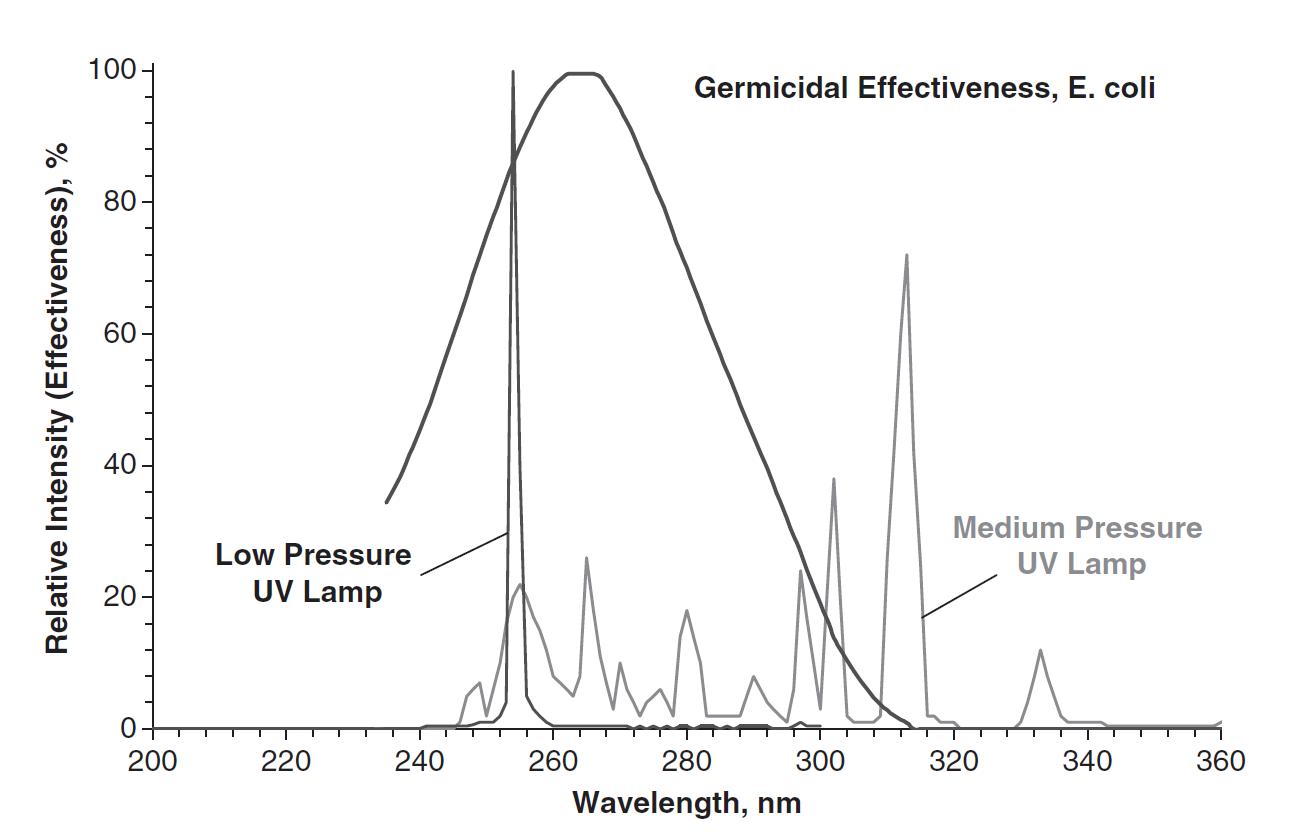
Ultraviolet Germicidal Irradiation
Ultraviolet germicidal irradiation (UVGI) is a disinfection method that uses short-wavelength ultraviolet ( ultraviolet C or UV-C) light to kill or inactivate microorganisms by destroying nucleic acids and disrupting their DNA, leaving them unable to perform vital cellular functions. UVGI is used in a variety of applications, such as food, surface, air, and water purification. UV-C light is weak at the Earth's surface since the ozone layer of the atmosphere blocks it. UVGI devices can produce strong enough UV-C light in circulating air or water systems to make them inhospitable environments to microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, molds, and other pathogens. Recent studies have proven the ability of UVC light in inactivating the novel Coronavirus (COVID-19). UVGI can be coupled with a filtration system to sanitize air and water. The application of UVGI to disinfection has been an accepted practice since the mid-20th century. It has been used primarily in medical sanitati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
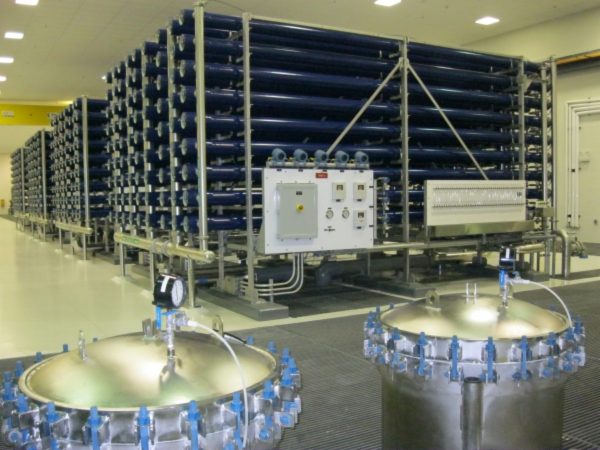
Reverse Osmosis
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a water purification process that uses a partially permeable membrane to separate ions, unwanted molecules and larger particles from drinking water. In reverse osmosis, an applied pressure is used to overcome osmotic pressure, a colligative property that is driven by chemical potential differences of the solvent, a thermodynamic parameter. Reverse osmosis can remove many types of dissolved and suspended chemical species as well as biological ones (principally bacteria) from water, and is used in both industrial processes and the production of potable water. The result is that the solute is retained on the pressurized side of the membrane and the pure solvent is allowed to pass to the other side. To be "selective", this membrane should not allow large molecules or ions through the pores (holes), but should allow smaller components of the solution (such as solvent molecules, e.g., water, H2O) to pass freely. In the normal osmosis process, the solvent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microfiltration
Microfiltration is a type of physical filtration process where a contaminated fluid is passed through a special pore-sized membrane filter to separate microorganisms and suspended particles from process liquid. It is commonly used in conjunction with various other separation processes such as ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis to provide a product stream which is free of undesired contaminants. General principles Microfiltration usually serves as a pre-treatment for other separation processes such as ultrafiltration, and a post-treatment for granular media filtration. The typical particle size used for microfiltration ranges from about 0.1 to 10 μm.Baker, R 2012, ''Microfiltration, in Membrane Technology and Applications'', 3rd edn, John Wiley & Sons Ltd, California. p. 303 In terms of approximate molecular weight these membranes can separate macromolecules of molecular weights generally less than 100,000 g/mol.Microfiltration/Ultrafiltration, 2008, Hyflux Membranes, access ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |