|
West Feliciana Parish
West Feliciana Parish (French: ''Paroisse de Feliciana Ouest''; Spanish: ''Parroquia de West Feliciana'') is a civil parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. At the 2010 census, the population was 15,625, and 15,310 at the 2020 census. The parish seat is St. Francisville. The parish was established in 1824. In 1824 Feliciana Parish was divided into East Feliciana Parish and West Feliciana Parish, in recognition of the increases in population throughout the parish. West Feliciana Parish is part of the Baton Rouge metropolitan statistical area. The River Bend Nuclear Generating Station, operated by Entergy Nuclear, is located in West Feliciana Parish below St. Francisville. It produces approximately 10 percent of the total electric power demand in Louisiana. The Louisiana State Penitentiary is also located in the parish, in Angola. It occupies 18,000 acres at a site in a river bend, surrounded on three sides by water. History 18th and 19th centuries Following the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louisiana Parishes
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is bordered by the state of Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, Mississippi to the east, and the Gulf of Mexico to the south. A large part of its eastern boundary is demarcated by the Mississippi River. Louisiana is the only U.S. state with political subdivisions termed parishes, which are equivalent to counties, making it one of only two U.S. states not subdivided into counties (the other being Alaska and its boroughs). The state's capital is Baton Rouge, and its largest city is New Orleans, with a population of roughly 383,000 people. Some Louisiana urban environments have a multicultural, multilingual heritage, being so strongly influenced by a mixture of 18th century Louisiana French, Dominican Creole, Spanish, French Canadian, Acadian, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayou Sacra Luisiana Henry Lewis
In usage in the Southern United States, a bayou () is a body of water typically found in a flat, low-lying area. It may refer to an extremely slow-moving stream, river (often with a poorly defined shoreline), marshy lake, wetland, or creek. They typically contain brackish water highly conducive to fish life and plankton. Bayous are commonly found in the Gulf Coast region of the southern United States, especially in the Mississippi River Delta, though they also exist elsewhere. A bayou is often an anabranch or minor braid of a braided channel that is slower than the mainstem, often becoming boggy and stagnant. Though fauna varies by region, many bayous are home to crawfish, certain species of shrimp, other shellfish, catfish, frogs, toads, salamanders, newts, American alligators, American crocodiles, herons, lizards, turtles, tortoises, spoonbills, snakes, and leeches, as well as many other species. Etymology The word entered American English via Louisiana French in Lou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Territory Of Orleans
The Territory of Orleans or Orleans Territory was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from October 1, 1804, until April 30, 1812, when it was admitted to the Union as the State of Louisiana. History In 1804, all of the Louisiana Purchase south of the 33rd parallel became the Orleans Territory, and the remainder became the District of Louisiana. (The District of Louisiana was later renamed the Louisiana Territory; and still later, when the Orleans Territory became the State of Louisiana, the Louisiana Territory was renamed the Missouri Territory.) The Organic Act of 1804, passed on March 26 for October 1 implementation, also created the United States District Court for the District of Orleans—the only time Congress has ever provided a territory with a United States district court equal in its authority and jurisdiction to those of the states. Congress also established the Superior Court for the Territory of Orleans whose three judges wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florida Parishes
The Florida Parishes ( es, Parroquias de Florida, french: Paroisses de Floride), on the east side of the Mississippi River—an area also known as the Northshore or Northlake region—are eight parishes in the southeastern portion of the U.S. state of Louisiana; the Florida Parishes were part of West Florida in the 18th and early 19th centuries. Unlike most of the state, this region was not part of the 1803 Louisiana Purchase; it had been under British and then Spanish control since 1763. History The area that became the Florida Parishes was at one time part of French Louisiana. Following the French and Indian War, however, the region—like most of the rest of French Louisiana east of the Mississippi River (excluding New Orleans)—was transferred to Great Britain. This region became part of the British colonial province of West Florida. Following the American Revolutionary War, West Florida was the subject of a border dispute between the newly formed United States and Spain, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase (french: Vente de la Louisiane, translation=Sale of Louisiana) was the acquisition of the territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. In return for fifteen million dollars, or approximately eighteen dollars per square mile, the United States nominally acquired a total of in Middle America. However, France only controlled a small fraction of this area, most of which was inhabited by Native Americans; effectively, for the majority of the area, the United States bought the "preemptive" right to obtain "Indian" lands by treaty or by conquest, to the exclusion of other colonial powers. The Kingdom of France had controlled the Louisiana territory from 1699 until it was ceded to Spain in 1762. In 1800, Napoleon, the First Consul of the French Republic, regained ownership of Louisiana as part of a broader effort to re-establish a French colonial empire in North America. However, France's failure to suppress a revol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
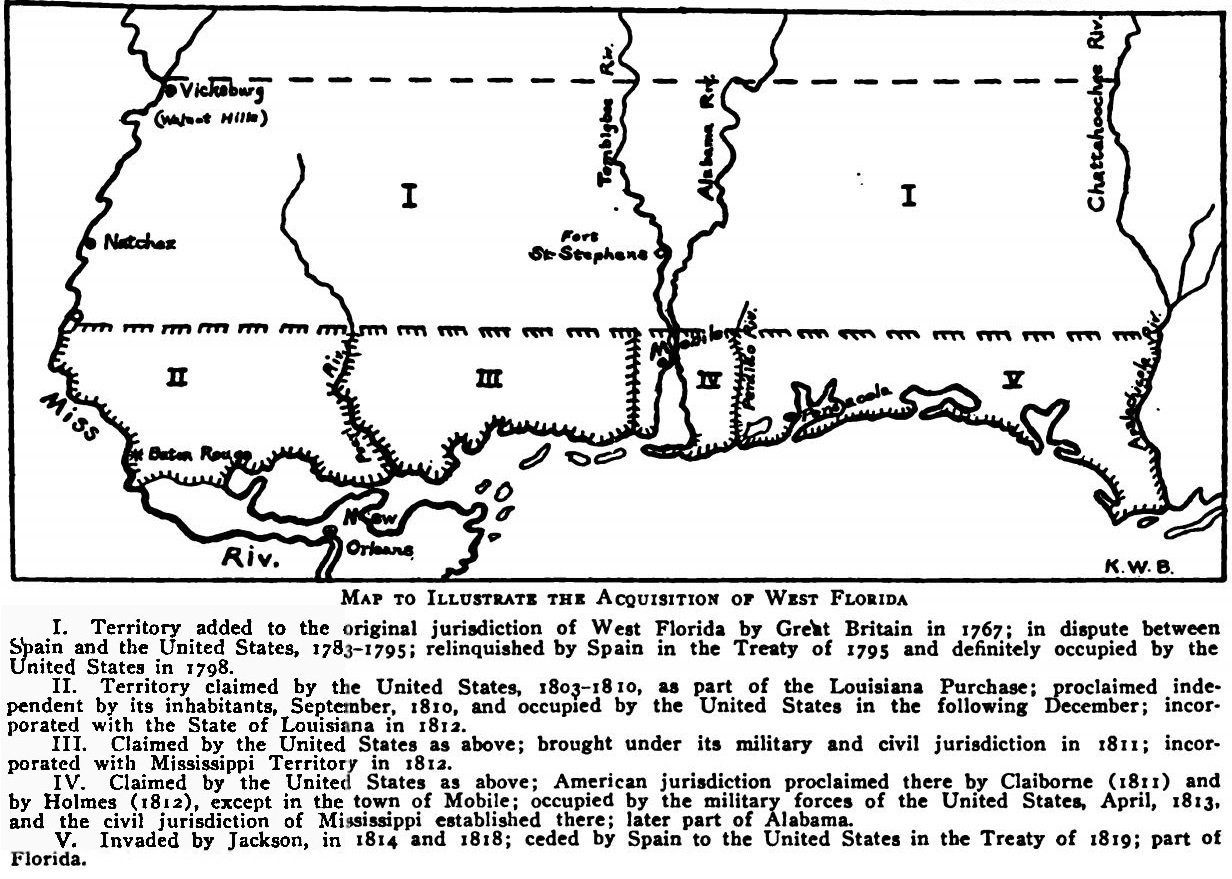
Republic Of West Florida
The Republic of West Florida ( es, República de Florida Occidental, french: République de Floride occidentale), officially the State of Florida, was a short-lived republic in the western region of Spanish West Florida for just over months during 1810. It was annexed and occupied by the United States later in 1810; it subsequently became part of Eastern Louisiana. Boundaries The boundaries of the Republic of West Florida included all territory south of parallel 31°N, east of the Mississippi River, and north of the waterway formed by the Iberville River, Amite River, Lake Maurepas, Pass Manchac, Lake Pontchartrain, and the Rigolets. The Pearl River, with its branch that flowed into the Rigolets, formed the eastern boundary of the republic. A military expedition from the republic attempted but failed to capture the Spanish outpost at Mobile, which was situated between the Pearl and the Perdido River, farther to the east. Despite its name, none of the Republic of West Florida w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spain In The American Revolutionary War
Spain, through its alliance with France and as part of its conflict with Britain, played a role in the independence of the United States. Spain declared war on Britain as an ally of France, itself an ally of the American colonies. Most notably, Spanish forces attacked British positions in the south and captured West Florida from Britain in the siege of Pensacola. This secured the southern route for supplies and closed off the possibility of any British offensive through the western frontier of the United States via the Mississippi River. Spain also provided money, supplies, and munitions to the American forces. Beginning in 1776, it jointly funded Roderigue Hortalez and Company, a trading company that provided critical military supplies. Spain provided financing for the final siege of Yorktown in 1781 with a collection of gold and silver in Havana, then Spanish Cuba. Spain was allied with France through the Bourbon Family Compact and the Revolution was an opportunity to confro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Americas and having its capital in Mexico City. Its jurisdiction comprised a huge area that included what is now Mexico, the Western and Southwestern United States (from California to Louisiana and parts of Wyoming, but also Florida) in North America; Central America, the Caribbean, very northern parts of South America, and several territorial Pacific Ocean archipelagos. After the 1521 Spanish conquest of the Aztec empire, conqueror Hernán Cortés named the territory New Spain, and established the new capital, Mexico City, on the site of the Tenochtitlan, the capital of the Mexica (Aztec) Empire. Central Mexico became the base of expeditions of exploration and conquest, expanding the territory claimed by the Spanish Empire. With the polit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Florida
West Florida ( es, Florida Occidental) was a region on the northern coast of the Gulf of Mexico that underwent several boundary and sovereignty changes during its history. As its name suggests, it was formed out of the western part of former Spanish Florida (East Florida formed the eastern part, with the Apalachicola River as the border), along with lands taken from French Louisiana; Pensacola became West Florida's capital. The colony included about two thirds of what is now the Florida Panhandle, as well as parts of the modern U.S. states of Louisiana, Mississippi, and Alabama. Great Britain established West and East Florida in 1763 out of land acquired from France and Spain after the Seven Years' War. As the newly acquired territory was too large to govern from one administrative center, the British divided it into two new colonies separated by the Apalachicola River. British West Florida included the part of formerly Spanish Florida which lay west of the Apalachicola, as wel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a Sovereign state, sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England (which included Wales) and Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland to form a single kingdom encompassing the whole island of Great Britain and its outlying islands, with the exception of the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. The unitary state was governed by a single Parliament of Great Britain, parliament at the Palace of Westminster, but distinct legal systems – English law and Scots law – remained in use. The formerly separate kingdoms had been in personal union since the 1603 "Union of the Crowns" when James VI of Scotland became King of England and King of Ireland. Since James's reign, who had been the first to refer to himself as "king of Great Britain", a political un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louisiana (New France)
Louisiana (french: La Louisiane; ''La Louisiane Française'') or French Louisiana was an administrative district of New France. Under French control from 1682 to 1769 and 1801 (nominally) to 1803, the area was named in honor of King Louis XIV, by French explorer René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de la Salle. It originally covered an expansive territory that included most of the drainage basin of the Mississippi River and stretched from the Great Lakes to the Gulf of Mexico and from the Appalachian Mountains to the Rocky Mountains. Louisiana included two regions, now known as Upper Louisiana (), which began north of the Arkansas River, and ''Lower Louisiana'' (). The U.S. state of Louisiana is named for the historical region, although it is only a small part of the vast lands claimed by France.La Louisiane française 1682-1803 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754–1763), the Carnatic Wars and the Anglo-Spanish War (1762–1763). The opposing alliances were led by Great Britain and France respectively, both seeking to establish global pre-eminence at the expense of the other. Along with Spain, France fought Britain both in Europe and overseas with land-based armies and naval forces, while Britain's ally Prussia sought territorial expansion in Europe and consolidation of its power. Long-standing colonial rivalries pitting Britain against France and Spain in North America and the West Indies were fought on a grand scale with consequential results. Prussia sought greater influence in the German states, while Austria wanted to regain Silesia, captured by Prussia in the previous war, and to contain Pruss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |