|
Werner Dannhauser
Werner Joseph Dannhauser (May 1, 1929 – April 26, 2014) was an American political philosophy professor and magazine editor. A German-Jewish émigré, he became an expert on the philosophy of Friedrich Nietzsche and on Judaism and politics and was a longtime professor of government at Cornell University. A protégé of Leo Strauss at the University of Chicago, Dannhauser had earlier been a writer and editor at ''Commentary'' magazine during the 1960s. Early years Dannhauser was born on May 1, 1929, in Buchau in southwestern Germany. In early 1939, at the age of nine, Dannhauser came to the United States in order to escape Nazi Germany. An older brother Jacob (1922–1998) and an older sister Rose (1924–2018) also came with him. He became an American citizen in 1944. He completed the rest of his childhood in Cleveland, Ohio, where he was active in the congregation known as The Temple. Dannhauser earned a bachelor's degree from the New School for Social Research in 1951. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Philosophy
Political philosophy or political theory is the philosophical study of government, addressing questions about the nature, scope, and legitimacy of public agents and institutions and the relationships between them. Its topics include politics, liberty, justice, property, rights, law, and the enforcement of laws by authority: what they are, if they are needed, what makes a government legitimate, what rights and freedoms it should protect, what form it should take, what the law is, and what duties citizens owe to a legitimate government, if any, and when it may be legitimately overthrown, if ever. Political theory also engages questions of a broader scope, tackling the political nature of phenomena and categories such as identity, culture, sexuality, race, wealth, human-nonhuman relations, ethics, religion, and more. Political science, the scientific study of politics, is generally used in the singular, but in French and Spanish the plural (''sciences politiques'' and ''cienci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Clearing (Ellison Bay, Wisconsin)
The Clearing Folk School, usually called just The Clearing, is a continuing education institution located near Ellison Bay, Wisconsin, United States. It was founded by Jens Jensen in 1935. A successful landscape architect, Jensen began acquiring a private summer estate in 1919; the estate, re-landscaped by Jensen, became the nucleus of the school. Jensen was inspired by the folk high schools of his native Denmark. History Jensen lived in ''The Clearing'' as a widower from 1935 until 1951. After his death, The Clearing was operated by the Wisconsin Farm Bureau for 37 years as a rural retreat, conference center, and continuing-education institution. Following The Clearing's independence as a nonprofit corporation in 1988, The Clearing has continued to fulfill these roles, with a concentration on adult education and as a meeting place for senior citizens. The Clearing describes itself as a place for "classes in natural sciences, fine arts, skilled crafts and humanities." The Cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allan Bloom
Allan David Bloom (September 14, 1930 – October 7, 1992) was an American philosopher, classicist, and academician. He studied under David Grene, Leo Strauss, Richard McKeon, and Alexandre Kojève. He subsequently taught at Cornell University, the University of Toronto, Tel Aviv University, Yale University, École normale supérieure, and the University of Chicago. Bloom championed the idea of Great Books education and became famous for his criticism of contemporary American higher education, with his views being expressed in his bestselling 1987 book, ''The Closing of the American Mind''. Characterized as a conservative in the popular media, Bloom denied the label, asserting that what he sought to defend was the "theoretical life". Saul Bellow wrote ''Ravelstein'', a ''roman à clef'' based on Bloom, his friend and colleague at the University of Chicago. Early life and education Bloom was born in Indianapolis, Indiana to second-generation Jewish parents who were both soci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Wisconsin–Madison
A university () is an educational institution, institution of higher education, higher (or Tertiary education, tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate education, undergraduate and postgraduate education, postgraduate programs. In the United States, the designation is reserved for colleges that have a graduate school. The word ''university'' is derived from the Latin ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". The first universities were created in Europe by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (''Università di Bologna''), founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *Being a high degree-awarding institute. *Having independence from the ecclesiastic schools, although conducted by both clergy and non-clergy. *Using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semitic Languages
The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken by more than 330 million people across much of West Asia, the Horn of Africa, and latterly North Africa, Malta, West Africa, Chad, and in large immigrant and expatriate communities in North America, Europe, and Australasia. The terminology was first used in the 1780s by members of the Göttingen school of history, who derived the name from Shem, one of the three sons of Noah in the Book of Genesis. Semitic languages occur in written form from a very early historical date in West Asia, with East Semitic Akkadian and Eblaite texts (written in a script adapted from Sumerian cuneiform) appearing from the 30th century BCE and the 25th century BCE in Mesopotamia and the north eastern Levant respectively. The only earlier attested languages are Sumerian and Elamite (2800 BCE to 550 BCE), both language isolates, and Egyptian (a sister branch of the Afroasiatic family, related to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Left
The New Left was a broad political movement mainly in the 1960s and 1970s consisting of activists in the Western world who campaigned for a broad range of social issues such as civil and political rights, environmentalism, feminism, gay rights, gender roles and drug policy reforms. Some see the New Left as an oppositional reaction to earlier Marxist and labor union movements for social justice that focused on dialectical materialism and social class, while others who used the term see the movement as a continuation and revitalization of traditional leftist goals. Some who self-identified as "New Left" rejected involvement with the labor movement and Marxism's historical theory of class struggle, although others gravitated to their own takes on established forms of Marxism and Marxism–Leninism, such as the New Communist movement (which drew from Maoism) in the United States or the K-GruppenThe K-Gruppen, K groups originally referred to the mainly Maoism, Maoist-oriented small par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservatism In The United States
Conservatism in the United States is a political and social philosophy based on a belief in limited government, individualism, traditionalism, republicanism, and limited federal governmental power in relation to U.S. states. Conservative and Christian media organizations, along with American conservative figures, are influential, and American conservatism is one of the majority political ideologies within the Republican Party. American social conservatives typically support what they consider Christian values, moral absolutism, traditional family values, and American exceptionalism, while opposing abortion, euthanasia, and same-sex marriage. It favours economic individualism, and is generally pro-business and pro-capitalism, while supporting anti-communism and opposing labor unions. It often advocates a strong national defense, gun rights, free trade, and a defense of Western culture from perceived threats posed by both communism and moral relativism. Since the late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
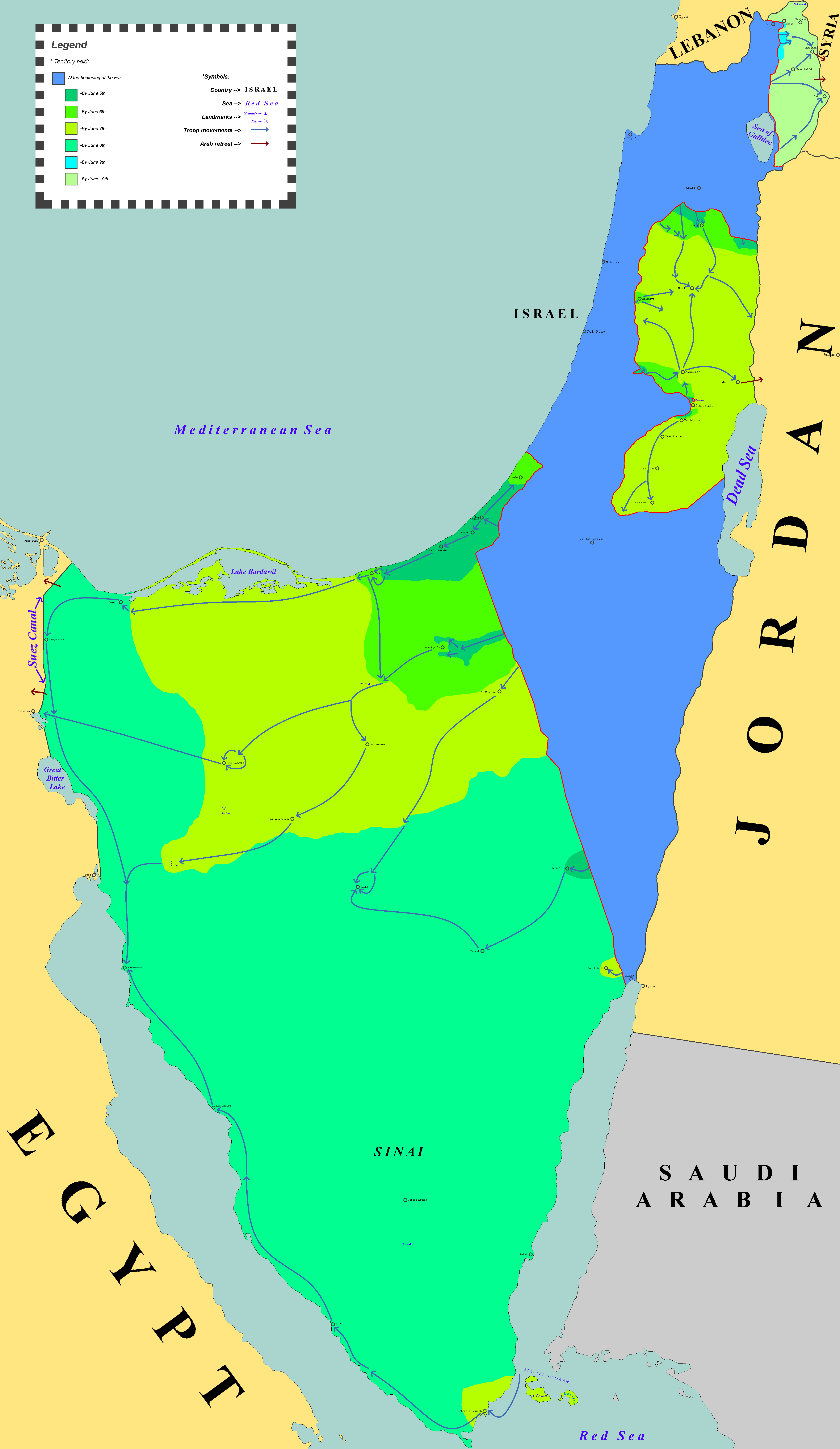
Six-Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states (primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, Syria, and Jordan) from 5 to 10 June 1967. Escalated hostilities broke out amid poor relations between Israel and its Arab neighbours following the 1949 Armistice Agreements, which were signed at the end of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, First Arab–Israeli War. Earlier, in 1956, regional tensions over the Straits of Tiran escalated in what became known as the Suez Crisis, when Israel invaded Egypt over the Israeli passage through the Suez Canal and Straits of Tiran, Egyptian closure of maritime passageways to Israeli shipping, ultimately resulting in the re-opening of the Straits of Tiran to Israel as well as the deployment of the United Nations Emergency Force (UNEF) along the Borders of Israel#Border with Egypt, Egypt–Israel border. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. The north was supported by the Soviet Union, China, and other communist states, while the south was United States in the Vietnam War, supported by the United States and other anti-communism, anti-communist Free World Military Forces, allies. The war is widely considered to be a Cold War-era proxy war. It lasted almost 20 years, with direct U.S. involvement ending in 1973. The conflict also spilled over into neighboring states, exacerbating the Laotian Civil War and the Cambodian Civil War, which ended with all three countries becoming communist states by 1975. After the French 1954 Geneva Conference, military withdrawal from Indochina in 1954 – following their defeat in the First Indochina War – the Viet Minh to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ted Solotaroff
Theodore "Ted" Solotaroff (October 9, 1928 – August 8, 2008) was an American writer, editor and literary critic. Life and career Born into a working-class Jewish family in Elizabeth, New Jersey, Solotaroff attended the University of Michigan, graduating in 1952, and did graduate work at the University of Chicago, where he became friends with Philip Roth and dedicated himself to literature. He was an editor at ''Commentary'' from 1960 to 1966, then in 1967 founded '' The New American Review'', which was an influential literary journal in paperback, not magazine, format for the decade of its existence. After it folded, he became an editor at Harper & Row, where he edited works by Russell Banks, Sue Miller, Robert Bly, Bobbie Ann Mason, and others. "In 1989, when Rupert Murdoch bought Harper & Row, Solotaroff began to do less editing and more writing. He left the book business with a parting shot at what he labeled 'the literary-industrial complex.'"Joe HolleObituary latimes.com; ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman Podhoretz
Norman Podhoretz (; born January 16, 1930) is an American magazine editor, writer, and conservative political commentator, who identifies his views as " paleo-neoconservative".An Interview with Norman Podhoretz April 16, 2019, Claremont He is a writer for '''' magazine, and previously served as the publication's editor-in-chief from 1960 to 1995. Early life and education The son of Julius and Helen (Woliner) Podhoretz, Jewish immigrants from the Central European region of Galicia (t ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
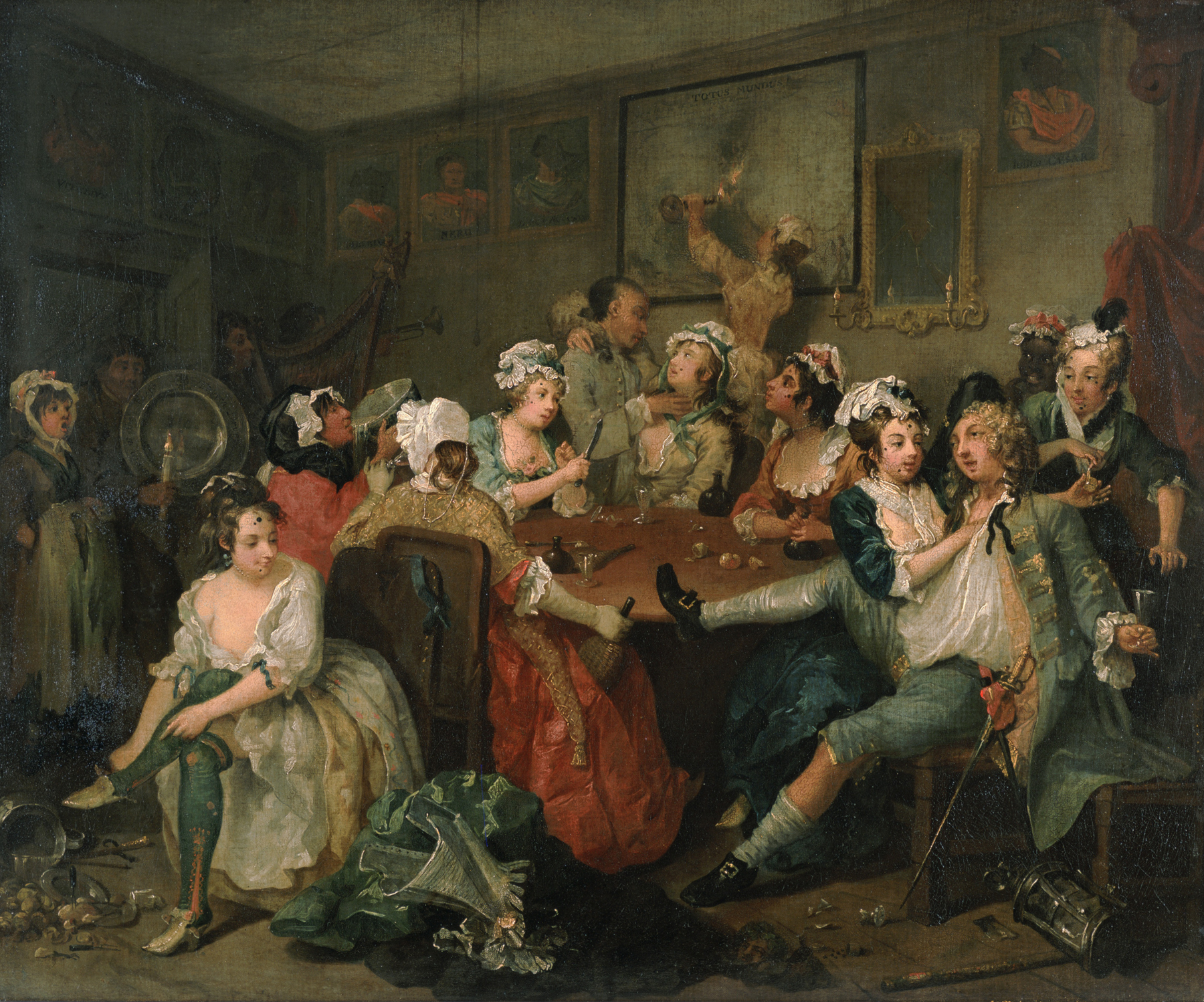
Rake (stock Character)
In a historical context, a rake (short for rakehell, analogous to "hellraiser") was a man who was habituated to immoral conduct, particularly womanizing. Often, a rake was also prodigal, wasting his (usually inherited) fortune on gambling, wine, women, and song, and incurring lavish debts in the process. Cad is a closely related term. Comparable terms are "libertine" and "debauchee". The Restoration rake was a carefree, witty, sexually irresistible aristocrat whose heyday was during the English Restoration period (1660–1688) at the court of King Charles II. They were typified by the "Merry Gang" of courtiers, who included as prominent members the John Wilmot; George Villiers; and Charles Sackville, who combined riotous living with intellectual pursuits and patronage of the arts. At this time the rake featured as a stock character in Restoration comedy. After the reign of Charles II, and especially after the Glorious Revolution of 1688, the cultural perception of the ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |