|
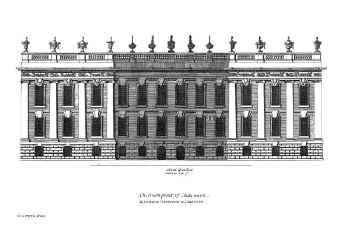
Wentworth Castle
Wentworth Castle is a grade-I listed country house, the former seat of the Earls of Strafford, at Stainborough, near Barnsley in South Yorkshire, England. It is now home to the Northern College for Residential and Community Education. An older house existed on the estate, then called Stainborough, when it was purchased by Thomas Wentworth, Baron Raby (later Earl of Strafford), in 1708. It was still called Stainborough in Jan Kip's engraved bird's-eye view of parterres and avenues, 1714, and in the first edition of ''Vitruvius Britannicus'', 1715. The name was changed in 1731. The original name survives in the form of Stainborough Castle, a sham ruin constructed as a garden folly on the estate. The estate was in the care of the Wentworth Castle Heritage Trust from 2001 to June 2019 and was open to the public year-round seven days a week. Despite massive restoration, the castle gardens were closed to the public in 2017 amidst a funding crisis. In September 2018 it was anno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wentworth Castle02 2007-08-13
Wentworth may refer to: People * Wentworth (surname) * Judith Blunt-Lytton, 16th Baroness Wentworth (1873–1957), Lady Wentworth, notable Arabian horse breeder * S. Wentworth Horton (1885–1960), New York state senator * Wentworth Miller (born 1972), American actor Places Australia * Division of Wentworth, an electoral district in the Australian House of Representatives in New South Wales * Electoral district of Wentworth, a former electoral district in the New South Wales Legislative Assembly * Wentworth, New South Wales, a town * Wentworth Gaol, former prison in New South Wales Canada * Ski Wentworth, a ski hill in Wentworth, Nova Scotia, Canada * Wentworth, Nova Scotia, a rural community * Wentworth, Quebec, a township municipality * Wentworth County, Ontario, a defunct county ** Wentworth (electoral district), a former riding in the Canadian House of Commons ** Wentworth (provincial electoral district). a former riding in the Legislative Assembly of Ontario * Wentworth, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wentworth Woodhouse
Wentworth Woodhouse is a Grade I listed country house in the village of Wentworth, in the Metropolitan Borough of Rotherham in South Yorkshire, England. It is currently owned by the Wentworth Woodhouse Preservation Trust. The building has more than 300 rooms, although the precise number is unclear, with of floorspace ( of living area). It covers an area of more than , and is surrounded by a park, and an estate of . The original Jacobean house was rebuilt by Thomas Watson-Wentworth, 1st Marquess of Rockingham (1693–1750), and vastly expanded by his son, the 2nd Marquess, who was twice Prime Minister, and who established Wentworth Woodhouse as a Whig centre of influence. In the 18th century, the house was inherited by the Earls Fitzwilliam who owned it until 1979, when it passed to the heirs of the 8th and 10th Earls, its value having appreciated from the large quantities of coal discovered on the estate. Architecture Wentworth Woodhouse comprises two joined hou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plate Glass
Plate glass, flat glass or sheet glass is a type of glass, initially produced in plane form, commonly used for windows, glass doors, transparent walls, and windscreens. For modern architectural and automotive applications, the flat glass is sometimes bent after production of the plane sheet. Flat glass stands in contrast to ''container glass'' (used for bottles, jars, cups) and '' glass fibre'' (used for thermal insulation, in fibreglass composites, and for optical communication). Flat glass has a higher magnesium oxide and sodium oxide content than container glass, and a lower silica, calcium oxide, and aluminium oxide content."High temperature glass melt property database for process modeling"; Eds.: Thomas P. Seward III and Terese Vascott; The American Ceramic Society, Westerville, Ohio, 2005, From the lower soluble oxide content comes the better chemical durability of container glass against water, which is required especially for storage of beverages and food. Most f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown Glass (window)
Crown glass was an early type of window glass. In this process, glass was blown into a "crown" or hollow globe. This was then transferred from the blowpipe to a punty and then flattened by reheating and spinning out the bowl-shaped piece of glass (bullion) into a flat disk by centrifugal force, up to 5 or 6 feet (1.5 to 1.8 metres) in diameter. The glass was then cut to the size required. The thinnest glass was in a band at the edge of the disk, with the glass becoming thicker and more opaque toward the center. Known as a bullseye, the thicker center area around the pontil mark was used for less expensive windows. To fill large window spaces with the best glass, many small diamond shapes were cut from the edge of the disk, and then some might be halved into triangles. These were mounted in a lead lattice work and fitted into the window frame. Crown glass was one of the two most common processes for making window glass until the 19th century. The other was blown plate. Crown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Architectural History (journal)
''Architectural History'' is an annual peer-reviewed journal published by the Society of Architectural Historians of Great Britain (SAHGB). The journal is published each autumn. The architecture of the British Isles is a major theme of the journal, but articles can consider all places and periods. All members of the SAHGB receive the journal, as do subscribing institutional libraries. Older issues from its inception in 1958 onwards are available online through JSTOR. . . The is Alistair Fair, of the |
Margaret Whinney
Margaret Dickens Whinney (4 February 1897 – 1975) was an English art historian who taught at the Courtauld Institute of Art. Her published works included books on British sculpture and architecture. Life Whinney was the daughter of Thomas Bostock Whinney, an architect, and Sydney Margaret Dickens, the granddaughter of Charles Dickens. She was educated at the University of London, graduating in art history in 1935. She had published her first article in 1930, under the supervision of her mentor Tancred Borenius. Immediately after graduating she joined the staff of the recently established Courtauld Institute, where she did a variety of jobs including managing the slide library, and also continued her studies. The Courtauld closed for a year following the beginning of the Second World War. When it reopened in 1940, Whinney was effectively in sole charge, both teaching and handling most of the administrative duties. That year, the research she had done on 17th-century drawings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Talman (architect)
William Talman (1650–1719) was an English architect and landscape designer. Career A pupil of Sir Christopher Wren, in 1678 he and Thomas Apprice gained the office of King's Waiter in the Port of London (perhaps through his patron Henry Hyde, 2nd Earl of Clarendon). From May 1689 until William III of England, William III's death in 1702, he was comptroller of the king's works, Comptroller of the Royal Works, and also in 1689 William Bentinck, 1st Earl of Portland appointed Talman and George London (landscape architect), George London as his deputies in his new role as Superintendent of the Royal Gardens. In these roles Talman worked with Wren in his rebuilding of Hampton Court Palace and its gardens and, by proposing a cheaper interior decoration scheme for the new building, won that commission over Wren's head. Works Talman's principal work is recognised to be Chatsworth House, considered to be the first baroque private house in Britain, and he was possibly the architect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Gibbs
James Gibbs (23 December 1682 – 5 August 1754) was one of Britain's most influential architects. Born in Aberdeen, he trained as an architect in Rome, and practised mainly in England. He is an important figure whose work spanned the transition between English Baroque architecture and Georgian architecture heavily influenced by Andrea Palladio. Among his most important works are St Martin-in-the-Fields (at Trafalgar Square), the cylindrical, domed Radcliffe Camera at Oxford University, and the Senate House at Cambridge University. Gibbs very privately was a Roman Catholic and a Tory. Because of this and his age, he had a somewhat removed relation to the Palladian movement which came to dominate English architecture during his career. The Palladians were largely Whigs, led by Lord Burlington and Colen Campbell, a fellow Scot who developed a rivalry with Gibbs. Gibbs' professional Italian training under the Baroque master Carlo Fontana also set him uniquely apart from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Howard Colvin
Sir Howard Montagu Colvin (15 October 1919 – 27 December 2007) was a British architectural historian who produced two of the most outstanding works of scholarship in his field: ''A Biographical Dictionary of British Architects, 1600–1840'' and ''The History of the King's Works''. Life and works Born in Sidcup, Colvin was educated at Trent College and University College London. In 1948, he became a Fellow of St John's College, Oxford where he remained until his death in 2007. He was a member of the Royal Commission on the Historical Monuments of England 1963–76, the Historic Buildings Council for England 1970–84, the Royal Fine Art Commission 1962–72, and other official bodies. He is most notably the author of ''A Biographical Dictionary of British Architects, 1600–1840'' which appeared in its original form in 1954. Yale University Press produced a third edition in 1995, and he had just completed his work on the fourth edition at the time of his death. On first p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Utrecht
The Peace of Utrecht was a series of peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vacant throne of Spain, and involved much of Europe for over a decade. The main action saw France as the defender of Spain against a multinational coalition. The war was very expensive and bloody and finally stalemated. Essentially, the treaties allowed Philip V (grandson of King Louis XIV of France) to keep the Spanish throne in return for permanently renouncing his claim to the French throne, along with other necessary guarantees that would ensure that France and Spain should not merge, thus preserving the balance of power in Europe. The treaties between several European states, including Spain, Great Britain, France, Portugal, Savoy and the Dutch Republic, helped end the war. The treaties were concluded between the representatives of Louis XIV of Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William III Of England
William III (William Henry; ; 4 November 16508 March 1702), also widely known as William of Orange, was the sovereign Prince of Orange from birth, Stadtholder of County of Holland, Holland, County of Zeeland, Zeeland, Lordship of Utrecht, Utrecht, Guelders, and Lordship of Overijssel, Overijssel in the Dutch Republic from the 1670s, and King of England, Monarchy of Ireland, Ireland, and List of Scottish monarchs, Scotland from 1689 until his death in 1702. As King of Scotland, he is known as William II. He is sometimes informally known as "King Billy" in Ireland and Scotland. His victory at the Battle of the Boyne in 1690 is The Twelfth, commemorated by Unionism in the United Kingdom, Unionists, who display Orange Order, orange colours in his honour. He ruled Britain alongside his wife and cousin, Queen Mary II, and popular histories usually refer to their reign as that of "William and Mary". William was the only child of William II, Prince of Orange, and Mary, Princess Royal an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal To Stella
''A Journal to Stella'' is a work by Jonathan Swift first partly published posthumously in 1766. It consists of 65 letters to his friend, Esther Johnson, whom he called ''Stella'' and whom he may have secretly married. They were written between 1710 and 1713, from various locations in England, and though clearly intended for Stella's eyes were sometimes addressed to her companion Rebecca Dingley. Amongst the references to contemporaries of Dean Swift, frequent mention is made of Elizabeth Germain. There is also mention of St. George Ashe, Bishop of Clogher, an old friend who by some accounts secretly married Swift to Stella in 1716. Notes External links ''Journal to Stella'' – e-text at the University of Adelaide The University of Adelaide (informally Adelaide University) is a public research university located in Adelaide, South Australia. Established in 1874, it is the third-oldest university in Australia. The university's main campus is located on N ... {{DEFA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |