|
Weismann-Netter–Stuhl Syndrome
Weismann-Netter–Stuhl syndrome, also known as Weismann-Netter syndrome or tibioperoneal diaphyseal toxopachyosteosis, is a rare disorder characterized by bowing of the lower legs and an abnormal thickening of thinner bone in the leg. The main sign is anterior bowing and posterior cortical thickening of the diaphyses of both the tibiae and fibulae. It is thought to be inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion and is most often bilateral and symmetric in nature. Associated features include dwarfism and mild intellectual disability as well as a process known as tibialization of the fibulae, which involves thickening and enlargement of these bones to an extent resembling the tibiae. The combination of the presence of tibialization of the fibulae, which is highly specific for the disorder, and the absence of laboratory abnormalities, ruling out alternative diagnoses including rickets, essentially confirms the diagnosis. Cause This condition is currently felt to be a genetic disorde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal Dominant
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second recessive. This state of having two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new (''de novo'') or inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes ( autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child (see Sex linkage). Since there is only one copy of the Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, there are other forms of dominance such as incomplete d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
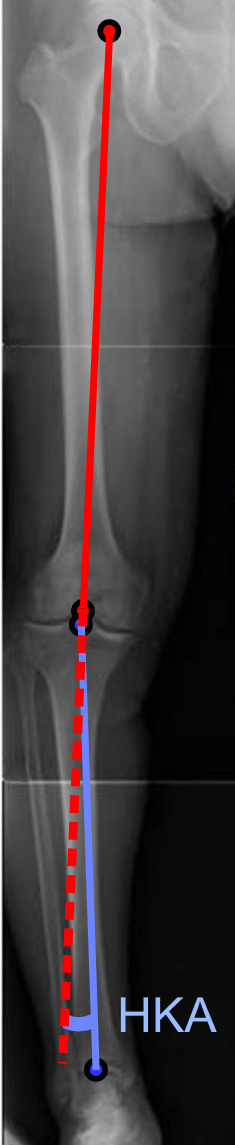
Bowed Legs
Genu varum (also called bow-leggedness, bandiness, bandy-leg, and tibia vara) is a varus deformity marked by (outward) bowing at the knee, which means that the lower leg is angled inward ( medially) in relation to the thigh's axis, giving the limb overall the appearance of an archer's bow. Usually medial angulation of both lower limb bones (femur and tibia) is involved. Causes If a child is sickly, either with rickets or any other ailment that prevents ossification of the bones or is improperly fed, the bowed condition may persist. Thus the chief cause of this deformity is rickets. Skeletal problems, infection, and tumors can also affect the growth of the leg, sometimes giving rise to a one-sided bow-leggedness. The remaining causes are occupational, especially among jockeys, and from physical trauma, the condition being very likely to supervene after accidents involving the condyles of the femur. Childhood Children until the age of 3 to 4 have a degree of genu varum. The c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphyses
The diaphysis is the main or midsection (shaft) of a long bone. It is made up of cortical bone and usually contains bone marrow and adipose tissue (fat). It is a middle tubular part composed of compact bone which surrounds a central marrow cavity which contains red or yellow marrow. In diaphysis, primary ossification occurs. Ewing sarcoma tends to occur at the diaphysis.Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Board Review, Cuccurullo Additional images Illu long bone.jpg File:EpiMetaDiaphyse.jpg, Long bone See also *Epiphysis *Metaphysis The metaphysis is the neck portion of a long bone between the epiphysis and the diaphysis. It contains the growth plate, the part of the bone that grows during childhood, and as it grows it ossifies near the diaphysis and the epiphyses. The metaph ... References Skeletal system Long bones {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibiae
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects the knee with the ankle. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute ''tibia''. It is the second largest bone in the human body, after the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body. Structure In human anatomy, the tibia is the second largest bone next to the femur. As in other vertebrates the tibia is one of two bones in the lower leg, the other being the fibula, and is a component of the knee and ankle joints. The ossification or formation of the bone st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibulae
The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is small, placed toward the back of the head of the tibia, below the knee joint and excluded from the formation of this joint. Its lower extremity inclines a little forward, so as to be on a plane anterior to that of the upper end; it projects below the tibia and forms the lateral part of the ankle joint. Structure The bone has the following components: * Lateral malleolus * Interosseous membrane connecting the fibula to the tibia, forming a syndesmosis joint * The superior tibiofibular articulation is an arthrodial joint between the lateral condyle of the tibia and the head of the fibula. * The inferior tibiofibular articulation (tibiofibular syndesmosis) is formed by the rough, convex surface of the medial side of the lower end of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dwarfism
Dwarfism is a condition wherein an organism is exceptionally small, and mostly occurs in the animal kingdom. In humans, it is sometimes defined as an adult height of less than , regardless of sex; the average adult height among people with dwarfism is , although some individuals with dwarfism are slightly taller. ''Disproportionate dwarfism'' is characterized by either short limbs or a short torso. In cases of ''proportionate dwarfism'', both the limbs and torso are unusually small. Intelligence is usually normal, and most have a nearly normal life expectancy. People with dwarfism can usually bear children, though there are additional risks to the mother and child dependent upon the underlying condition. The most common and recognisable form of dwarfism in humans (comprising 70% of cases) is achondroplasia, a genetic disorder whereby the limbs are diminutive. Growth hormone deficiency is responsible for most other cases. Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Those w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intellectual Disability
Intellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disability in the United Kingdom and formerly mental retardation,Rosa's Law, Pub. L. 111-256124 Stat. 2643(2010). is a generalized neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by significantly impaired intellectual and adaptive functioning. It is defined by an IQ under 70, in addition to deficits in two or more adaptive behaviors that affect everyday, general living. Intellectual functions are defined under DSM-V as reasoning, problem‑solving, planning, abstract thinking, judgment, academic learning, and learning from instruction and experience, and practical understanding confirmed by both clinical assessment and standardized tests. Adaptive behavior is defined in terms of conceptual, social, and practical skills involving tasks performed by people in their everyday lives. Intellectual disability is subdivided into syndromic intellectual disability, in which intellectual deficits associated with other medical and be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rickets
Rickets is a condition that results in weak or soft bones in children, and is caused by either dietary deficiency or genetic causes. Symptoms include bowed legs, stunted growth, bone pain, large forehead, and trouble sleeping. Complications may include bone deformities, bone pseudofractures and fractures, muscle spasms, or an abnormally curved spine. The most common cause of rickets is a vitamin D deficiency, although hereditary genetic forms also exist. This can result from eating a diet without enough vitamin D, dark skin, too little sun exposure, exclusive breastfeeding without vitamin D supplementation, celiac disease, and certain genetic conditions. Other factors may include not enough calcium or phosphorus. The underlying mechanism involves insufficient calcification of the growth plate. Diagnosis is generally based on blood tests finding a low calcium, low phosphorus, and a high alkaline phosphatase together with X-rays. Prevention for exclusively breastfed babies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Syphilis
Congenital syphilis is syphilis present ''in utero'' and at birth, and occurs when a child is born to a mother with syphilis. Untreated early syphilis infections results in a high risk of poor pregnancy outcomes, including saddle nose, lower extremity abnormalities, miscarriages, premature births, stillbirths, or death in newborns. Some infants with congenital syphilis have symptoms at birth, but many develop symptoms later. Symptoms may include rash, fever, an enlarged liver and spleen, and skeletal abnormalities. Newborns will typically not develop a primary syphilitic chancre but may present with signs of secondary syphilis (i.e. generalized body rash). Often these babies will develop syphilitic rhinitis ("snuffles"), the mucus from which is laden with the ''T. pallidum'' bacterium, and therefore highly infectious. If a baby with congenital syphilis is not treated early, damage to the bones, teeth, eyes, ears, and brain can occur. Classification Early This is a subset of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteopathies
Osteopathic medicine is a branch of the medical profession in the United States that promotes the practice of allopathic medicine with a set of philosophy and principles set by its earlier form, osteopathy. Osteopathic physicians (DOs) are licensed to practice medicine and surgery in all 50 US states. Only graduates of American osteopathic medical colleges may practice the full scope of medicine and surgery generally considered to be medicine by the general public; US DO graduates have historically applied for medical licensure in 87 countries outside of the United States, 85 of which provided them with the full scope of medical and surgical practice. The field is distinct from osteopathic practices offered in nations outside of the U.S., whose practitioners are generally not considered part of core medical staff nor of medicine itself. The other major branch of medicine in the United States is referred to by practitioners of osteopathic medicine as allopathic medicine. By the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |