|
Weigand Von Redwitz
Weigand of Redwitz (1476 in Tüschnitz, now part of Küps – 20 May 1556 in Kronach) was Prince-Bishop of Bamberg from 1522 until his death. Background Weigand of Redwitz was a member of the Franconian Redwitz family. The Redwitzes were Imperial Knights; the family was named after Redwitz an der Rodach, a village in Lichtenfels district in Upper Franconia. Weigand was a son of Henry of Redwitz at Theisenort and Tüschnitz and his wife, Agatha of Bibra. His relative Catherine II of Redwitz (d. 1560) was Abbess of Obermünster Abbey in Regensburg from 1533 to 1536. Life Weigand of Redwitz became a canon in Bamberg in 1490. He made a pilgrimage to Jerusalem. In 1520, he was the senior pastor of Kronach. Among his congregation was the reformer Johannes Grau, who had to flee to Wittenberg after he married the daughter of a citizen of Kronach. During his time as bishop, Weigand acted against Luther's followers and removed Lutheran clergy from office. However, under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Salver
Johann Salver (ca. 1670–1738) was a German Engraving, engraver from the town of Forchheim, and the father of Johann Octavian Salver. Salver is the author of ''Die Gross und Landmeister des Deutschen Ordens'' containing 51 plates, published in Würzburg in 1716, and the series on the Würzburg prince-bishops titled ''Geschicht-Schreiber von dem Bischoffthum Wirtzburg'', published in 1713. German engravers 1670s births 1738 deaths People from Forchheim Artists from Würzburg {{Germany-artist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wittenberg
Wittenberg ( , ; Low Saxon language, Low Saxon: ''Wittenbarg''; meaning ''White Mountain''; officially Lutherstadt Wittenberg (''Luther City Wittenberg'')), is the fourth largest town in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Wittenberg is situated on the River Elbe, north of Leipzig and south-west of Berlin, and has a population of 46,008 (2018). Wittenberg is famous for its close connection with Martin Luther and the Protestant Reformation, for which it received the honourific ''Lutherstadt''. Several of Wittenberg's buildings are associated with the events, including a preserved part of the Augustinians, Augustinian monastery in which Luther lived, first as a monk and later as owner with his wife Katharina von Bora and family, considered to be the world's premier museum dedicated to Luther. Wittenberg was also the seat of the Elector of Saxony, a dignity held by the dukes of Duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg, Saxe-Wittenberg, making it one of the most powerful cities in the Holy Roman Empire. To ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bamberg
Bamberg (, , ; East Franconian: ''Bambärch'') is a town in Upper Franconia, Germany, on the river Regnitz close to its confluence with the river Main. The town dates back to the 9th century, when its name was derived from the nearby ' castle. Cited as one of Germany's most beautiful towns, with medieval streets and Europe's largest intact old city wall, the old town of Bamberg has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1993. From the 10th century onwards, Bamberg became a key link with the Slav peoples, notably those of Poland and Pomerania. It experienced a period of great prosperity from the 12th century onwards, during which time it was briefly the centre of the Holy Roman Empire. Emperor Henry II was also buried in the old town, alongside his wife Kunigunde. The town's architecture from this period strongly influenced that in Northern Germany and Hungary. From the middle of the 13th century onwards, the bishops were princes of the Empire and ruled Bamberg, overseeing the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forchheim
Forchheim () is a town in Upper Franconia (german: Oberfranken) in northern Bavaria, and also the seat of the administrative district of Forchheim. Forchheim is a former royal city, and is sometimes called the Gateway to the Franconian Switzerland, referring to the region of outstanding natural beauty to the north east of the town. Nowadays Forchheim is most famous for its ten day long beer and music festival (Annafest) which takes place in late July in an idyllic wooded hillside, home to 24 beer gardens, on the outskirts of the town. Forchheim's population, as of December 2013, was 30,705, and its land area is . Its position is 49° 44' N, 11° 04' E and its elevation is above sea level. Name and coat of arms When the coat of arms was bestowed upon the town at the beginning of the 13th century, people wrongly believed that their town's name, "Vorchheim" originates from the Old High German word ''vorhe'' (“trout”). This resulted in the coat of arms showing two trout (above ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Alcibiades, Margrave Of Brandenburg-Kulmbach
Albert II (german: Albrecht; 28 March 15228 January 1557) was the Margrave of Brandenburg-Kulmbach (Brandenburg-Bayreuth) from 1527 to 1553. He was a member of the Franconian branch of the House of Hohenzollern. Because of his bellicose nature, Albert was given the cognomen ''Bellator'' ("the Warlike") during his lifetime. Posthumously, he became known as ''Alcibiades''. Biography Albert was born in Ansbach and, losing his father Casimir in 1527, he came under the guardianship of his uncle George, Margrave of Brandenburg-Ansbach, a strong adherent of Protestantism. In 1541, he received Bayreuth as his share of the family lands, but as the chief town of his principality was Kulmbach, he is sometimes referred to as the Margrave of Brandenburg-Kulmbach. His restless and turbulent nature marked him out for a military career; and having collected a small band of soldiers, he assisted Emperor Charles V in his war with France in 1543. The Peace of Crépy in September 1544 deprived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Margrave War
The Second Margrave War () was a conflict in the Holy Roman Empire between 1552 and 1555. Instigated by Albert Alcibiades, Margrave of Brandenburg-Kulmbach and Brandenburg-Bayreuth, it involved numerous raids, plunderings, and the destruction of many towns and castles in the empire, especially in Franconia. Other towns in other areas were also affected, such as Mainz, Worms, Oppenheim, Metz, Verdun, Frankfurt, and Speyer. * 19 June 1552: Nuremberg capitulates to Albert Alcibiades; capture of Forchheim and Bamberg. * 9 July 1553: Battle of Sievershausen; Maurice, Elector of Saxony and Henry V, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg defeat Albert Alcibiades; Maurice is killed in the battle and Henry loses his two sons. * 1553 :The city of Hof was successfully besieged by the opponents of Margrave Albert II Alcibiades. * 26 November 1553: Capture and destruction of Kulmbach, Albert's residence, by troops from Brunswick-Lüneburg, Bohemia, Bamberg, Nuremberg, Würzburg and other areas of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgraviate Of Nuremberg
The Burgraviate of Nuremberg (german: Burggrafschaft Nürnberg) was a state of the Holy Roman Empire from the early 12th to the late 15th centuries. As a burgraviate, it was a county seated in the town of Nuremberg; almost two centuries passed before the burgraviate lost power over the city, which became independent from 1219. Eventually, the burgraviate was partitioned to form Brandenburg-Ansbach and Brandenburg-Bayreuth. History Nuremberg was probably founded around the turn of the 11th century, according to the first documentary mention of the city in 1050, as the location of an Imperial castle between the East Franks and the Bavarian March of the Nordgau.Nürnberg, Reichsstadt: Politische und soziale Entwicklung (Political and Social Developmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg, Truchsess Von Waldburg
Georg III Truchsess von Waldburg-Zeil ( Waldsee, 25 January 1488 – Bad Waldsee, 29 May 1531), also known as Bauernjörg, was a Swabian League Army Commander in the German Peasants' War. Life He was a member of the House of Waldburg, which received through him in 1525 the hereditary title of ''Truchsess'' (''Seneschal'', or ''Steward'', in English) of the Holy Roman Empire and the right to put it in their family name. He served since 1508 Duke Ulrich von Württemberg and helped him crush the Poor Conrad rebellion. In 1516 he fought for Bavaria alongside Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor in Italy against France and their allies. In the next years he was in the service of the Swabian League and chased his former employer, Ulrich von Württemberg out of Württemberg. In 1525 he succeeded his cousin Wilhelm as governor of Württemberg. Both received the hereditary title of Imperial Steward (''Reichserbtruchsess'') from the hands of Emperor Charles V on 27 July 1526 in Toledo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathedral Chapter
According to both Catholic and Anglican canon law, a cathedral chapter is a college of clerics ( chapter) formed to advise a bishop and, in the case of a vacancy of the episcopal see in some countries, to govern the diocese during the vacancy. In the Roman Catholic Church their creation is the purview of the pope. They can be "numbered", in which case they are provided with a fixed " prebend", or "unnumbered", in which case the bishop indicates the number of canons according to the rents. These chapters are made up of canons and other officers, while in the Church of England chapters now include a number of lay appointees. In some Church of England cathedrals there are two such bodies, the lesser and greater chapters, which have different functions. The smaller body usually consists of the residentiary members and is included in the larger one. Originally, it referred to a section of a monastic rule that was read out daily during the assembly of a group of canons or other clergy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swabian League
The Swabian League (''Schwäbischer Bund'') was a mutual defence and peace keeping association of Imperial State, Imperial Estates – free Imperial cities, prelates, principalities and knights – principally in the territory of the early medieval stem duchy of Duchy of Swabia, Swabia established on 14 February 1488. The religious revolution of the Protestant Reformation divided its members, and the Swabian League disbanded in 1534. History The Swabian League was established in 1488 at the behest of Emperor Frederick III, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick III of Habsburg and supported as well by Bertold von Henneberg-Römhild, Bertold von Henneberg-Römhild, archbishop of Mainz, whose conciliar rather than monarchic view of the ''Reich'' often put him at odds with Frederick's successor Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor, Maximilian. The Swabian League cooperated towards the keeping of the imperial peace and at least in the beginning curbing the expansionist History of Bavaria, Bavaria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
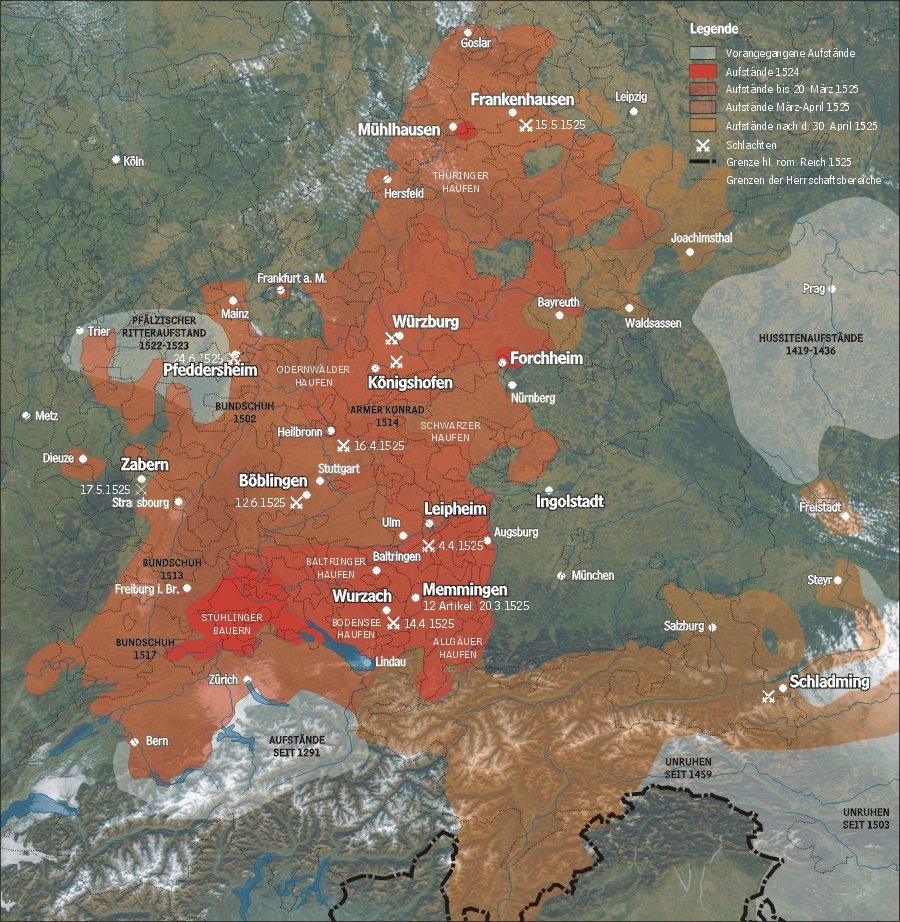
German Peasants' War
The German Peasants' War, Great Peasants' War or Great Peasants' Revolt (german: Deutscher Bauernkrieg) was a widespread popular revolt in some German-speaking areas in Central Europe from 1524 to 1525. It failed because of intense opposition from the aristocracy, who slaughtered up to 100,000 of the 300,000 poorly armed peasants and farmers. The survivors were fined and achieved few, if any, of their goals. Like the preceding Bundschuh movement and the Hussite Wars, the war consisted of a series of both economic and religious revolts in which peasants and farmers, often supported by Anabaptist clergy, took the lead. The German Peasants' War was Europe's largest and most widespread popular uprising before the French Revolution of 1789. The fighting was at its height in the middle of 1525. The war began with separate insurrections, beginning in the southwestern part of what is now Germany and Alsace, and spread in subsequent insurrections to the central and eastern areas of Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |