|
Wei Kang
Wei Kang (died 213), courtesy name Yuanjiang, was a Chinese politician who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. Early life and career Wei Kang was from Jingzhao Commandery (京兆郡), which is around present-day Xi'an, Shaanxi. His father, Wei Duan (韋端), initially served as the Governor (牧) of Liang Province (涼州), but was later recalled to the imperial capital to serve as Minister Coachman (太僕). Kong Rong once told Wei Duan, "Two days ago, Yuanjiang visited me. He is knowledgeable, talented, bright, elegant and resilient. He will become a great man." Wei Kang also had a younger brother, Wei Dan (韋誕), who served as a Household Counsellor (光祿大夫) in the Han imperial court. The ''Sanfu Juelu'' recorded that Wei Kang was already eight ''chi'' and five '' cun'' tall (approximately 1.96 metres) when he was just 14 years old. Wei Kang was recommended by Xun Yu to join the Han civil service. He initially served as a Registrar (主簿) in Jingzhao Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Xian Of Han
Emperor Xian of Han (2 April 181 – 21 April 234), personal name Liu Xie (劉協), courtesy name Bohe, was the 14th and last emperor of the Eastern Han dynasty in China. He reigned from 28 September 189 until 11 December 220. Liu Xie was a son of Liu Hong (Emperor Ling) and was a younger half-brother of his predecessor, Liu Bian (Emperor Shao). In 189, at the age of eight, he became emperor after the warlord Dong Zhuo, who had seized control of the Han central government, deposed Emperor Shao and replaced him with Liu Xie. The newly enthroned Liu Xie, historically known as Emperor Xian, was in fact a puppet ruler under Dong Zhuo's control. In 190, when a coalition of regional warlords launched a punitive campaign against Dong Zhuo in the name of freeing Emperor Xian, Dong Zhuo ordered the destruction of the imperial capital, Luoyang, and forcefully relocated the imperial capital along with its residents to Chang'an. After Dong Zhuo's assassination in 192, Emperor Xian f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
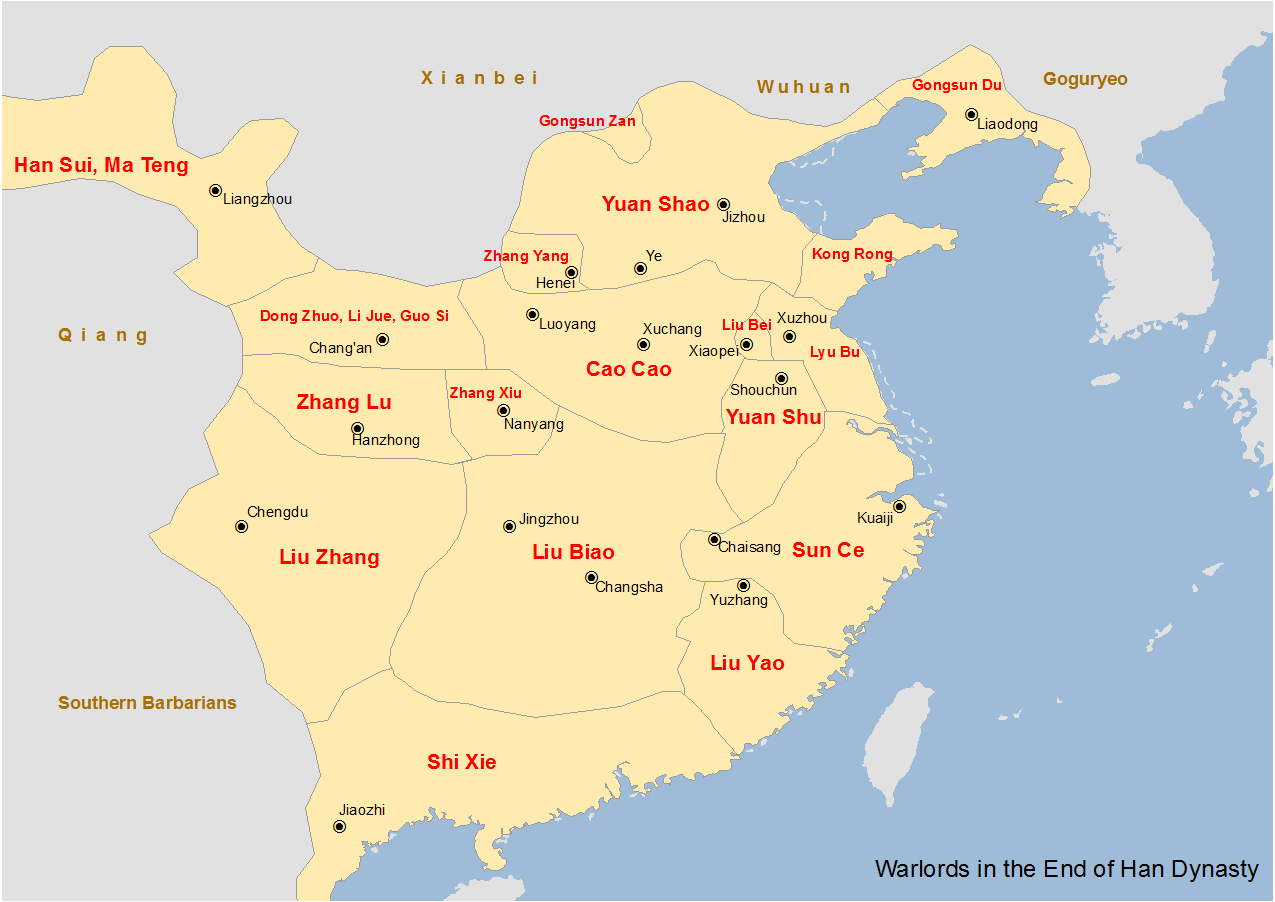
Han Sui
Han Sui () (140s - June or July 215According to Cao Cao's biography in ''Sanguozhi'', Han Sui was killed in the 5th month of the 20th year of the ''Jian'an'' era of Liu Xie's reign. This corresponds to 15 June to 13 July 215 on the Julian calendar. 建安二十年)五月,公攻屠之。西平、金城诸将麹演、蒋石等共斩送韩遂首。''Sanguozhi'' vol.01), courtesy name Wenyue, was a military general and minor warlord who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. For most of his life, he was active in Liang Province (涼州; covering parts of present-day Shaanxi and Gansu) and was involved in several rebellions against the Han government and the warlord Cao Cao. Life With the backing of the Qiang people who populated much of Liang Province, Han Sui participated in the Liang Province Rebellion against the Han dynasty during the rule of Emperor Ling. He joined forces with others in the area, such as Bian Zhang, Beigong Yu (北宫玉) and Liwen Hou ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sima Guang
Sima Guang (17 November 1019 – 11 October 1086), courtesy name Junshi, was a Chinese historian, politician, and writer. He was a high-ranking Song dynasty scholar-official who authored the monumental history book ''Zizhi Tongjian''. Sima was a political conservative who opposed Wang Anshi's reforms. Early life Sima Guang was named after his birthplace Guāng Prefecture, where his father Sima Chi () served as a county magistrate in Guangshan County. The Simas were originally from Xia County in Shǎn Prefecture, and claimed descent from Cao Wei's official Sima Fu in the 3rd century. A famous anecdote relates how the young Sima Guang once saved a playmate who had fallen into an enormous vat full of water. As other children scattered in panic, Sima Guang calmly picked up a rock and smashed a hole in the base of the pot. Water leaked out, and his friend was saved from drowning. At age 6, Sima Guang once heard a lecture on the 4th-century BC history book '' Zuo Zhuan''. Fasci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annotations To Records Of The Three Kingdoms
Annotations to Records of the Three Kingdoms () by Pei Songzhi (372-451) is an annotation completed in the 5th century of the 3rd century historical text '' Records of the Three Kingdoms'', compiled by Chen Shou. After leaving his native land, Pei Songzhi became the Gentleman of Texts under the Liu Song Dynasty, and was given the assignment of editing the book, which was completed in 429. This became the official history of the Three Kingdoms period, under the title ''Sanguozhi zhu'' (''zhu'' meaning "notes"). He went about providing detailed explanations to some of the geography and other elements mentioned in the original. More importantly, he made corrections to the work, in consultation with records he collected of the period. In regard to historical events and figures, as well as Chen Shou's opinions, he added his own commentary. From his broad research, he was able to create a history which was relatively complete, without many of the loose ends of the original. Some of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pei Songzhi
Pei Songzhi (372–451), courtesy name Shiqi, was a Chinese historian and politician who lived in the late Eastern Jin dynasty and Liu Song dynasty. His ancestral home was in Wenxi County, Shanxi, but he moved to the Jiangnan region later. He is best known for making annotations to the historical text ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' (''Sanguozhi'') written by Chen Shou in the third century, providing additional details omitted from the original work. His commentary, completed in 429, became integral to later editions of the ''Sanguozhi'', making the joint work three times as long as the original.Yuet Keung Lo, "Pei Songzhi", in ''A Global Encyclopedia of Historical Writing'', edited by D. R. Woolf (Garland Reference Library, 1998), p. 701. His son, Pei Yin (裴駰), and great-grandson Pei Ziye (裴子野), were also well-known historians. Life Pei was born in a family of officials who served in the Eastern Jin government. His grandfather, Pei Mei (裴昧), served as a Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Records Of The Three Kingdoms
The ''Records or History of the Three Kingdoms'', also known by its Chinese name as the Sanguo Zhi, is a Chinese historical text which covers the history of the late Eastern Han dynasty (c. 184–220 AD) and the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). It is widely regarded as the official and authoritative source historical text for that period. Written by Chen Shou in the third century, the work synthesizes the histories of the rival states of Cao Wei, Shu Han and Eastern Wu in the Three Kingdoms period into a single compiled text. The ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' is the main source of influence for the 14th century historical novel '' Romance of the Three Kingdoms,'' considered one of the great four novels of Chinese classical literature. Major chunks of the records have been translated into English, but the tome has yet to be fully translated. Origin and structure The '' Records of the Grand Historian'', '' Book of Han'' and ''Book of the Later Han'', and the ''Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chen Shou
Chen Shou (; 233–297), courtesy name Chengzuo (), was a Chinese historian, politician, and writer who lived during the Three Kingdoms period and Jin dynasty of China. Chen Shou is most known for his most celebrated work, the ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' (''Sanguozhi''), which records the history of the late Eastern Han dynasty and the Three Kingdoms period. Chen Shou wrote the Sanguozhi primarily in the form of biographies of notable persons of those eras. Today, Chen's ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' is part of the '' Twenty-Four Histories'' canon of ancient Chinese history. Historical sources on Chen Shou's life There are two biographies of Chen Shou. The first one is in the '' Chronicles of Huayang'', which was written by Chang Qu in the fourth century during the Eastern Jin dynasty. The second one is in the '' Book of Jin'', which was written by Fang Xuanling and others in the seventh century during the Tang dynasty. Life He started his career as an official ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lists Of People Of The Three Kingdoms
The following are lists of people significant to the Three Kingdoms period (220–280) of Chinese history. Their names in Mandarin pinyin are sorted in alphabetical order. Fictional characters in the 14th-century historical novel '' Romance of the Three Kingdoms'' and those found in other cultural references to the Three Kingdoms are listed separately in List of fictional people of the Three Kingdoms. Notes The states of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu were officially established in 220, 221, and 229 respectively. Therefore, certain people in the list who died before these years have their respective lords' names, in place of either of the three states, listed in the allegiance column. Take Guan Yu for example — he died before Liu Bei Liu Bei (, ; ; 161 – 10 June 223), courtesy name Xuande (), was a warlord in the late Eastern Han dynasty who founded the state of Shu Han in the Three Kingdoms period and became its first ruler. Although he was a distant relative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yang Fu (Han Dynasty)
Yang Fu ( 210s–230s), courtesy name Yishan, was a Chinese politician of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China. He previously served as a regional official in Liang Province during the late Eastern Han dynasty. In the 210s, when the warlord Ma Chao rebelled against the Han central government, occupied Liang Province by force and murdered some of the provincial officials, Yang Fu and his colleagues pretended to submit to Ma Chao. Later, they plotted a revolt against him and succeeded in forcing him out of Liang Province. During the reign of the second Wei emperor Cao Rui, Yang Fu proposed to the emperor to scale down his extravagant construction projects but the emperor ignored him. Early life Yang Fu was from Ji County (冀縣; or Jicheng 冀城), Tianshui Commandery (), which is around present-day Gangu County, Gansu. He served as a minor official in the local commandery office in his youth. Once, when the military officers in his home commandery so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhao Ang
Zhao Ang ( 210s), courtesy name Weizhang, was a Chinese politician who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty and was aligned with the faction that would later become the state of Cao Wei in the Three Kingdoms period. He is best known for resisting the warlord Ma Chao in Liang Province (covering roughly present-day Gansu and Ningxia) in the 210s. His wife, Wang Yi, is famous for supporting her husband throughout their conflict with Ma Chao. Early career Zhao Ang was from Tianshui Commandery (), which is in present-day Tianshui, Gansu. In his early years, he served as an Assistant Officer () in Liang Province, alongside Yang Fu and Yin Feng (), who were also from Tianshui Commandery. Later, while Zhao Ang was serving as the Prefect () of Qiangdao County (羌道縣; around present-day Zhugqu County, Gansu), Liang Shuang () started a revolt in the county and conquered Xi (), a district in Qiangdao where Zhao Ang's family members lived. Zhao Ang's two sons were killed, while h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiahou Yuan
Xiahou Yuan () (died 219), courtesy name Miaocai, was a Chinese military general and politician serving under the warlord Cao Cao in the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He is known for his exploits in western China (in parts of present-day Gansu, Ningxia and Shaanxi provinces) in the 210s, during which he defeated Cao Cao's rivals Ma Chao and Han Sui in Liang Province and the surrounding areas, and forced several Di and Qiang tribal peoples into submission. He was killed in action at the Battle of Mount Dingjun while defending Hanzhong Commandery from attacks by a rival warlord Liu Bei. Xiahou Yuan's death was highly dramatised in the 14th-century historical novel '' Romance of the Three Kingdoms'', in which he was slain by Liu Bei's general Huang Zhong during a surprise raid. Early life and career Xiahou Yuan was from Qiao County (), Pei State (), which is in present-day Bozhou, Anhui. He was a younger cousin of Xiahou Dun and a descendant of Xiahou Ying, who ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Jicheng
The siege of Jicheng was a part of the campaign Ma Chao initiated in an attempt to retake Liang Province after the coalition of Guanxi (west of Hangu Pass) was defeated at the Battle of Tong Pass in the winter of 211 in the late Eastern Han dynasty. Background After the coalition melted down, Ma Chao took the remainder of his army towards Lantian, where he could prepare a stand against Cao Cao. Unexpectedly, Su Bo in Hejian rebelled, and Cao Cao decided to lead his main army to quell the uprising, sparing Ma Chao the time to recuperate. Thus, Ma Chao gradually regained his strength, and once again wielded great influence over local non-Han people. To resist Cao Cao, Ma Chao had recruited many Qiang and Hu soldiers, and received reinforcements from Zhang Lu of Hanzhong. He had planned to conquer all counties in Longxi (west of Long Ridges), and within a year, all cities except Jicheng (capital of Tianshui Commandery) in the area surrendered to the allied force. The siege ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |