|
Wee (cell Cycle)
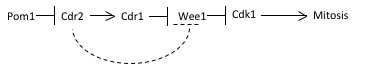
Wee1 is a nuclear kinase belonging to the Ser/Thr family of protein kinases in the fission yeast ''Schizosaccharomyces pombe'' (''S. pombe'')Wee1has a molecular mass of 96 kDa and is a key regulator of cell cycle progression. It influences cell size by inhibiting the entry into mitosis, through inhibiting Cdk1. Wee1 has homologues in many other organisms, including mammals. Introduction The regulation of cell size is critical to ensure functionality of a cell. Besides environmental factors such as nutrients, growth factors and functional load, cell size is also controlled by a cellular cell size checkpoint. Wee1 is a component of this checkpoint. It is a kinase determining the timepoint of entry into mitosis, thus influencing the size of the daughter cells. Loss of Wee1 function will produce smaller than normal daughter cell, because cell division occurs prematurely. Its name is derived from the Scottish dialect word wee, meaning small - its discoverer Paul Nurse was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Kinase
A protein kinase is a kinase which selectively modifies other proteins by covalently adding phosphates to them (phosphorylation) as opposed to kinases which modify lipids, carbohydrates, or other molecules. Phosphorylation usually results in a functional change of the target protein ( substrate) by changing enzyme activity, cellular location, or association with other proteins. The human genome contains about 500 protein kinase genes and they constitute about 2% of all human genes. There are two main types of protein kinase. The great majority are serine/threonine kinases, which phosphorylate the hydroxyl groups of serines and threonines in their targets and most of the others are tyrosine kinases, although additional types exist. Protein kinases are also found in bacteria and plants. Up to 30% of all human proteins may be modified by kinase activity, and kinases are known to regulate the majority of cellular pathways, especially those involved in signal transduction. Chemical ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pom1
Pom1 is a polarity protein kinase in fission yeast, ''Schizosaccharomyces pombe'' (''S. pombe''), that localizes to cell ends and regulates cell division. As the cell lengthens, the level of Pom1 in the middle declines, which triggers mitosis.Bahler, J., and Pringle, J.R. “Pom1p, a fission yeast protein kinase that provides positional information for both polarized growth and cytokinesis.” Genes and Development 12, 1356-1370 (1998). The genebr>''pom1''codes for a protein 1087 amino acids long with the protein kinase domain likely located at the carboxyl terminus. Pom1 regulates a signaling pathway that includes Cdk1 and ultimately regulates mitotic entry.Moseley, J.B., Mayeux, A., Paoletti, A. and Nurse, P. “A spatial gradient coordinates cell size and mitotic entry in fission yeast.” Nature 459, 857-861 (2009). Cells with mutant pom1 form a septa and growth zone, but show a host of abnormalities including misplaced or misoriented septa, bi-polar growth replaced with r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-terminus
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from N-terminus to C-terminus. The convention for writing peptide sequences is to put the C-terminal end on the right and write the sequence from N- to C-terminus. Chemistry Each amino acid has a carboxyl group and an amine group. Amino acids link to one another to form a chain by a dehydration reaction which joins the amine group of one amino acid to the carboxyl group of the next. Thus polypeptide chains have an end with an unbound carboxyl group, the C-terminus, and an end with an unbound amine group, the N-terminus. Proteins are naturally synthesized starting from the N-terminus and ending at the C-terminus. Function C-terminal retention signals While the N-terminus of a protein often c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorylation
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Protein phosphorylation often activates (or deactivates) many enzymes. Glucose Phosphorylation of sugars is often the first stage in their catabolism. Phosphorylation allows cells to accumulate sugars because the phosphate group prevents the molecules from diffusing back across their transporter. Phosphorylation of glucose is a key reaction in sugar metabolism. The chemical equation for the conversion of D-glucose to D-glucose-6-phosphate in the first step of glycolysis is given by :D-glucose + ATP → D-glucose-6-phosphate + ADP : ΔG° = −16.7 kJ/mol (° indicates measurement at standard condition) Hepatic cells are freely permeable to glucose, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CHEK1
Checkpoint kinase 1, commonly referred to as Chk1, is a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase that, in humans, is encoded by the ''CHEK1'' gene. Chk1 coordinates the DNA damage response (DDR) and cell cycle checkpoint response. Activation of Chk1 results in the initiation of cell cycle checkpoints, cell cycle arrest, DNA repair and cell death to prevent damaged cells from progressing through the cell cycle. Discovery In 1993, Beach and associates initially identified Chk1 as a serine/threonine kinase which regulates the G2/M phase transition in fission yeast. Constitutive expression of Chk1 in fission yeast was shown to induce cell cycle arrest. The same gene called Rad27 was identified in budding yeast by Carr and associates. In 1997, homologs were identified in more complex organisms including the fruit fly, human and mouse. Through these findings, it is apparent Chk1 is highly conserved from yeast to humans. Structure Human Chk1 is located on chromosome 11 on the cytogenic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polo Kinase
In enzymology, a polo kinase () is a kinase enzyme i.e. one that catalyzes the chemical reaction :ATP + a protein \rightleftharpoons ADP + a phosphoprotein Thus, the two substrates of these enzymes are ATP and protein, whereas their two products are ADP and phosphoprotein. These enzymes belong to the family of transferases, specifically those transferring a phosphate group to the sidechain oxygen atom of serine or threonine residues in proteins (protein-serine/threonine kinases). The systematic name of this like.html"_;"title="olo[-like">olo[-likekinaseenzyme_class_is_ATP:protein_phosphotransferase_(olo[-likekinase.html"_;"title="like.html"_;"title="olo[-like">olo[-likekinase">like.html"_;"title="olo[-like">olo[-likekinaseenzyme_class_is_ATP:protein_phosphotransferase_(Spindle_apparatus">spindle-pole-dependent). Examples_and_other_names_in_common_use_include_Cdc5,_Cdc5p,_Plk,_PLK,_PLK1.html" "title="Spindle_apparatus.html" "title="like">olo[-likekinase.html" ;"title="lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cdc25C
M-phase inducer phosphatase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''CDC25C'' gene. This gene is highly conserved during evolution and it plays a key role in the regulation of cell division. The encoded protein is a tyrosine phosphatase and belongs to the Cdc25 phosphatase family. It directs dephosphorylation of cyclin B-bound CDC2 (CDK1) and triggers entry into mitosis. It is also thought to suppress p53-induced growth arrest. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been described, however, the full-length nature of many of them is not known. Interactions CDC25C has been shown to interact with MAPK14, CHEK1, PCNA, PIN1, PLK3 and NEDD4. See also * Cdc25 Cdc25 is a dual-specificity phosphatase first isolated from the yeast '' Schizosaccharomyces pombe'' as a cell cycle defective mutant. As with other cell cycle proteins or genes such as Cdc2 and Cdc4, the "cdc" in its name refers to "cell divis ... References Further reading * * * * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maturation Promoting Factor
Maturation-promoting factor (abbreviated MPF, also called mitosis-promoting factor or M-Phase-promoting factor) is the cyclin-Cdk complex that was discovered first in frog eggs. It stimulates the mitotic and meiotic phases of the cell cycle. MPF promotes the entrance into mitosis (the M phase) from the G2 phase by phosphorylating multiple proteins needed during mitosis. MPF is activated at the end of G2 by a phosphatase, which removes an inhibitory phosphate group added earlier. The MPF is also called the M phase kinase because of its ability to phosphorylate target proteins at a specific point in the cell cycle and thus control their ability to function. Discovery In 1971, two independent teams of researchers ( Yoshio Masui and Clement Markert, as well as Dennis Smith and Robert Ecker) found that frog oocytes arrested in G2 could be induced to enter M phase by microinjection of cytoplasm from oocytes that had been hormonally stimulated with progesterone. Because the entry of oo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclin B
Cyclin B is a member of the cyclin family. Cyclin B is a mitotic cyclin. The amount of cyclin B (which binds to Cdk1) and the activity of the cyclin B-Cdk complex rise through the cell cycle until mitosis, where they fall abruptly due to degradation of cyclin B (Cdk1 is constitutively present). The complex of Cdk and cyclin B is called maturation promoting factor or mitosis promoting factor (MPF). Function Cyclin B is necessary for the progression of the cells into and out of M phase of the cell cycle. At the end of S phase the phosphatase cdc25c dephosphorylates tyrosine15 and this activates the cyclin B/CDK1 complex. Upon activation the complex is shuttled to the nucleus where it serves to trigger for entry into mitosis. However, if DNA damage is detected alternative proteins are activated which results in the inhibitory phosphorylation of cdc25c and therefore cyclinB/CDK1 is not activated. In order for the cell to progress out of mitosis, the degradation of cyclin B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saccharomyces Cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungus microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have been originally isolated from the skin of grapes. It is one of the most intensively studied eukaryotic model organisms in molecular biology, molecular and cell biology, much like ''Escherichia coli'' as the model bacteria, bacterium. It is the microorganism behind the most common type of fermentation (biochemistry), fermentation. ''S. cerevisiae'' cells are round to ovoid, 5–10 micrometre, μm in diameter. It reproduces by budding. Many proteins important in human biology were first discovered by studying their Homology (biology), homologs in yeast; these proteins include cell cycle proteins, signaling proteins, and protein-processing enzymes. ''S. cerevisiae'' is currently the only yeast cell known to have Berkeley body, Berkeley bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |