|
Web Archive File
Web archiving is the process of collecting, preserving, and providing access to material from the World Wide Web. The aim is to ensure that information is preserved in an archival format for research and the public. Web archivists typically employ automated web crawlers to capturing the massive amount of information on the Web. A widely known web archive service is the Wayback Machine, run by the Internet Archive. The growing portion of human culture created and recorded on the web makes it inevitable that more and more libraries and archives will have to face the challenges of web archiving. National libraries, national archives, and various consortia of organizations are also involved in archiving Web content to prevent its loss. Commercial web archiving software and services are also available to organizations that need to archive their own web content for corporate heritage, regulatory, or legal purposes. History and development While curation and organization of the web ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Wide Web
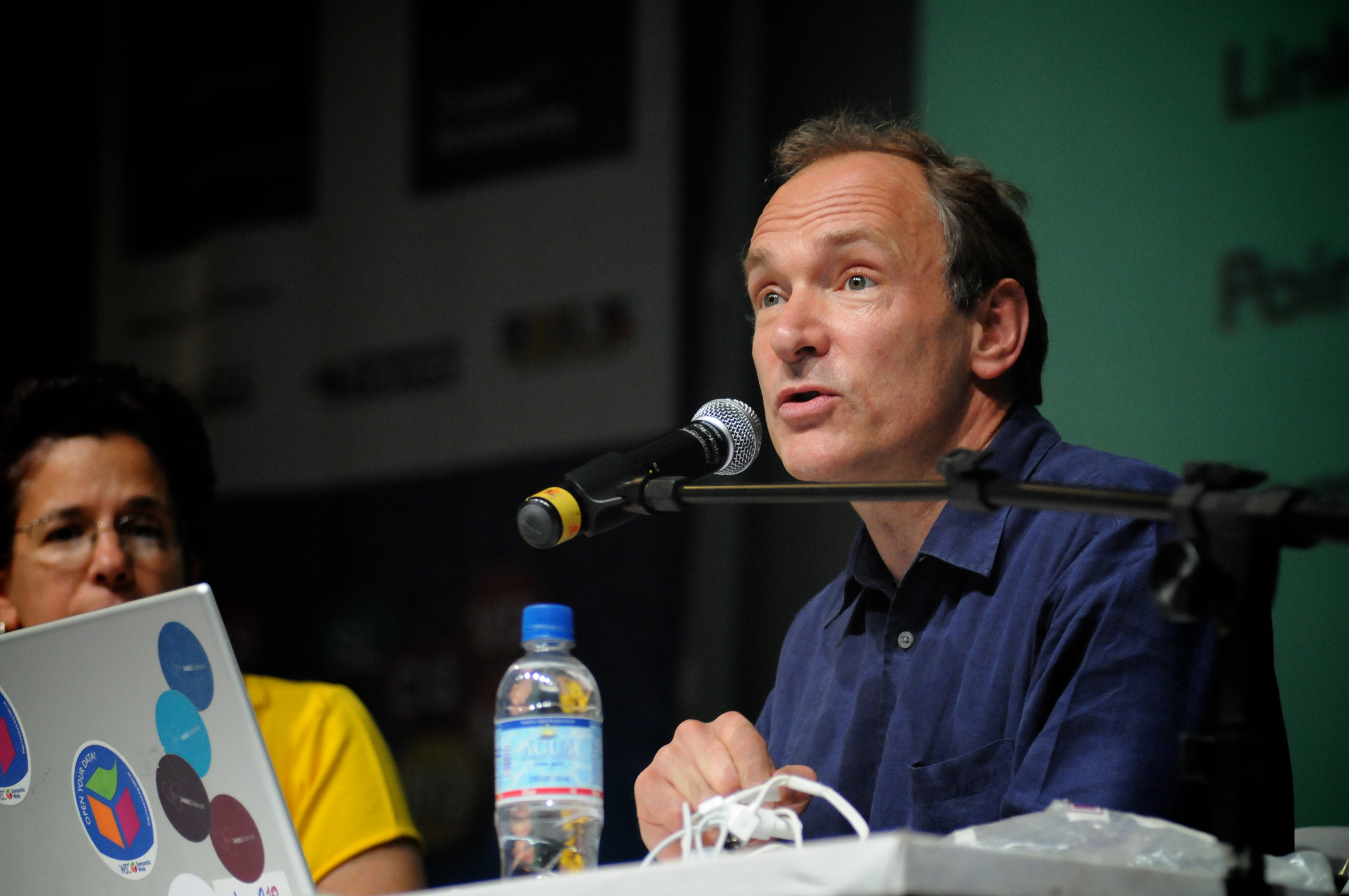
The World Wide Web (WWW or simply the Web) is an information system that enables Content (media), content sharing over the Internet through user-friendly ways meant to appeal to users beyond Information technology, IT specialists and hobbyists. It allows documents and other web resources to be accessed over the Internet according to specific rules of the HTTP, Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). The Web was invented by English computer scientist Tim Berners-Lee while at CERN in 1989 and opened to the public in 1993. It was conceived as a "universal linked information system". Documents and other media content are made available to the network through web servers and can be accessed by programs such as web browsers. Servers and resources on the World Wide Web are identified and located through character strings called uniform resource locators (URLs). The original and still very common document type is a web page formatted in Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). This markup lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Style Sheet (web Development)
A web style sheet is a form of separation of content and presentation for web design in which the markup (i.e., HTML or XHTML) of a webpage contains the page's semantic content and structure, but does not define its visual layout (style). Instead, the style is defined in an external style sheet file using a style sheet language such as CSS or XSLT. This design approach is identified as a "separation" because it largely supersedes the antecedent methodology in which a page's markup defined both style and structure. The philosophy underlying this methodology is a specific case of separation of concerns. Benefits Separation of style and content has advantages, but has only become practical after improvements in popular web browsers' CSS implementations. Speed Overall, users experience of a site utilising style sheets will generally be quicker than sites that don’t use the technology. ‘Overall’ as the first page will probably load more slowly – because the style sheet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Web (search Indexing)
The deep web, invisible web, or hidden web are parts of the World Wide Web whose contents are not indexed by standard web search-engine programs. This is in contrast to the " surface web", which is accessible to anyone using the Internet. Computer scientist Michael K. Bergman is credited with inventing the term in 2001 as a search-indexing term. Deep web sites can be accessed by a direct URL or IP address, but may require entering a password or other security information to access actual content. Uses of deep web sites include web mail, online banking, cloud storage, restricted-access social-media pages and profiles, and web forums that require registration for viewing content. It also includes paywalled services such as video on demand and some online magazines and newspapers. Terminology The first conflation of the terms "deep web" and "dark web" happened during 2009 when deep web search terminology was discussed together with illegal activities occurring on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robots Exclusion Protocol
robots.txt is the filename used for implementing the Robots Exclusion Protocol, a standard used by websites to indicate to visiting web crawlers and other web robots which portions of the website they are allowed to visit. The standard, developed in 1994, relies on voluntary compliance. Malicious bots can use the file as a directory of which pages to visit, though standards bodies discourage countering this with security through obscurity. Some archival sites ignore robots.txt. The standard was used in the 1990s to mitigate server overload. In the 2020s, websites began denying bots that collect information for generative artificial intelligence. The "robots.txt" file can be used in conjunction with sitemaps, another robot inclusion standard for websites. History The standard was proposed by Martijn Koster, when working for Nexor in February 1994 on the ''www-talk'' mailing list, the main communication channel for WWW-related activities at the time. Charles Stross claims to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HTTP
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, where hypertext documents include hyperlinks to other resources that the user can easily access, for example by a Computer mouse, mouse click or by tapping the screen in a web browser. Development of HTTP was initiated by Tim Berners-Lee at CERN in 1989 and summarized in a simple document describing the behavior of a client and a server using the first HTTP version, named 0.9. That version was subsequently developed, eventually becoming the public 1.0. Development of early HTTP Requests for Comments (RFCs) started a few years later in a coordinated effort by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) and the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), with work later moving to the IETF. HTTP/1 was finalized and fully documented (as version 1.0) in 1996 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Website
A website (also written as a web site) is any web page whose content is identified by a common domain name and is published on at least one web server. Websites are typically dedicated to a particular topic or purpose, such as news, education, commerce, entertainment, or social media. Hyperlinking between web pages guides the navigation of the site, which often starts with a home page. The most-visited sites are Google, YouTube, and Facebook. All publicly-accessible websites collectively constitute the World Wide Web. There are also private websites that can only be accessed on a private network, such as a company's internal website for its employees. Users can access websites on a range of devices, including desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones. The app used on these devices is called a web browser. Background The World Wide Web (WWW) was created in 1989 by the British CERN computer scientist Tim Berners-Lee. On 30 April 1993, CERN announced that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Web Browser
A web browser, often shortened to browser, is an application for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers can also display content stored locally on the user's device. Browsers are used on a range of devices, including desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones, smartwatches and consoles. As of 2024, the most used browsers worldwide are Google Chrome (~66% market share), Safari (~16%), Edge (~6%), Firefox (~3%), Samsung Internet (~2%), and Opera (~2%). As of 2023, an estimated 5.4 billion people had used a browser. Function The purpose of a web browser is to fetch content and display it on the user's device. This process begins when the user inputs a Uniform Resource Locator (URL), such as ''https://en.wikipedia.org/'', into the browser's address bar. Virtually all URLs on the Web start with either ''http:'' or ''h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Web Server
A web server is computer software and underlying Computer hardware, hardware that accepts requests via Hypertext Transfer Protocol, HTTP (the network protocol created to distribute web content) or its secure variant HTTPS. A user agent, commonly a web browser or web crawler, initiates communication by making a request for a web page or other Web Resource, resource using HTTP, and the server (computing), server responds with the content of that resource or an List of HTTP status codes, error message. A web server can also accept and store resources sent from the user agent if configured to do so. The hardware used to run a web server can vary according to the volume of requests that it needs to handle. At the low end of the range are embedded systems, such as a router (computing), router that runs a small web server as its configuration interface. A high-traffic Internet website might handle requests with hundreds of servers that run on racks of high-speed computers. A reso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provenance
Provenance () is the chronology of the ownership, custody or location of a historical object. The term was originally mostly used in relation to works of art, but is now used in similar senses in a wide range of fields, including archaeology, paleontology, archival science, circular economy, economy, computing, and Scientific method, scientific inquiry in general. The primary purpose of tracing the provenance of an object or entity is normally to provide contextual and circumstantial evidence for its original production or discovery, by establishing, as far as practicable, its later history, especially the sequences of its formal ownership, custody and places of storage. The practice has a particular value in helping Authentication, authenticate objects. Comparative techniques, expert opinions and the results of scientific tests may also be used to these ends, but establishing provenance is essentially a matter of documentation. The term dates to the 1780s in English. Provenance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Authentication
Authentication (from ''authentikos'', "real, genuine", from αὐθέντης ''authentes'', "author") is the act of proving an Logical assertion, assertion, such as the Digital identity, identity of a computer system user. In contrast with identification, the act of indicating a person or thing's identity, authentication is the process of verifying that identity. Authentication is relevant to multiple fields. In art, antiques, and anthropology, a common problem is verifying that a given artifact was produced by a certain person, or in a certain place (i.e. to assert that it is not counterfeit), or in a given period of history (e.g. by determining the age via carbon dating). In computer science, verifying a user's identity is often required to allow access to confidential data or systems. It might involve validating personal identity documents. In art, antiques and anthropology Authentication can be considered to be of three types: The ''first'' type of authentication is accep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIME Type
In information and communications technology, a media type, content type or MIME type is a two-part identifier for file formats and content formats. Their purpose is comparable to filename extensions and uniform type identifiers, in that they identify the intended data format. They are mainly used by technologies underpinning the Internet, and also used on Linux desktop systems. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) is the official authority for the standardization and publication of these classifications. Media types were originally defined in Request for Comments (MIME) Part One: Format of Internet Message Bodies (Nov 1996) in November 1996 as a part of the ''MIME (Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions)'' specification, for denoting type of email message content and attachments; hence the original name, ''MIME type''. Media types are also used by other internet protocols such as HTTP, document file formats such as HTML, and the XDG specifications implemented by Linux ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metadata
Metadata (or metainformation) is "data that provides information about other data", but not the content of the data itself, such as the text of a message or the image itself. There are many distinct types of metadata, including: * Descriptive metadata – the descriptive information about a resource. It is used for discovery and identification. It includes elements such as title, abstract, author, and keywords. * Structural metadata – metadata about containers of data and indicates how compound objects are put together, for example, how pages are ordered to form chapters. It describes the types, versions, relationships, and other characteristics of digital materials. * Administrative metadata – the information to help manage a resource, like resource type, and permissions, and when and how it was created. * Reference metadata – the information about the contents and quality of Statistical data type, statistical data. * Statistical metadata – also called process data, may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |