|
Weak Formulation
Weak formulations are important tools for the analysis of mathematical equations that permit the transfer of concepts of linear algebra to solve problems in other fields such as partial differential equations. In a weak formulation, equations or conditions are no longer required to hold absolutely (and this is not even well defined) and has instead weak solutions only with respect to certain "test vectors" or " test functions". In a strong formulation, the solution space is constructed such that these equations or conditions are already fulfilled. The Lax–Milgram theorem, named after Peter Lax and Arthur Milgram who proved it in 1954, provides weak formulations for certain systems on Hilbert spaces. General concept Let V be a Banach space, V' its dual space, A\colon V \to V', and f \in V'. Finding the solution u \in V of the equation Au = f is equivalent to finding u\in V such that, for all v \in V, uv) = f(v). Here, v is called a test vector or test function. To br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equation
In mathematics, an equation is a formula that expresses the equality of two expressions, by connecting them with the equals sign . The word ''equation'' and its cognates in other languages may have subtly different meanings; for example, in French an ''équation'' is defined as containing one or more variables, while in English, any well-formed formula consisting of two expressions related with an equals sign is an equation. ''Solving'' an equation containing variables consists of determining which values of the variables make the equality true. The variables for which the equation has to be solved are also called unknowns, and the values of the unknowns that satisfy the equality are called solutions of the equation. There are two kinds of equations: identities and conditional equations. An identity is true for all values of the variables. A conditional equation is only true for particular values of the variables. An equation is written as two expressions, connected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boundary (topology)
In topology and mathematics in general, the boundary of a subset of a topological space is the set of points in the closure of not belonging to the interior of . An element of the boundary of is called a boundary point of . The term boundary operation refers to finding or taking the boundary of a set. Notations used for boundary of a set include \operatorname(S), \operatorname(S), and \partial S. Some authors (for example Willard, in ''General Topology'') use the term frontier instead of boundary in an attempt to avoid confusion with a different definition used in algebraic topology and the theory of manifolds. Despite widespread acceptance of the meaning of the terms boundary and frontier, they have sometimes been used to refer to other sets. For example, ''Metric Spaces'' by E. T. Copson uses the term boundary to refer to Hausdorff's border, which is defined as the intersection of a set with its boundary. Hausdorff also introduced the term residue, which is defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
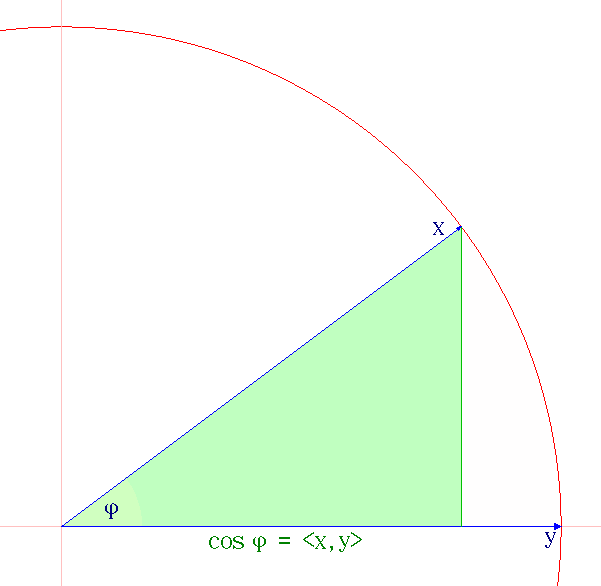
Cauchy–Schwarz Inequality
The Cauchy–Schwarz inequality (also called Cauchy–Bunyakovsky–Schwarz inequality) is considered one of the most important and widely used inequalities in mathematics. The inequality for sums was published by . The corresponding inequality for integrals was published by and . Schwarz gave the modern proof of the integral version. Statement of the inequality The Cauchy–Schwarz inequality states that for all vectors \mathbf and \mathbf of an inner product space it is true that where \langle \cdot, \cdot \rangle is the inner product. Examples of inner products include the real and complex dot product; see the examples in inner product. Every inner product gives rise to a norm, called the or , where the norm of a vector \mathbf is denoted and defined by: \, \mathbf\, := \sqrt so that this norm and the inner product are related by the defining condition \, \mathbf\, ^2 = \langle \mathbf, \mathbf \rangle, where \langle \mathbf, \mathbf \rangle is always a non-nega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poincaré Inequality
In mathematics, the Poincaré inequality is a result in the theory of Sobolev spaces, named after the French mathematician Henri Poincaré. The inequality allows one to obtain bounds on a function using bounds on its derivatives and the geometry of its domain of definition. Such bounds are of great importance in the modern, direct methods of the calculus of variations. A very closely related result is Friedrichs' inequality. Statement of the inequality The classical Poincaré inequality Let ''p'', so that 1 ≤ ''p'' < ∞ and Ω a subset bounded at least in one direction. Then there exists a constant ''C'', depending only on Ω and ''p'', so that, for every function ''u'' of the ''W''01,''p''(Ω) of zero-trace (a.k.a. zero on the boundary) functions, : ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eigenvalue
In linear algebra, an eigenvector () or characteristic vector of a linear transformation is a nonzero vector that changes at most by a scalar factor when that linear transformation is applied to it. The corresponding eigenvalue, often denoted by \lambda, is the factor by which the eigenvector is scaled. Geometrically, an eigenvector, corresponding to a real nonzero eigenvalue, points in a direction in which it is stretched by the transformation and the eigenvalue is the factor by which it is stretched. If the eigenvalue is negative, the direction is reversed. Loosely speaking, in a multidimensional vector space, the eigenvector is not rotated. Formal definition If is a linear transformation from a vector space over a field into itself and is a nonzero vector in , then is an eigenvector of if is a scalar multiple of . This can be written as T(\mathbf) = \lambda \mathbf, where is a scalar in , known as the eigenvalue, characteristic value, or characteristic roo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Number
In mathematics, a complex number is an element of a number system that extends the real numbers with a specific element denoted , called the imaginary unit and satisfying the equation i^= -1; every complex number can be expressed in the form a + bi, where and are real numbers. Because no real number satisfies the above equation, was called an imaginary number by René Descartes. For the complex number a+bi, is called the , and is called the . The set of complex numbers is denoted by either of the symbols \mathbb C or . Despite the historical nomenclature "imaginary", complex numbers are regarded in the mathematical sciences as just as "real" as the real numbers and are fundamental in many aspects of the scientific description of the natural world. Complex numbers allow solutions to all polynomial equations, even those that have no solutions in real numbers. More precisely, the fundamental theorem of algebra asserts that every non-constant polynomial equation with re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coercive Function
In mathematics, a coercive function is a function that "grows rapidly" at the extremes of the space on which it is defined. Depending on the context different exact definitions of this idea are in use. Coercive vector fields A vector field ''f'' : R''n'' → R''n'' is called coercive if :\frac \to + \infty \mbox \, x \, \to + \infty, where "\cdot" denotes the usual dot product and \, x\, denotes the usual Euclidean norm of the vector ''x''. A coercive vector field is in particular norm-coercive since \, f(x)\, \geq (f(x) \cdot x) / \, x \, for x \in \mathbb^n \setminus \ , by Cauchy–Schwarz inequality. However a norm-coercive mapping ''f'' : R''n'' → R''n'' is not necessarily a coercive vector field. For instance the rotation ''f'' : R''2'' → R''2'', ''f(x) = (-x2, x1)'' by 90° is a norm-coercive mapping which fails to be a coercive vector field since f(x) \cdot x = 0 for every x \in \mathbb^2. Coercive operators and forms A self-adjoint operator A:H\to H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilinear Form
In mathematics, a bilinear form is a bilinear map on a vector space (the elements of which are called '' vectors'') over a field ''K'' (the elements of which are called '' scalars''). In other words, a bilinear form is a function that is linear in each argument separately: * and * and The dot product on \R^n is an example of a bilinear form. The definition of a bilinear form can be extended to include modules over a ring, with linear maps replaced by module homomorphisms. When is the field of complex numbers , one is often more interested in sesquilinear forms, which are similar to bilinear forms but are conjugate linear in one argument. Coordinate representation Let be an - dimensional vector space with basis . The matrix ''A'', defined by is called the ''matrix of the bilinear form'' on the basis . If the matrix represents a vector with respect to this basis, and analogously, represents another vector , then: B(\mathbf, \mathbf) = \mathbf^\texts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weak Derivative
In mathematics, a weak derivative is a generalization of the concept of the derivative of a function (''strong derivative'') for functions not assumed differentiable, but only integrable, i.e., to lie in the L''p'' space L^1( ,b. The method of integration by parts holds that for differentiable functions u and \varphi we have :\begin \int_a^b u(x) \varphi'(x) \, dx & = \Big (x) \varphi(x)\Biga^b - \int_a^b u'(x) \varphi(x) \, dx. \\ pt \end A function ''u''' being the weak derivative of ''u'' is essentially defined by the requirement that this equation must hold for all infinitely differentiable functions ''φ'' vanishing at the boundary points (\varphi(a)=\varphi(b)=0). Definition Let u be a function in the Lebesgue space L^1( ,b. We say that v in L^1( ,b is a weak derivative of u if :\int_a^b u(t)\varphi'(t) \, dt=-\int_a^b v(t)\varphi(t) \, dt for ''all'' infinitely differentiable functions \varphi with \varphi(a)=\varphi(b)=0. Generalizing to n dimensi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sobolev Space
In mathematics, a Sobolev space is a vector space of functions equipped with a norm that is a combination of ''Lp''-norms of the function together with its derivatives up to a given order. The derivatives are understood in a suitable weak sense to make the space complete, i.e. a Banach space. Intuitively, a Sobolev space is a space of functions possessing sufficiently many derivatives for some application domain, such as partial differential equations, and equipped with a norm that measures both the size and regularity of a function. Sobolev spaces are named after the Russian mathematician Sergei Sobolev. Their importance comes from the fact that weak solutions of some important partial differential equations exist in appropriate Sobolev spaces, even when there are no strong solutions in spaces of continuous functions with the derivatives understood in the classical sense. Motivation In this section and throughout the article \Omega is an open subset of \R^n. There are ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derivative
In mathematics, the derivative of a function of a real variable measures the sensitivity to change of the function value (output value) with respect to a change in its argument (input value). Derivatives are a fundamental tool of calculus. For example, the derivative of the position of a moving object with respect to time is the object's velocity: this measures how quickly the position of the object changes when time advances. The derivative of a function of a single variable at a chosen input value, when it exists, is the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the function at that point. The tangent line is the best linear approximation of the function near that input value. For this reason, the derivative is often described as the "instantaneous rate of change", the ratio of the instantaneous change in the dependent variable to that of the independent variable. Derivatives can be generalized to functions of several real variables. In this generalization, the deriv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Function (mathematics)
In mathematics, a function from a set to a set assigns to each element of exactly one element of .; the words map, mapping, transformation, correspondence, and operator are often used synonymously. The set is called the domain of the function and the set is called the codomain of the function.Codomain ''Encyclopedia of Mathematics'Codomain. ''Encyclopedia of Mathematics''/ref> The earliest known approach to the notion of function can be traced back to works of Persian mathematicians Al-Biruni and Sharaf al-Din al-Tusi. Functions were originally the idealization of how a varying quantity depends on another quantity. For example, the position of a planet is a ''function'' of time. Historically, the concept was elaborated with the infinitesimal calculus at the end of the 17th century, and, until the 19th century, the functions that were considered were differentiable (that is, they had a high degree of regularity). The concept of a function was formalized at the end of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |