|
Wave Nonlinearity
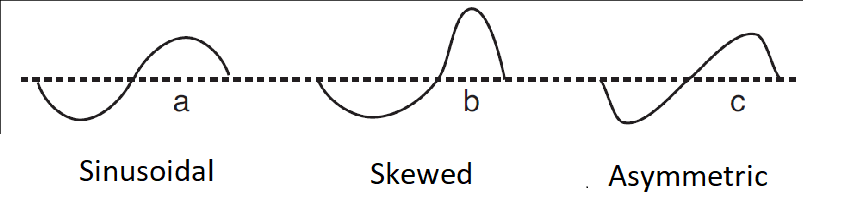
The nonlinearity of surface gravity waves refers to their deviations from a Sine wave, sinusoidal shape. In the fields of physical oceanography and coastal engineering, the two categories of nonlinearity are skewness and asymmetry. Wave skewness and asymmetry occur when waves encounter an opposing current (fluid), current or a shallow area. As waves shoal in the nearshore zone, in addition to their wavelength and height changing, their asymmetry and skewness also change. Wave skewness and asymmetry are often implicated in Offshore construction, ocean engineering and coastal engineering for the modelling of random sea states, in particular regarding the distribution of wave height, wavelength and crest length. For practical engineering purposes, it is important to know the probability of these wave characteristics in seas and oceans at a given place and time. This knowledge is crucial for the prediction of Rogue wave, extreme waves, which are a danger for ships and offshore construct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Gravity Wave
In fluid dynamics, gravity waves are waves generated in a fluid medium or at the interface between two media when the force of gravity or buoyancy tries to restore equilibrium. An example of such an interface is that between the atmosphere and the ocean, which gives rise to wind waves. A gravity wave results when fluid is displaced from a position of equilibrium. The restoration of the fluid to equilibrium will produce a movement of the fluid back and forth, called a ''wave orbit''. Gravity waves on an air–sea interface of the ocean are called surface gravity waves (a type of surface wave), while gravity waves that are the body of the water (such as between parts of different densities) are called ''internal waves''. Wind-generated waves on the water surface are examples of gravity waves, as are tsunamis and ocean tides. The period of wind-generated gravity waves on the free surface of the Earth's ponds, lakes, seas and oceans are predominantly between 0.3 and 30 sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)