|
Water Pinch Analysis
Water pinch analysis (WPA) originates from the concept of heat pinch analysis. WPA is a systematic technique for reducing water consumption and wastewater generation through integration of water-using activities or processes. WPA was first introduced by Wang and Smith. Since then, it has been widely used as a tool for water conservation in industrial process plants. Water Pinch Analysis has recently been applied for urban/domestic buildings. It was extended in 1998 by Nick Hallale at the University of Cape Town, who developed it as a special case of mass exchange networks for capital cost targeting. Techniques for setting targets for maximum water recovery capable of handling any type of water-using operation including mass-transfer-based and non-mass-transfer based systems include the source and sink composite curves (Nick Hallale (2002). A New Graphical Targeting Method for Water Minimisation. Advances in Environmental Research. 6(3): 377–390) and water cascade analysis (WCA) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinch Analysis
Pinch analysis is a methodology for minimising energy consumption of process (engineering), chemical processes by calculating thermodynamically feasible ''energy targets'' (or minimum energy consumption) and achieving them by optimising heat recovery systems, energy supply methods and process operating conditions. It is also known as ''process integration'', ''heat integration'', ''energy integration'' or ''pinch technology''. The process data is represented as a set of energy flows, or streams, as a function of heat load (product of specific enthalpy and mass flow rate; SI unit watt, W) against temperature (SI unit kelvin, K). These data are combined for all the streams in the plant to give ''composite curves'', one for all ''hot streams'' (releasing heat) and one for all ''cold streams'' (requiring heat). The point of closest approach between the hot and cold composite curves is the ''pinch (plasma physics), pinch point'' (or just ''pinch'') with a hot stream pinch temperature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
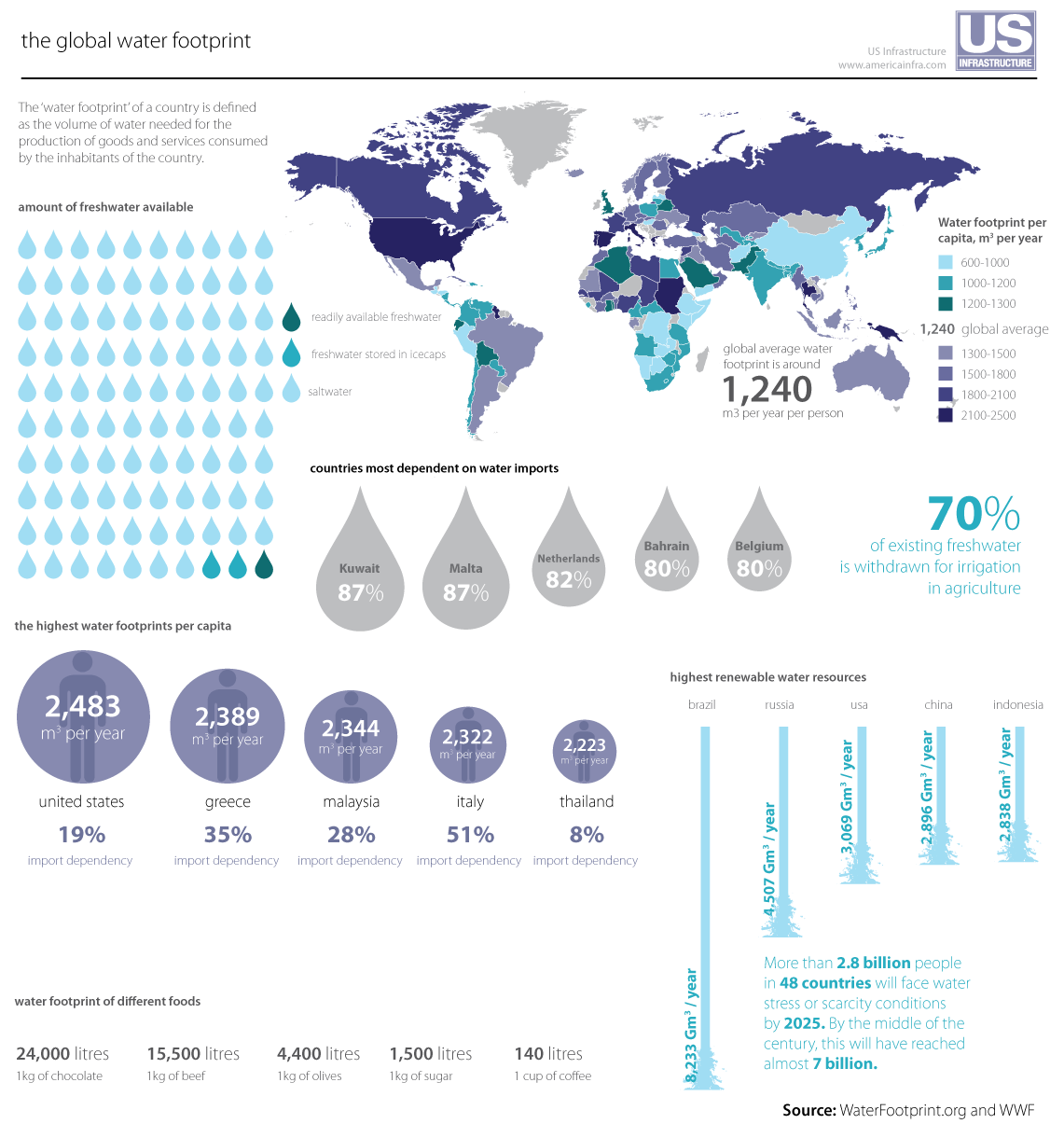
Water Footprint
A water footprint shows the extent of water use in relation to consumption by people. The water footprint of an individual, community, or business is defined as the total volume of fresh water used to produce the goods and services consumed by the individual or community or produced by the business. Water use is measured in water volume consumed (evaporated) and/or polluted per unit of time. A water footprint can be calculated for any well-defined group of consumers (e.g., an individual, family, village, city, province, state, or nation) or producers (e.g., a public organization, private enterprise, or economic sector), for a single process (such as growing rice) or for any product or service. Traditionally, water use has been approached from the production side, by quantifying the following three columns of water use: water withdrawals in the agricultural, industrial, and domestic sector. While this does provide valuable data, it is a limited way of looking at water use in a g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wastewater
Wastewater is water generated after the use of freshwater, raw water, drinking water or saline water in a variety of deliberate applications or processes. Another definition of wastewater is "Used water from any combination of domestic, industrial, commercial or agricultural activities, surface runoff / storm water, and any sewer inflow or sewer infiltration". In everyday usage, wastewater is commonly a synonym for sewage (also called sewerage, domestic wastewater, or municipal wastewater), which is wastewater that is produced by a community of people. As a generic term wastewater may also be used to describe water containing contaminants accumulated in other settings, such as: * Industrial wastewater: waterborne waste generated from a variety of industrial processes, such as manufacturing operations, mineral extraction, power generation, or water and wastewater treatment. ** Cooling water, released with potential thermal pollution after use to condense steam or reduce machi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Conservation
Water conservation includes all the policies, strategies and activities to sustainably manage the natural resource of fresh water, to protect the hydrosphere, and to meet the current and future human demand (thus avoiding water scarcity). Population, household size and growth and affluence all affect how much water is used. Factors such as climate change have increased pressures on natural water resources especially in manufacturing and agricultural irrigation. Many countries have already implemented policies aimed at water conservation, with much success. The key activities to conserve water are as follows: any beneficial reduction in Drying, water loss, use and waste of resources, avoiding any damage to water quality; and improving water management practices that reduce the use or enhance the beneficial use of water. Technology solutions exist for households, commercial and agricultural applications. Water conservation programs involved in social solutions are typically initiated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Cascade Analysis
Water cascade analysis (WCA) is a technique to calculate the minimum flowrate target for feedwater and wastewater for continuous water-using processes. Principle It is a tabular and numerical alternative to the water surplus diagram in Water Pinch which can be used to identify opportunities for reduction in feedwater usage and the design of water distribution networks. The WCA is done in three steps, a global analysis of water distribution and consumption in the network, establishing baseline minimum water targets and redesign of the water network to achieve these targets. History WCA was first introduced by Manan, Tan and Foo in 2004. Since then, it has been widely used as a tool for water conservation in industrial process plants. A Time dependent water cascade analysis was presented later on. A variation of the WCA is the gas cascade analysis (GCA). References {{Reflist See also * Cost effective minimum water network *Water management hierarchy Water Management Hierarchy (WMH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cost-effective Minimum Water Network
Cost-effective minimum water network is a holistic framework for water conservation which considers all conceivable methods to save water based on the water management hierarchy. This framework, which is applicable for industrial as well as urban systems was first developed by Wan Alwi and Manan.Wan Alwi, S. R. and Manan, Z. A. (2007). A new holistic framework for cost effective minimum water network in industrial and urban sector. Journal of Environmental Management. 46, 5968–76. The framework is applicable for grassroots design and retrofit of water systems and ensures that a desired payback period for design of a water recovery system is satisfied using the systematic hierarchical approach for resilient process screening (SHARPS) technique. References {{Reflist See also * Water cascade analysis * Water pinch *Water conservation *Water reuse Water reclamation (also called wastewater reuse, water reuse or water recycling) is the process of converting municipal waste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Pinch
Hydrogen pinch analysis (HPA) is a hydrogen management method that originates from the concept of heat pinch analysis. HPA is a systematic technique for reducing hydrogen consumption and hydrogen generation through integration of hydrogen-using activities or processes in the petrochemical industry, petroleum refineries hydrogen distribution networks and hydrogen purification. Principle A mass analysis is done by representing the purity and flowrate for each stream from the hydrogen consumers (sinks), such as hydrotreaters, hydrocrackers, isomerization units and lubricant plants and the hydrogen producers (sources), such as hydrogen plants and naphtha reformers, streams from hydrogen purifiers, membrane reactors, pressure swing adsorption and continuous distillation and off-gas streams from low- or high-pressure separators. The source-demand diagram shows bottlenecks, surplus or shortages. The hydrogen pinch is the purity at which the hydrogen network has neither hydrogen surplus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reclaimed Water
Water reclamation (also called wastewater reuse, water reuse or water recycling) is the process of converting municipal wastewater Sewage (or domestic sewage, domestic wastewater, municipal wastewater) is a type of wastewater that is produced by a community of people. It is typically transported through a sewer system. Sewage consists of wastewater discharged from residen ... (sewage) or Industrial wastewater treatment, industrial wastewater into water that can be reused for a variety of purposes. Types of reuse include: urban reuse, agricultural reuse (irrigation), environmental reuse, industrial reuse, planned potable reuse, de facto wastewater reuse (unplanned potable reuse). For example, reuse may include irrigation of gardens and agricultural fields or replenishing surface water and groundwater (i.e., groundwater recharge). Reused water may also be directed toward fulfilling certain needs in residences (e.g. Flush toilet, toilet flushing), businesses, and industry, and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Management Hierarchy
Water Management Hierarchy (WMH)Manan, Z. A., Wan Alwi, S. R. and Ujang Z. (2006). Systematic Design of a Maximum Water Recovery Network for an Urban System Based on Pinch Analysis. IEM Journal. 1 (67): 57-64. is a hierarchy of water conservation priorities. Levels of the hierarchy from the highest to the lowest in terms of the priority for water conservation include elimination, reduction, outsourcing/reuse and regeneration. The most preferred option is elimination, followed by reduction of water demand. After that, direct reuse/recycling and water outsourcing through method such as rainwater harvesting are preferred. This is followed by regeneration or treatment of wastewater before being reused. Freshwater will only be used when all water-saving options have been explored. The WMH was used as an effective screening tool in cost effective minimum water network methodology to stretch the limits of water savings beyond those achievable using conventional pinch analysis approac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Resources Management
Water resources are natural resources of water that are potentially useful for humans, for example as a source of drinking water supply or irrigation water. 97% of the water on the Earth is salt water and only three percent is fresh water; slightly over two thirds of this is frozen in glaciers and polar ice caps. The remaining unfrozen freshwater is found mainly as groundwater, with only a small fraction present above ground or in the air. Natural sources of fresh water include surface water, under river flow, groundwater and frozen water. Artificial sources of fresh water can include treated wastewater (wastewater reuse) and desalinated seawater. Human uses of water resources include agricultural, industrial, household, recreational and environmental activities. Water resources are under threat from water scarcity, water pollution, water conflict and climate change. Fresh water is a renewable resource, yet the world's supply of groundwater is steadily decreasing, with depletion o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |