|
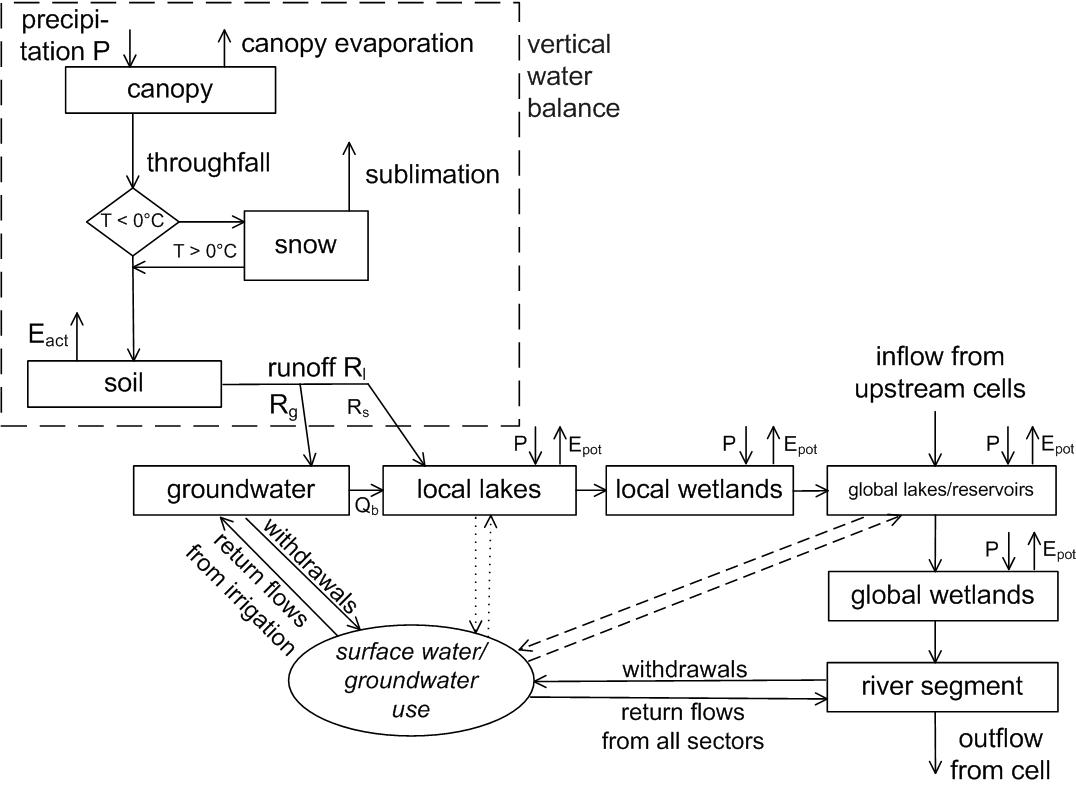
WaterGAP
The global Fresh water, freshwater model WaterGAP calculates flows and storages of water on all continents of the globe (except Antarctica), taking into account the human influence on the natural freshwater system by water abstractions and dams. It supports understanding the freshwater situation across the world's river basins during the 20th and the 21st centuries, and is applied to assess water scarcity, droughts and floods and to quantify the impact of human actions on e.g. groundwater, wetlands, streamflow and Sea level rise, sea-level rise. Modelling results of WaterGAP have contributed to international assessment of the global environmental situation including the UN World Water Development Reports, the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment, the Global Environment Outlook, UN Global Environmental Outlooks as well as to reports of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. WaterGAP contributes to the Intersectoral Impact Model Intercomparison Project ISIMIP, where consistent en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WaterGAP WGHM Computed Water Storages And Flows
The global Fresh water, freshwater model WaterGAP calculates flows and storages of water on all continents of the globe (except Antarctica), taking into account the human influence on the natural freshwater system by water abstractions and dams. It supports understanding the freshwater situation across the world's river basins during the 20th and the 21st centuries, and is applied to assess water scarcity, droughts and floods and to quantify the impact of human actions on e.g. groundwater, wetlands, streamflow and Sea level rise, sea-level rise. Modelling results of WaterGAP have contributed to international assessment of the global environmental situation including the UN World Water Development Reports, the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment, the Global Environment Outlook, UN Global Environmental Outlooks as well as to reports of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. WaterGAP contributes to the Intersectoral Impact Model Intercomparison Project ISIMIP, where consistent en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fresh Water
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Although the term specifically excludes seawater and brackish water, it does include non- salty mineral-rich waters such as chalybeate springs. Fresh water may encompass frozen and meltwater in ice sheets, ice caps, glaciers, snowfields and icebergs, natural precipitations such as rainfall, snowfall, hail/ sleet and graupel, and surface runoffs that form inland bodies of water such as wetlands, ponds, lakes, rivers, streams, as well as groundwater contained in aquifers, subterranean rivers and lakes. Fresh water is the water resource that is of the most and immediate use to humans. Water is critical to the survival of all living organisms. Many organisms can thrive on salt water, but the great majority of higher plants and most insects, amphibians, reptiles, mammals and birds need fresh water to survive. Fresh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow Crop, crops, Landscape plant, landscape plants, and Lawn, lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been developed by many cultures around the world. Irrigation helps to grow crops, maintain landscapes, and revegetation, revegetate disturbed soils in dry areas and during times of below-average rainfall. In addition to these uses, irrigation is also employed to protect crops from frost, suppress weed growth in grain fields, and prevent soil consolidation. It is also used to cool livestock, reduce dust, dispose of sewage, and support mining operations. Drainage, which involves the removal of surface and sub-surface water from a given location, is often studied in conjunction with irrigation. There are several methods of irrigation that differ in how water is supplied to plants. Surface irrigation, also known as gravity irri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anny Cazenave
Anny Cazenave () is a French space geodesist and one of the pioneers in satellite altimetry. She works for the French space agency CNES and has been deputy director of the (LEGOS) at Observatoire Midi-Pyrénées in Toulouse since 1996. Since 2013, she is director of Earth sciences at the International Space Science Institute (ISSI), in Bern (Switzerland). As one of the leading scientists in the joint French/American satellite altimetry missions TOPEX/Poseidon, Jason-1, and the Ocean Surface Topography Mission, she has contributed to a greater understanding of sea level rise caused by global warming. Cazenave is a member of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change and was the lead author of the sea level sections for their fourth and fifth Assessment Reports. Early life and education Not from an academic background, Cazenave was not destined to work in the sciences. However, she achieved a postgraduate doctorate in fundamental astronomy (Paris, 1969) as well as receivi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overdrafting
Overdrafting is the process of extracting groundwater beyond the equilibrium yield of an aquifer. Groundwater is one of the largest sources of fresh water and is found underground. Groundwater depletion is comparable to a bank account in which more money is withdrawn than deposited. The primary cause of groundwater depletion is the excessive pumping of groundwater up from underground aquifers. There are two sets of yields: safe yield and sustainable yield. Safe yield is the amount of groundwater that can be withdrawn over a period of time without exceeding the long-term recharge rate or affecting the aquifer integrity. Sustainable yield is the amount of water extraction that can be sustained indefinitely without negative hydrological impacts, taking into account both recharge rate and surface water impacts. There are two types of aquifers: confined and unconfined. In confined aquifers, there is an overbearing layer called aquitard, which contains impermeable materials through wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effects Of Climate Change
The effects of climate change impact the physical environment, ecosystems and human societies. The environmental effects of climate change are broad and far-reaching. They affect the water cycle, oceans, sea and land ice (glaciers), sea level, as well as weather and climate extreme events. The changes in climate are not uniform across the Earth. In particular, most land areas have warmed faster than most ocean areas, and the Arctic is warming faster than most other regions. The regional changes vary: at high latitudes it is the average temperature that is increasing, while for the oceans and tropics it is in particular the rainfall and the water cycle where changes are observed. The magnitude of future impacts of climate change can be reduced by climate change mitigation and adaptation. Climate change has degraded land by raising temperatures, drying soils and increasing wildfire risk. Recent warming has strongly affected natural biological systems. Species worldwide are mig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GRACE And GRACE-FO
The Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) was a joint mission of NASA and the German Aerospace Center (DLR). Twin satellites took detailed measurements of Earth's gravity field anomalies from its launch in March 2002 to the end of its science mission in October 2017. The GRACE Follow-On (GRACE-FO) is a continuation of the mission on near-identical hardware, launched in May 2018. By measuring gravity anomalies, GRACE showed how mass is distributed around the planet and how it varies over time. Data from the GRACE satellites is an important tool for studying Earth's ocean, geology, and climate. GRACE was a collaborative endeavor involving the Center for Space Research at the University of Texas at Austin, NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, the German Aerospace Center and Germany's National Research Center for Geosciences, Potsdam. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory was responsible for the overall mission management under the NASA ESSP (Earth System Science Pathfinder) program ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogeology
Hydrogeology (''hydro-'' meaning water, and ''-geology'' meaning the study of the Earth) is the area of geology that deals with the distribution and movement of groundwater in the soil and rocks of the Earth's crust (commonly in aquifers). The terms groundwater hydrology, geohydrology, and hydrogeology are often used interchangeably. Hydrogeology is the study of the laws governing the movement of subterranean water, the mechanical, chemical, and thermal interaction of this water with the porous solid, and the transport of energy, chemical constituents, and particulate matter by flow (Domenico and Schwartz, 1998). Groundwater engineering, another name for hydrogeology, is a branch of engineering which is concerned with groundwater movement and design of wells, pumps, and drains. The main concerns in groundwater engineering include groundwater contamination, conservation of supplies, and water quality.Walton, William C. (November 1990). ''Principles of Groundwater Engin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. Precipitation occurs when a portion of the atmosphere becomes saturated with water vapor (reaching 100% relative humidity), so that the water condenses and "precipitates" or falls. Thus, fog and mist are not precipitation but colloids, because the water vapor does not condense sufficiently to precipitate. Two processes, possibly acting together, can lead to air becoming saturated: cooling the air or adding water vapor to the air. Precipitation forms as smaller droplets coalesce via collision with other rain drops or ice crystals within a cloud. Short, intense periods of rain in scattered locations are called showers. Moisture that is lifted or otherwise forced to rise over a layer of sub-freezing air at the surface may be condensed into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Groundwater Recharge
Groundwater recharge or deep drainage or deep percolation is a hydrologic process, where water moves downward from surface water to groundwater. Recharge is the primary method through which water enters an aquifer. This process usually occurs in the vadose zone below plant roots and is often expressed as a flux to the water table surface. Groundwater recharge also encompasses water moving away from the water table farther into the saturated zone. Recharge occurs both naturally (through the water cycle) and through anthropogenic processes (i.e., "artificial groundwater recharge"), where rainwater and or reclaimed water is routed to the subsurface. Processes Water is recharged naturally by rain and snow melt and to a smaller extent by surface water (rivers and lakes). Recharge may be impeded somewhat by human activities including paving, development, or logging. These activities can result in loss of topsoil resulting in reduced water infiltration, enhanced surface runoff and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Runoff
Surface runoff (also known as overland flow) is the flow of water occurring on the ground surface when excess rainwater, stormwater, meltwater, or other sources, can no longer sufficiently rapidly infiltrate in the soil. This can occur when the soil is saturated by water to its full capacity, and the rain arrives more quickly than the soil can absorb it. Surface runoff often occurs because impervious areas (such as roofs and pavement) do not allow water to soak into the ground. Furthermore, runoff can occur either through natural or man-made processes. Surface runoff is a major component of the water cycle. It is the primary agent of soil erosion by water. The land area producing runoff that drains to a common point is called a drainage basin. Runoff that occurs on the ground surface before reaching a channel can be a nonpoint source of pollution, as it can carry man-made contaminants or natural forms of pollution (such as rotting leaves). Man-made contaminants in runoff i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reservoir
A reservoir (; from French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to store fresh water or it may be a natural formation. Reservoirs can be created in a number of ways, including controlling a watercourse that drains an existing body of water, interrupting a watercourse to form an embayment within it, through excavation, or building any number of retaining walls or levees. In other contexts, "reservoirs" may refer to storage spaces for various fluids; they may hold liquids or gasses, including hydrocarbons. ''Tank reservoirs'' store these in ground-level, elevated, or buried tanks. Tank reservoirs for water are also called cisterns. Most underground reservoirs are used to store liquids, principally either water or petroleum. Types Dammed valleys Dammed reservoirs are artificial lakes created and controlled by a dam A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |