|
Washington, West Sussex
Washington is a village and civil parish in the Horsham District of West Sussex, England. It is located west of Steyning and east of Storrington on the A24 between Horsham and Worthing. The parish covers an area of . In the 2001 census 1,930 people lived in 703 households, of whom 820 were economically active. At the 2011 Census the population of the civil parish was 1,867. The village lies at the foot of the South Downs escarpment. The Anglican parish church is dedicated to St Mary. There is one pub, the ''Frankland Arms'', a primary school and a village hall with an adjoining sports field. The hamlet named Rock lies to the north of the A283 road. Landmarks Chanctonbury Ring, a hill fort based ring of trees atop Chanctonbury Hill on the South Downs, lies on the border of the parish and the neighbouring parish of Wiston. Chanctonbury Hill is a Site of Special Scientific Interest A Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) in Great Britain or an Area of Spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom Census 2001
A nationwide census, known as Census 2001, was conducted in the United Kingdom on Sunday, 29 April 2001. This was the 20th UK census and recorded a resident population of 58,789,194. The 2001 UK census was organised by the Office for National Statistics (ONS) in England and Wales, the General Register Office for Scotland (GROS) and the Northern Ireland Statistics and Research Agency (NISRA). Detailed results by region, council area, ward and output area are available from their respective websites. Organisation Similar to previous UK censuses, the 2001 census was organised by the three statistical agencies, ONS, GROS, and NISRA, and coordinated at the national level by the Office for National Statistics. The Orders in Council to conduct the census, specifying the people and information to be included in the census, were made under the authority of the Census Act 1920 in Great Britain, and the Census Act (Northern Ireland) 1969 in Northern Ireland. In England and Wales these re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of the largest branches of Christianity, with around 110 million adherents worldwide . Adherents of Anglicanism are called ''Anglicans''; they are also called ''Episcopalians'' in some countries. The majority of Anglicans are members of national or regional ecclesiastical provinces of the international Anglican Communion, which forms the third-largest Christian communion in the world, after the Roman Catholic Church and the Eastern Orthodox Church. These provinces are in full communion with the See of Canterbury and thus with the Archbishop of Canterbury, whom the communion refers to as its '' primus inter pares'' (Latin, 'first among equals'). The Archbishop calls the decennial Lambeth Conference, chairs the meeting of primates, and is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock Mill, Washington
Rock Mill is a Grade II listed In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Irel ... smock mill at Washington, West Sussex, England, which has been converted to residential use. History Rock Mill was built in 1823. The mill was working at the outbreak of the First World War but was converted to a house in about 1919, using the machinery as decoration. The composer John Ireland bought the mill in 1953 and died there in 1962. As of 2007, the mill is used as offices. Description ''Rock Mill'' is a three-storey smock mill on a single-storey base, formerly carrying a beehive cap winded by a fantail. It had four Patent sails and drove three pairs of millstones (two pairs French Burr and one pair of Peak stones). Millers *Thomas Harwood, 1837 *Henry Harwood, 1837-40 *E. Mitchell, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Ireland (composer)
John Nicholson Ireland (13 August 187912 June 1962) was an English composer and teacher of music. The majority of his output consists of piano miniatures and of songs with piano. His best-known works include the short instrumental or orchestral work " The Holy Boy", a setting of the poem " Sea-Fever" by John Masefield, a formerly much-played Piano Concerto, the hymn tune Love Unknown and the choral motet "Greater Love Hath No Man". Life John Ireland was born in Bowdon, near Altrincham, Cheshire, into a family of English and Scottish descent and some cultural distinction. His father, Alexander Ireland, a publisher and newspaper proprietor, was aged 69 at John's birth. John was the youngest of the five children from Alexander's second marriage (his first wife had died). His mother, Annie Elizabeth Nicholson Ireland, was a biographer and 30 years younger than Alexander. She died in October 1893, when John was 14, and Alexander died the following year, when John was 15. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triturus Cristatus
The northern crested newt, great crested newt or warty newt (''Triturus cristatus'') is a newt species native to Great Britain, northern and central continental Europe and parts of Western Siberia. It is a large newt, with females growing up to long. Its back and sides are dark brown, while the belly is yellow to orange with dark blotches. Males develop a conspicuous jagged crest on their back and tail during the breeding season. The northern crested newt spends most of the year on land, mainly in forested areas in lowlands. It moves to aquatic breeding sites, mainly larger fish-free ponds, in spring. Males court females with a ritualised display and deposit a spermatophore on the ground, which the female then picks up with her cloaca. After fertilisation, a female lays around 200 eggs, folding them into water plants. The larvae develop over two to four months before metamorphosing into terrestrial juveniles (efts). Both larvae and land-dwelling newts mainly feed on different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Site Of Special Scientific Interest
A Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) in Great Britain or an Area of Special Scientific Interest (ASSI) in the Isle of Man and Northern Ireland is a conservation designation denoting a protected area in the United Kingdom and Isle of Man. SSSI/ASSIs are the basic building block of site-based nature conservation legislation and most other legal nature/geological conservation designations in the United Kingdom are based upon them, including national nature reserves, Ramsar sites, Special Protection Areas, and Special Areas of Conservation. The acronym "SSSI" is often pronounced "triple-S I". Selection and conservation Sites notified for their biological interest are known as Biological SSSIs (or ASSIs), and those notified for geological or physiographic interest are Geological SSSIs (or ASSIs). Sites may be divided into management units, with some areas including units that are noted for both biological and geological interest. Biological Biological SSSI/ASSIs may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chanctonbury Hill
Chanctonbury Hill is an biological Site of Special Scientific Interest west of Steyning in West Sussex. Part of it is Chanctonbury Ring, an early Iron Age hillfort which contains two Romano-Celtic temples and which is a Scheduled Monument. This site on the steep slope of the South Downs is mainly woodland with some areas of chalk grassland. A dew pond has great crested newts, a species protected under the Wildlife and Countryside Act 1981. More than sixty species of breeding birds have been recorded, including meadow pipits, corn buntings and green woodpecker There are four species of bird named green woodpecker: * European green woodpecker, ''Picus viridis'' * Iberian green woodpecker The Iberian green woodpecker (''Picus sharpei'') is a medium-sized woodpecker endemic to the Iberian peninsula. It wa ...s. References {{SSSIs West Sussex Sites of Special Scientific Interest in West Sussex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiston, West Sussex
Wiston is a scattered village and civil parish in the Horsham District of West Sussex, England. It lies on the A283 road northwest of Steyning. The parish covers an area of . In the 2001 census 221 people lived in 86 households, of whom 120 were economically active. Landmarks Chanctonbury Ring, a hill fort based ring of trees atop Chanctonbury Hill on the South Downs, lies on the border of the parish and the neighbouring parish of Washington. Chanctonbury Hill is a Site of Special Scientific Interest as an uncommon woodland type on a chalk escarpment, providing habitat for many species including the protected Great Crested Newt The northern crested newt, great crested newt or warty newt (''Triturus cristatus'') is a newt species native to Great Britain, northern and central continental Europe and parts of Western Siberia. It is a large newt, with females growing up to .... References Horsham District Villages in West Sussex {{WestSussex-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
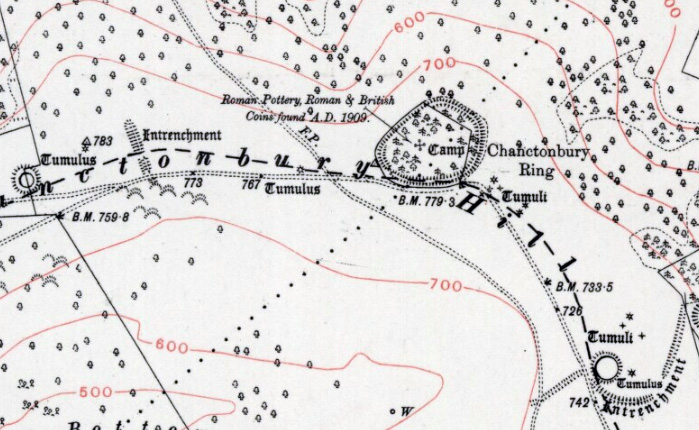
Chanctonbury Ring
Chanctonbury Ring is a prehistoric hill fort atop Chanctonbury Hill on the South Downs, on the border of the civil parishes of Washington and Wiston in the English county of West Sussex. A ridgeway, now part of the South Downs Way, runs along the hill. It forms part of an ensemble of associated historical features created over a span of more than 2,000 years, including round barrows dating from the Bronze Age to the Saxon periods and dykes dating from the Iron Age and Roman periods. Consisting of a roughly circular low earthen rampart surrounded by a ditch, Chanctonbury Ring is thought to date to the late Bronze Age or early Iron Age. The purpose of the structure is unknown but it could have filled a variety of roles, including a defensive position, a cattle enclosure or even a religious shrine. After a few centuries of usage, it was abandoned for about five hundred years until it was reoccupied during the Roman period. Two Romano-British temples were built in the hill fort's in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A283 Road
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''a'' (pronounced ), plural ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version can be written in two forms: the double-storey a and single-storey ɑ. The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English grammar, " a", and its variant " an", are indefinite articles. History The earliest certain ancestor of "A" is aleph (also written 'aleph), the first letter of the Phoenician alphabet, which consisted entirely of consonants (for that reason, it is also called an abjad to distinguish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Mary
Mary; arc, ܡܪܝܡ, translit=Mariam; ar, مريم, translit=Maryam; grc, Μαρία, translit=María; la, Maria; cop, Ⲙⲁⲣⲓⲁ, translit=Maria was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Joseph and the mother of Jesus. She is a central figure of Christianity, venerated under various titles such as virgin or queen, many of them mentioned in the Litany of Loreto. The Eastern and Oriental Orthodox, Church of the East, Catholic, Anglican, and Lutheran churches believe that Mary, as mother of Jesus, is the Mother of God. Other Protestant views on Mary vary, with some holding her to have considerably lesser status. The New Testament of the Bible provides the earliest documented references to Mary by name, mainly in the canonical Gospels. She is described as a young virgin who was chosen by God to conceive Jesus through the Holy Spirit. After giving birth to Jesus in Bethlehem, she raised him in the city of Nazareth in Galilee, and was in Jerusalem a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parish Church
A parish church (or parochial church) in Christianity is the church which acts as the religious centre of a parish. In many parts of the world, especially in rural areas, the parish church may play a significant role in community activities, often allowing its premises to be used for non-religious community events. The church building reflects this status, and there is considerable variety in the size and style of parish churches. Many villages in Europe have churches that date back to the Middle Ages, but all periods of architecture are represented. Roman Catholic Church Each diocese (administrative unit, headed by a Bishop) is divided into parishes. Normally, a parish comprises all Catholics living within its geographically defined area. Within a diocese, there can also be overlapping parishes for Catholics belonging to a particular rite, language, nationality, or community. Each parish has its own central church called the parish church, where religious services take pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |