|
Warida
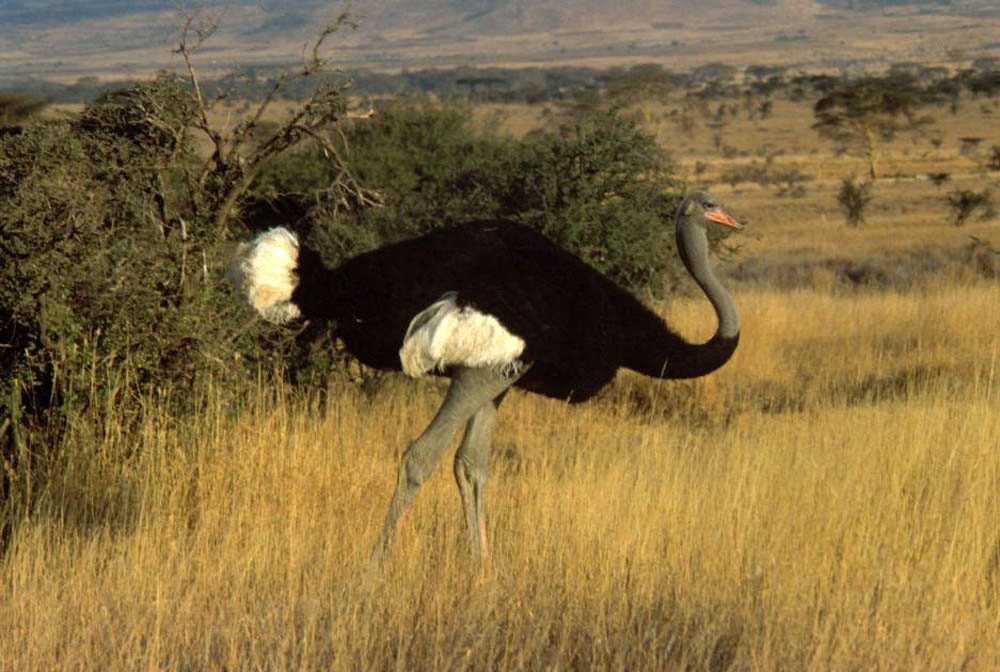
Warida or Al Warida is an asterism of the Arabs. In the star catalogue of Al Achsasi al Mouakket, four stars are mentioned as belonging to it: Gamma Sagittarii, Delta Sagittarii, Epsilon Sagittarii and Eta Sagittarii. The name is short for Arabic النعامة الواردة ''Al Naʽāma al Wārida'', meaning "the ostrich Ostriches are large flightless birds of the genus ''Struthio'' in the order Struthioniformes, part of the infra-class Palaeognathae, a diverse group of flightless birds also known as ratites that includes the emus, rheas, and kiwis. There are ... going down to the water". This ostrich was thought of as going down to the river (the Milky Way) to drink, and another ostrich (σ, φ, τ, and ζ Sagittarii, ''al Sadira'') was thought of as coming back up. References Sagittarius (constellation) Asterisms (astronomy) {{star-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epsilon Sagittarii
Epsilon Sagittarii ( Latinised from ε Sagittarii, abbreviated Epsilon Sgr, ε Sgr), formally named Kaus Australis , is a binary star system in the southern zodiac constellation of Sagittarius. The apparent visual magnitude of +1.85 makes it the brightest object in Sagittarius. Based upon parallax measurements, this star is around from the Sun. Stellar system The primary star, ε Sagittarii A, of this binary star system has a stellar classification of B9.5 III, with the luminosity class of III suggesting this is an evolved giant star that has exhausted the supply of hydrogen at its core. The interferometry-measured angular diameter of this star, after correcting for limb darkening, is , which, at its estimated distance, equates to a physical radius of about 6.8 times the radius of the Sun. This is a close match to the empirically-determined value of 6.9 solar radii. It has about 3.5 times the mass of the Sun and is radiating around 363 time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eta Sagittarii
Eta Sagittarii (Eta Sgr, η Sagittarii, η Sgr) is a binary star system in the southern zodiac constellation of Sagittarius. Based upon parallax measurements, it is located at a distance of from Earth. It was formerly known as Beta Telescopii (β Tel). In India, where part of the constellation of Sagittarius represents an Elephant, this star forms the creature's tail. The primary component, η Sagittarii A, is a red giant star with a stellar classification of M2 III. It is an evolved star that is currently at a stage called the asymptotic giant branch, having exhausted both the hydrogen and the helium at its core. This star is classified as an oxygen-rich irregular variable, as it undergoes small magnitude fluctuations between +3.08 and 3.12. The measured angular diameter of this star is . At the estimated distance of Eta Draconis, this yields a physical size of about 57 times the radius of the Sun. The companion, η Sagittarii B, was f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta Sagittarii
Delta Sagittarii (δ Sagittarii, abbreviated Delta Sgr, δ Sgr), formally named Kaus Media , is a double star in the southern zodiac constellation of Sagittarius. The apparent visual magnitude of this star is +2.70, making it easily visible to the naked eye. Parallax measurements place the distance at roughly from the Sun. Properties Eggleton and Tokovinin (2008) list Delta Sagittarii as a binary star system consisting of an evolved K-type giant star with a stellar classification of K3 III, and a white dwarf companion. The giant is a weak barium star, most likely having had its surface abundance of s-process elements enhanced through mass transfer from its orbiting companion. It has an estimated 3.21 times the mass of the Sun and is about 260million years old. Delta Sagittarii has three dim visual companions: * a 14th magnitude star at a separation of 26 arcseconds, * a 15th magnitude star at a separation of 40 arcseconds, and * a 13th magnitude s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asterism (astronomy)
An asterism is an observed pattern or group of stars in the sky. Asterisms can be any identified pattern or group of stars, and therefore are a more general concept than the formally defined 88 constellations. Constellations are based on asterisms, but unlike asterisms, constellations outline and today completely divide the sky and all its celestial objects into regions around their central asterisms. For example, the asterism known as the Big Dipper comprises the seven brightest stars in the constellation Ursa Major. Another is the asterism of the Southern Cross, within the constellation of Crux. Asterisms range from simple shapes of just a few stars to more complex collections of many stars covering large portions of the sky. The stars themselves may be bright naked-eye objects or fainter, even telescopic, but they are generally all of a similar brightness to each other. The larger brighter asterisms are useful for people who are familiarizing themselves with the night sky. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al Achsasi Al Mouakket
Muḥammad al-Akhṣāṣī al-Muwaqqit ( ar, محمد الاخصاصي الموقت) was an Egyptian astronomer whose and catalogue of stars, ('Pearls of brilliance upon the solar operations'), was written at Cairo about 1650. Al-Akhsasi was a shaykh, a learned elder, of the Grand Mosque of the university of Cairo, where his name ''al- Muwaqqit'' reflected his position regulating the times and hours at the mosque. His name Akhsasi connects him in origin to a village in the Faiyum, southwest of Cairo. No copies of his book were known to Western astronomers or historians of science The history of science covers the development of science from ancient times to the present. It encompasses all three major branches of science: natural, social, and formal. Science's earliest roots can be traced to Ancient Egypt and Mesop ... until 1895;Knobel 1895. thus he did not appear in the standard French and English bibliographies and library catalogues of the 19th century. Notes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Sagittarii
The Bayer designation γ Sagittarii (Gamma Sagittarii) is shared by two stars in the constellation A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object. The origins of the e ... Sagittarius: * γ1 Sagittarii, a Cepheid variable better-known as W Sagittarii * γ2 Sagittarii (10 Sagittarii), an orange giant * "-": none The two stars are separated by slightly under one degree. References {{Set index article , astronomical objects Sagittarius, Gamma Sagittarius (constellation) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostrich
Ostriches are large flightless birds of the genus ''Struthio'' in the order Struthioniformes, part of the infra-class Palaeognathae, a diverse group of flightless birds also known as ratites that includes the emus, rheas, and kiwis. There are two living species of ostrich: the common ostrich, native to large areas of sub-Saharan Africa and the Somali ostrich, native to the Horn of Africa. The common ostrich was also historically native to the Arabian Peninsula, and ostriches were present across Asia as far east as Mongolia during the Late Pleistocene and possibly into the Holocene. They lay the largest eggs of any living land animal. With the ability to run at 70 km/h (43.5 mph), they are the fastest birds on land. They are farmed worldwide, particularly for their feathers as they are used as decoration and feather dusters. Their skin is also used for leather products. They are the heaviest living birds. Taxonomic history The genus ''Struthio'' was first described b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monthly Notices Of The Royal Astronomical Society
''Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society'' (MNRAS) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research in astronomy and astrophysics. It has been in continuous existence since 1827 and publishes letters and papers reporting original research in relevant fields. Despite the name, the journal is no longer monthly, nor does it carry the notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. History The first issue of MNRAS was published on 9 February 1827 as ''Monthly Notices of the Astronomical Society of London'' and it has been in continuous publication ever since. It took its current name from the second volume, after the Astronomical Society of London became the Royal Astronomical Society (RAS). Until 1960 it carried the monthly notices of the RAS, at which time these were transferred to the newly established ''Quarterly Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society'' (1960–1996) and then to its successor journal ''Astronomy & Geophysics'' (since 1997). Until 1965, MNRAS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
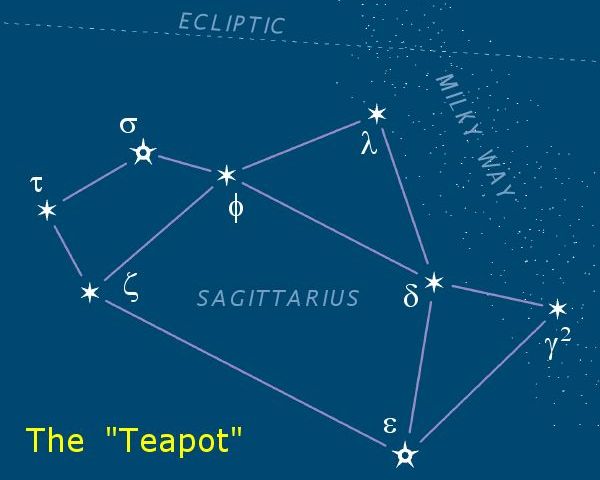
Sagittarius (constellation)
Sagittarius is one of the constellations of the zodiac and is located in the Southern celestial hemisphere. It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Its old astronomical symbol is (♐︎). Its name is Latin for "archer". Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur pulling back a bow. It lies between Scorpius and Ophiuchus to the west and Capricornus and Microscopium to the east. The center of the Milky Way lies in the westernmost part of Sagittarius (see Sagittarius A). Visualizations As seen from the northern hemisphere, the constellation's brighter stars form an easily recognizable asterism known as "the Teapot". The stars δ Sgr (Kaus Media), ε Sgr (Kaus Australis), ζ Sgr (Ascella), and φ Sgr form the body of the pot; λ Sgr (Kaus Borealis) is the point of the lid; γ2 Sgr (Alnasl) is the tip of the spout; and σ Sgr (Nunki) and τ Sgr the handle. These same sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |