|
Waltheof Of Melrose
Waltheof ( – 1159) was a 12th-century English abbot and saint. He was the son of Simon I of St Liz, 1st Earl of Northampton and Maud, 2nd Countess of Huntingdon, thus stepson to David I of Scotland, and the grandson of Waltheof, Earl of Northampton.Barlow ''The English Church 1066–1154'' p. 208-210 Whether as a result of being a younger son in the world of Norman succession laws, or being personally unsuited to court life, Waltheof chose a career in the church. Between 1128 and 1131 he entered Nostell Priory to become an Augustinian canon. His noble connections enabled him to rise quickly, and by 1139 he was Prior of Kirkham, North Yorkshire. Upon the death of Thurstan, Archbishop of York, in 1140, Waltheof was nominated to be his successor.Barlow ''The English Church 1066–1154'' p. 96 His candidacy was supported by William of Aumale, the Earl of York.Dalton "William Earl of York" ''Haskins Society Journal'' pp. 162–163 Stephen, probably sensing his links to David ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
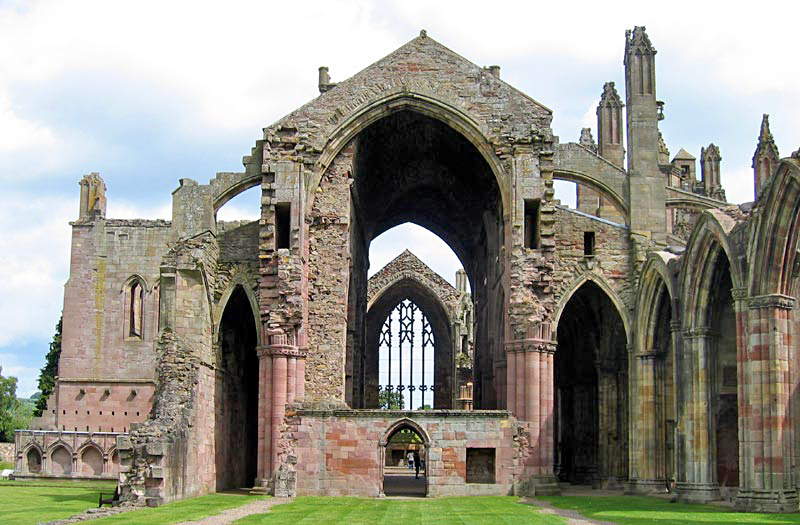
Abbot Of Melrose
The Abbot and then Commendator of Melrose was the head of the monastic community of Melrose Abbey, in Melrose in the Borders region of Scotland. The abbots of the earlier Northumbrian foundation from Lindisfarne are not included here. The second abbey was founded in 1136 on the patronage of David I (''Dabíd mac Maíl Choluim''), King of Scots, by Cistercian monks from Rievaulx Abbey, Yorkshire. Control of the abbey was secularized in the 16th century and after the accession of James Stewart, the abbey was held by commendators. The last commendator, James Douglas of Lochleven, resigned the abbacy to William Douglas, 6th Earl of Morton (his nephew) in December 1606, and the abbey itself to the king in 1608. The abbey (or most of its lands) was then erected into a secular lordship for viscount Haddington, John Ramsay, who in 1609 was created "Lord Melrose". Lochleven however resumed the title of commendator in 1613 until his death in 1620. List of Abbots * Richard, 1136-1148 * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
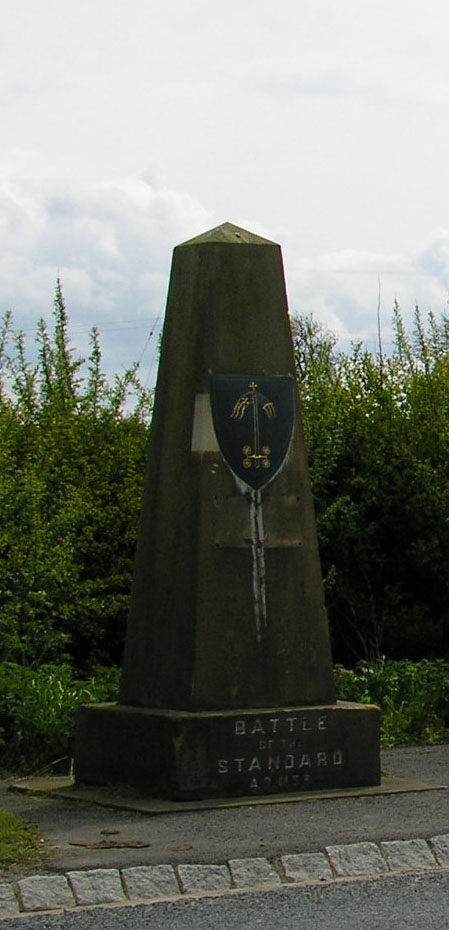
Thurstan
:''This page is about Thurstan of Bayeux (1070 – 1140) who became Archbishop of York. Thurstan of Caen became the first Norman Abbot of Glastonbury in circa 1077.'' Thurstan or Turstin of Bayeux ( – 6 February 1140) was a medieval Archbishop of York, the son of a priest. He served kings William II and Henry I of England before his election to the see of York in 1114. Once elected, his consecration was delayed for five years while he fought attempts by the Archbishop of Canterbury to assert primacy over York. Eventually, he was consecrated by the pope instead and allowed to return to England. While archbishop, he secured two new suffragan bishops for his province. When Henry I died, Thurstan supported Henry's nephew Stephen of Blois as king. Thurstan also defended the northern part of England from invasion by the Scots, taking a leading part in organising the English forces at the Battle of the Standard (1138). Shortly before his death, Thurstan resigned from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saintliness
In religious belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and denomination. In Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, Anglican, Oriental Orthodox, and Lutheran doctrine, all of their faithful deceased in Heaven are considered to be saints, but some are considered worthy of greater honor or emulation. Official ecclesiastical recognition, and consequently a public cult of veneration, is conferred on some denominational saints through the process of canonization in the Catholic Church or glorification in the Eastern Orthodox Church after their approval. While the English word ''saint'' originated in Christianity, historians of religion tend to use the appellation "in a more general way to refer to the state of special holiness that many religions attribute to certain people", referring to the Jewish tzadik, the Islamic walī, the Hindu rishi or Sikh gur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archbishop Of St Andrews
The Bishop of St. Andrews ( gd, Easbaig Chill Rìmhinn, sco, Beeshop o Saunt Andras) was the ecclesiastical head of the Diocese of St Andrews in the Catholic Church and then, from 14 August 1472, as Archbishop of St Andrews ( gd, Àrd-easbaig Chill Rìmhinn), the Archdiocese of St Andrews. The name St Andrews is not the town or church's original name. Originally it was ''Cellrígmonaid'' ("church of the king's mounth" hence ''Cill Rìmhinn'') located at ''Cennrígmonaid'' ("head of the king's mounth"); hence the town became ''Kilrymont'' (i.e. ''Cellrígmonaid'') in the non-Gaelic orthography of the High Middle Ages. Today St Andrews has replaced both Kilrymont (and variants) as well as the older English term Anderston as the name of the town and bishopric. The bishopric itself appears to originate in the period 700–900. By the 11th century, it is clear that it was the most important bishopric in Scotland. List of known abbots There had been a monastery there since the 8th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rievaulx Abbey
Rievaulx Abbey was a Cistercian abbey in Rievaulx, near Helmsley, in the North York Moors National Park, North Yorkshire, England. It was one of the great abbeys in England until it was seized in 1538 under Henry VIII during the Dissolution of the Monasteries. The wider site was awarded Scheduled Ancient Monument status in 1915 and the abbey was brought into the care of the then Ministry of Works in 1917. The striking ruins of its main buildings are today a tourist attraction, owned and maintained by English Heritage. Foundation Rievaulx Abbey was the first Cistercian monastery in the north of England, founded in 1132 by twelve monks from Clairvaux Abbey. Its remote location was well suited to the order's ideal of a strict life of prayer and self-sufficiency with little contact with the outside world. The abbey's patron, Walter Espec, also founded another Cistercian community, that of Wardon Abbey in Bedfordshire, on unprofitable wasteland on one of his inherited estate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wardon Abbey
Wardon or Warden Abbey, Bedfordshire, was one of the senior Cistercian houses of England, founded about 1135 from Rievaulx Abbey. It is a Grade I listed building. History The patron was Walter Espec, who had founded the mother house and settled the new community on one of his inherited estates, on unprofitable wasteland, as its early name, St Mary de Sartis, implied, just the kind of remote, uninhabited sites specified by the founders of the Cistercian order. The first abbot, Simon, was a pupil of Aelred, Abbot of Rievaulx. The success of the abbey may be inferred from the foundation of a daughter house, Sibton Abbey, Suffolk, as soon as 1150. The village of Old Warden, Bedfordshire grew up under the Abbey's protection. Great accumulated Cistercian wealth enabled Wardon Abbey to be rebuilt on a grand scale in the early fourteenth century, with complex tiling in carpet-patterns and pictorial vignettes pieced together in shaped tiles that approached a boldly scaled mosaic. Gildin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cistercian
The Cistercians, () officially the Order of Cistercians ( la, (Sacer) Ordo Cisterciensis, abbreviated as OCist or SOCist), are a Catholic religious order of monks and nuns that branched off from the Benedictines and follow the Rule of Saint Benedict, as well as the contributions of the highly-influential Saint Bernard of Clairvaux, known as the Latin Rule. They are also known as Bernardines, after Saint Bernard himself, or as White Monks, in reference to the colour of the "cuculla" or cowl (choir robe) worn by the Cistercians over their habits, as opposed to the black cowl worn by Benedictines. The term ''Cistercian'' derives from ''Cistercium,'' the Latin name for the locale of Cîteaux, near Dijon in eastern France. It was here that a group of Benedictine monks from the monastery of Molesme founded Cîteaux Abbey in 1098, with the goal of following more closely the Rule of Saint Benedict. The best known of them were Robert of Molesme, Alberic of Cîteaux and the English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint William Of York
William of York (late 11th century – 8 June 1154) was an English priest and twice Archbishop of York, before and after a rival, Henry Murdac. He was thought to be related to King Stephen of England, who helped to secure his election to the province after several candidates had failed to gain papal confirmation. William faced opposition from the Cistercians, who after the election of the Cistercian Pope Eugene III, had William deposed in favour of a Cistercian, Murdac. From 1147 until 1153, William worked to be restored to York, which he achieved after the deaths of Murdac and Eugene III. He did not hold the province long, dying shortly after his return, allegedly from poison in the chalice he used to celebrate Mass.Emma J. Wells, "Making Sense of Things", ''History Today'', Vol. 69, No. 5 (May 2019), p. 40 Miracles were reported at his tomb from 1177. He was canonised in 1226. Early life Born William fitzHerbert in York, William was the son of Herbert of Winchester, or Herb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sherburn-in-Elmet
Sherburn in Elmet (pronounced ) is a large village, civil parish and electoral ward in the Selby District of North Yorkshire, England, west of Selby and south of Tadcaster. It was part of the West Riding of Yorkshire until 1974. It is one of three placenames associated with the post-Roman kingdom of Elmet, the others being Barwick-in-Elmet and Scholes-in-Elmet. At the 2011 census, it had a population of 6,657. History The name derives from Old English "scir" (bright, pure) and "burn" (bourne, stream, spring). The earliest record of the name ('Scyreburnan') dates from 963 (Ekwall, Concise Oxford Dictionary of English Place-names, OUP, 4th ed, 1960, p. 416). Elmet refers to a little-understood post-Roman, Brittonic (non-Anglo-Saxon) kingdom in the area around what is now the Leeds conurbation, the precise boundaries of which are not known. Sherburn is situated on a low hill of Permian limestone jutting out into the valley of the River Ouse, so the name may refer to the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empress Matilda
Empress Matilda ( 7 February 110210 September 1167), also known as the Empress Maude, was one of the claimants to the English throne during the civil war known as the Anarchy. The daughter of King Henry I of England, she moved to Germany as a child when she married the future Holy Roman Emperor Henry V. She travelled with her husband to Italy in 1116, was controversially crowned in St Peter's Basilica, and acted as the imperial regent in Italy. Matilda and Henry V had no children, and when he died in 1125, the imperial crown was claimed by his rival Lothair of Supplinburg. Matilda's younger and only full brother, William Adelin, died in the ''White Ship'' disaster of 1120, leaving Matilda's father and realm facing a potential succession crisis. On Emperor Henry V's death, Matilda was recalled to Normandy by her father, who arranged for her to marry Geoffrey of Anjou to form an alliance to protect his southern borders. Henry I had no further legitimate children and nominated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen Of England
Stephen (1092 or 1096 – 25 October 1154), often referred to as Stephen of Blois, was King of England from 22 December 1135 to his death in 1154. He was Count of Boulogne '' jure uxoris'' from 1125 until 1147 and Duke of Normandy from 1135 until 1144. His reign was marked by the Anarchy, a civil war with his cousin and rival, the Empress Matilda, whose son, Henry II, succeeded Stephen as the first of the Angevin kings of England. Stephen was born in the County of Blois in central France as the fourth son of Stephen-Henry, Count of Blois, and Adela, daughter of William the Conqueror. His father died while Stephen was still young, and he was brought up by his mother. Placed into the court of his uncle Henry I of England, Stephen rose in prominence and was granted extensive lands. He married Matilda of Boulogne, inheriting additional estates in Kent and Boulogne that made the couple one of the wealthiest in England. Stephen narrowly escaped drowning with Henry I's son, William ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |