|
Walter Hindes Godfrey
Walter Hindes Godfrey, CBE, FSA, FRIBA (1881–1961), was an English architect, antiquary, and architectural and topographical historian. He was also a landscape architect and designer, and an accomplished draftsman and illustrator. He was (1941–60) the first director and the inspiration behind the foundation of the National Buildings Record, the basis of today's Historic England Archive, and edited or contributed to numerous volumes of the Survey of London. He devised a system of Service Heraldry for recording service in the European War. He was appointed a CBE in 1950. Early life Walter Hindes Godfrey was born at home at 102, Greenwood Road, Hackney, London, the eldest son of Walter Scott Godfrey, owner of a small wine business, and Gertrude Annie Rendall. His father later gave up his own business to become manager of a larger firm, then became a minister of religion and author of several works on the subject. Architect Godfrey first settled in Buxted in 1915, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
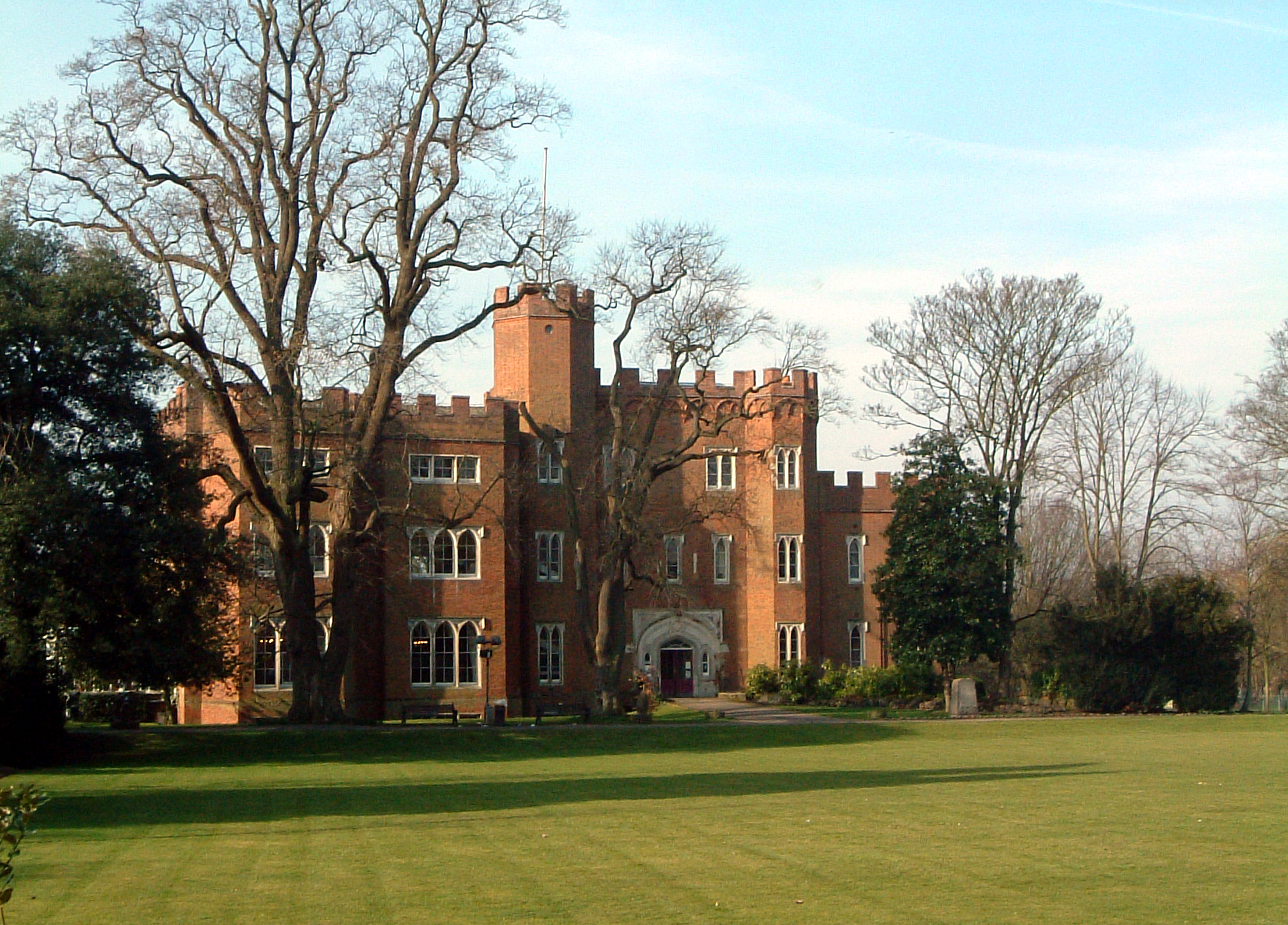
Herstmonceux Castle
Herstmonceux Castle is a brick-built castle, dating from the 15th century, near Herstmonceux, East Sussex, England. It is one of the oldest significant brick buildings still standing in England. The castle was renowned for being one of the first buildings to use that material in England, and was built using bricks taken from the local clay, by builders from Flanders. It dates from 1441. Construction began under the then-owner, Sir Roger Fiennes, and was continued after his death in 1449 by his son, Lord Dacre. The parks and gardens of Herstmonceux Castle and Place are Grade II* listed on the Register of Historic Parks and Gardens. Other listed structures on the Herstmonceux estate include the Grade II listed walled garden to the north of the castle, and the Grade II* listed telescopes and workshops of the Herstmonceux Science Centre. History Early history The first written evidence of the existence of the Herst settlement appears in William the Conqueror's Domesday Book wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidbrooke
Kidbrooke is an area of South East London, England, in the Royal Borough of Greenwich south-east of Charing Cross and north west of Eltham. The district takes its name from the Kyd Brook, a watercourse which runs from Orpington to Lewisham, by which point it is part of the River Quaggy. It is a tributary to the River Ravensbourne. Housing The area contains a large amount of 1920s and 1930s domestic housing, developed partly as the Kidbrooke Park Estate, between Shooters Hill and Rochester Way. A large RAF stores base, RAF Kidbrooke, formerly occupied much of the land around Kidbrooke railway station, north and south of the railway line. In 1965 the Government released most of the land to the Greater London Council for housing. The Ferrier Estate, built from 1968, was conceived to be a flagship scheme but became one of the largest and most deprived council housing developments in London. The housing estate was demolished in 2012 and has been redeveloped as Kidbrooke Vill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donnington, Gloucestershire
Donnington is a small village and civil parish in Gloucestershire, near the Roman Fosse Way in the Cotswold District Council area of south west England. It is situated on a hill a mile and a half north of Stow-on-the-Wold, of which until 1894 it formed a detached hamlet, so that the north transept in the parish church was reserved for the parish. There are fine views over the Evenlode valley. It is notable for its Cotswold stone houses. They include Donnington mill, on a medieval site, where the river Dikler emerges to form an artificial lake and mill pond of nearly five acres, which became Richard Arkell's Donnington Brewery in 1865; Little Barrow, a late Arts and Crafts movement country house on a medieval site remodelled and extended from a house of about 1800 in Cotswold manorial style with gardens by the distinguished Sussex architect Walter Godfrey in the 1930s; and Donnington Manor, just north of the village, which dates to the 18th century, when it may have been rebuilt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudeley Castle
Sudeley Castle is a Grade I listed castle in the parish of Sudeley, in the Cotswolds, near to the medieval market town of Winchcombe, Gloucestershire, England. The castle has 10 notable gardens covering some 15 acres within a 1,200-acre estate nestled within the Cotswold hills. Building of the castle began in 1443 for Ralph Boteler; the Lord High Treasurer of England, on the site of a previous 12th-century fortified manor house. It was later seized by the crown and became the property of King Edward IV and King Richard III, who built its famous banqueting hall. King Henry VIII and his then wife Anne Boleyn visited the castle in 1535; and it later became the home and final resting place of his sixth wife, Catherine Parr who remarried after the king's death. Parr is buried in the castle's church, making Sudeley the only privately owned castle in the world to have a Queen of England buried in its grounds. Sudeley soon became the home of the Chandos family, and the castle was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotswolds
The Cotswolds (, ) is a region in central-southwest England, along a range of rolling hills that rise from the meadows of the upper Thames to an escarpment above the Severn Valley and Evesham Vale. The area is defined by the bedrock of Jurassic limestone that creates a type of grassland habitat rare in the UK and that is quarried for the golden-coloured Cotswold stone. The predominantly rural landscape contains stone-built villages, towns, and stately homes and gardens featuring the local stone. Designated as an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB) in 1966, the Cotswolds covers making it the largest AONB. It is the third largest protected landscape in England after the Lake District and Yorkshire Dales national parks. Its boundaries are roughly across and long, stretching southwest from just south of Stratford-upon-Avon to just south of Bath near Radstock. It lies across the boundaries of several English counties; mainly Gloucestershire and Oxfordshire, and parts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertford
Hertford ( ) is the county town of Hertfordshire, England, and is also a civil parish in the East Hertfordshire district of the county. The parish had a population of 26,783 at the 2011 census. The town grew around a ford on the River Lea, near its confluences with the rivers Mimram, Beane, and Rib. The Lea is navigable from the Thames up to Hertford. Fortified settlements were established on each side of the ford at Hertford in 913AD. The county of Hertfordshire was established at a similar time, being named after and administered from Hertford. Hertford Castle was built shortly after the Norman Conquest in 1066 and remained a royal residence until the early seventeenth century. Hertfordshire County Council and East Hertfordshire District Council both have their main offices in the town and are major local employers, as is McMullen's Brewery, which has been based in the town since 1827. The town is also popular with commuters, being only north of central London and connect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
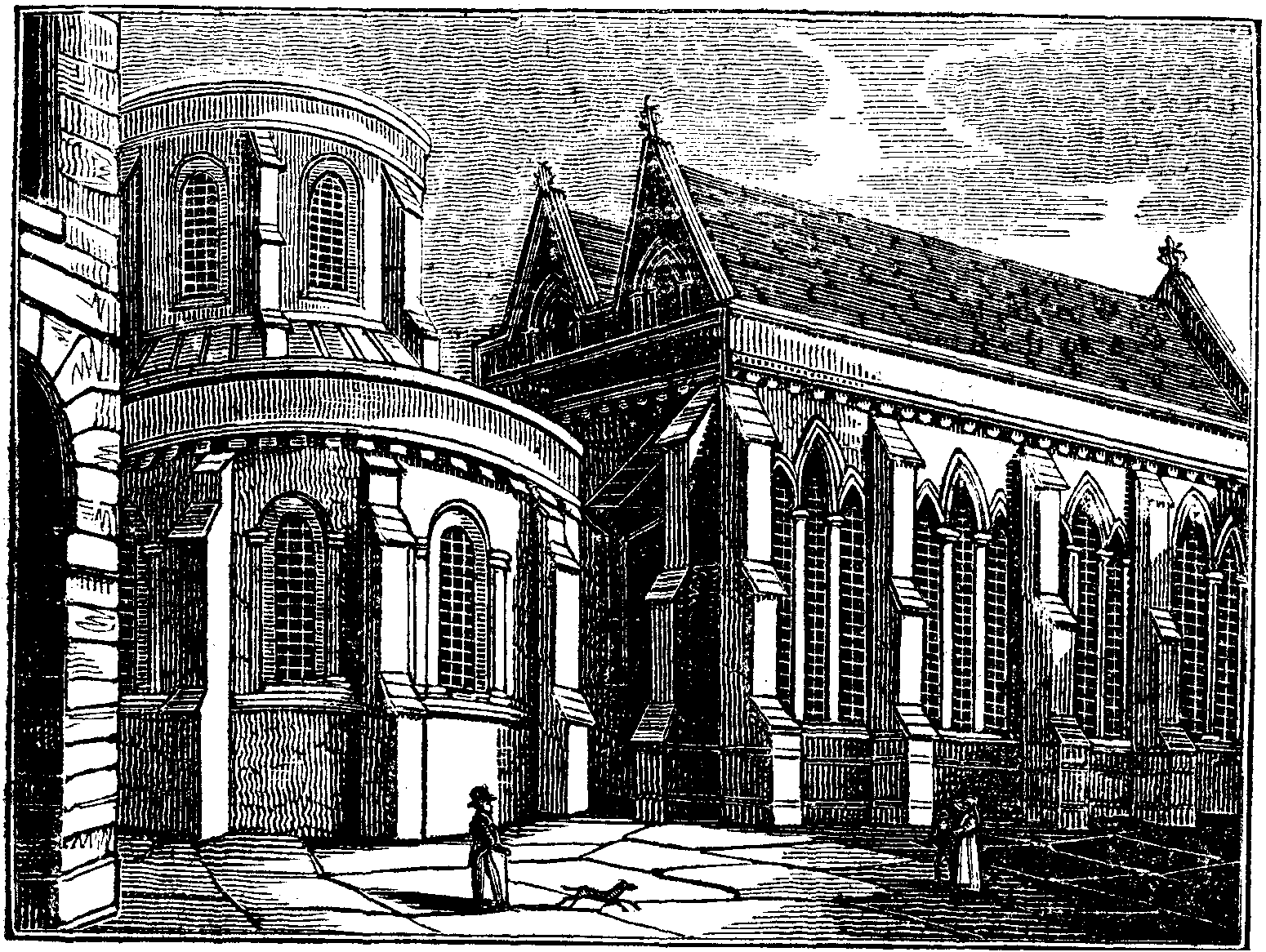
Dorchester Abbey
The Abbey Church of St Peter and St Paul, more usually called Dorchester Abbey, is a Church of England parish church in Dorchester on Thames, Oxfordshire, about southeast of Oxford. It was formerly a Norman abbey church and was built on the site of a Saxon cathedral. History Alexander, Bishop of Lincoln founded Dorchester Abbey in 1140 for the Arrouaisian Order of Augustinian Canons Regular (who wore white instead of the black of most Augustinian canons). Dorchester had been a Roman town and was later adopted by the Mercians. It had been the seat of a bishopric from AD 634 when Pope Honorius I had sent Saint Birinus, its first bishop, to that district, until 1085 when the Mercian See (hitherto at Dorchester) was transferred to Lincoln. The abbey, founded fifty-five years later, was dedicated in honour of Saints Peter and Paul and Birinus. It was richly endowed out of the lands and tithes of the former bishopric, and had twelve parishes subject to it, being included in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eton College
Eton College () is a public school in Eton, Berkshire, England. It was founded in 1440 by Henry VI under the name ''Kynge's College of Our Ladye of Eton besyde Windesore'',Nevill, p. 3 ff. intended as a sister institution to King's College, Cambridge, making it the 18th-oldest Headmasters' and Headmistresses' Conference (HMC) school. Eton is particularly well-known for its history, wealth, and notable alumni, called Old Etonians. Eton is one of only three public schools, along with Harrow (1572) and Radley (1847), to have retained the boys-only, boarding-only tradition, which means that its boys live at the school seven days a week. The remainder (such as Rugby in 1976, Charterhouse in 1971, Westminster in 1973, and Shrewsbury in 2015) have since become co-educational or, in the case of Winchester, as of 2021 are undergoing the transition to that status. Eton has educated prime ministers, world leaders, Nobel laureates, Academy Award and BAFTA award-winning actors, and ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas More
Sir Thomas More (7 February 1478 – 6 July 1535), venerated in the Catholic Church as Saint Thomas More, was an English lawyer, judge, social philosopher, author, statesman, and noted Renaissance humanist. He also served Henry VIII as Lord High Chancellor of England from October 1529 to May 1532. He wrote ''Utopia'', published in 1516, which describes the political system of an imaginary island state. More opposed the Protestant Reformation, directing polemics against the theology of Martin Luther, Huldrych Zwingli, John Calvin and William Tyndale. More also opposed Henry VIII's separation from the Catholic Church, refusing to acknowledge Henry as supreme head of the Church of England and the annulment of his marriage to Catherine of Aragon. After refusing to take the Oath of Supremacy, he was convicted of treason and executed. On his execution, he was reported to have said: "I die the King's good servant, and God's first". Pope Pius XI canonised More in 1935 as a martyr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crosby Hall, London
Crosby Hall is a historic building in London. The Great Hall was built in 1466 and originally known as Crosby Place in Bishopsgate, in the City of London. It was moved in 1910 to its present site in Cheyne Walk, Chelsea. It now forms part of a private residence, which in 2021 was renamed Crosby Moran Hall. The Great Hall, and additional work of 1910 and 1925–1926, are listed Grade II*. Although fragmentary and not on its original site, this is the only example of a medieval City merchant house surviving in London. Between 1988 and 2021 it was restored, and further buildings added, to create the present complex. The Great Hall is considered to be the most important surviving secular domestic medieval building in London. History Bishopsgate The Great Hall is the only surviving part of the medieval mansion of Crosby Place, Bishopsgate, in the City of London. It was built in 1466 on the grounds of St. Helen's Convent across from St. Helen's Church, Bishopsgate (Coordinates: ) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple Church
The Temple Church is a Royal peculiar church in the City of London located between Fleet Street and the River Thames, built by the Knights Templar as their English headquarters. It was consecrated on 10 February 1185 by Patriarch Heraclius of Jerusalem. During the reign of King John (1199–1216) it served as the royal treasury, supported by the role of the Knights Templar as proto-international bankers. It is now jointly owned by the Inner Temple and Middle Temple Inns of Court, bases of the English legal profession. It is famous for being a round church, a common design feature for Knights Templar churches, and for its 13th- and 14th-century stone effigies. It was heavily damaged by German bombing during World War II and has since been greatly restored and rebuilt. The area around the Temple Church is known as the Temple. Temple Bar, an ornamental processional gateway, formerly stood in the middle of Fleet Street. Nearby is Temple Underground station. History Construc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelsea Old Church
Chelsea Old Church, also known as All Saints, is an Church of England, Anglican church, on Old Church Street, Chelsea, London, Chelsea, London SW3, England, near Albert Bridge, London, Albert Bridge. It is the church for a parish in the Diocese of London, part of the Church of England. Inside the Grade I listed building, there is seating for 400 people. There is a memorial plaque to the author Henry James (1843–1916) who lived nearby on Cheyne Walk, and was buried in Cambridge, Massachusetts. To the west of the church is a small public garden containing a sculpture by Sir Jacob Epstein. History Norman origins Chelsea Old Church dates from 1157. It was formerly the parish church of Chelsea, before it was engulfed by London. The building consisted of a 13th-century chancel with chapels to the north and south (c. 1325) and a nave and tower built in 1670. 16th century and Sir Thomas More The chapels were private property. The one to the north was called the Lawrence Chapel and was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |