|
Walter De Heer
Walter Alexander "Walt" de Heer (born November 1949) is a Dutch physicist and nanoscience researcher known for discoveries in the electronic shell structure of metal clusters, magnetism in transition metal clusters, field emission and ballistic conduction in carbon nanotubes, and graphene-based electronics. Academic career De Heer earned a doctoral degree in Physics from the University of California, Berkeley in 1986 under the supervision of Walter D. Knight. He worked at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne in Switzerland from 1987 to 1997, and is currently a Regents' Professor of Physics at the Georgia Institute of Technology. He directs the Epitaxial Graphene Laboratory in the School of Physics and leads the Epitaxial Graphene Interdisciplinary Research Group at the Georgia Tech Materials Research Science and Engineering Center. Research De Heer and his research groups have made significant contributions to several important areas in nanoscopic physics. As a g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netherlands
) , anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau") , image_map = , map_caption = , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands , established_title = Before independence , established_date = Spanish Netherlands , established_title2 = Act of Abjuration , established_date2 = 26 July 1581 , established_title3 = Peace of Münster , established_date3 = 30 January 1648 , established_title4 = Kingdom established , established_date4 = 16 March 1815 , established_title5 = Liberation Day (Netherlands), Liberation Day , established_date5 = 5 May 1945 , established_title6 = Charter for the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Kingdom Charter , established_date6 = 15 December 1954 , established_title7 = Dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles, Caribbean reorganisation , established_date7 = 10 October 2010 , official_languages = Dutch language, Dutch , languages_type = Regional languages , languages_sub = yes , languages = , languages2_type = Reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel, St. Gallen a.o.). , coordinates = , largest_city = Zürich , official_languages = , englishmotto = "One for all, all for one" , religion_year = 2020 , religion_ref = , religion = , demonym = , german: Schweizer/Schweizerin, french: Suisse/Suissesse, it, svizzero/svizzera or , rm, Svizzer/Svizra , government_type = Federalism, Federal assembly-independent Directorial system, directorial republic with elements of a direct democracy , leader_title1 = Federal Council (Switzerland), Federal Council , leader_name1 = , leader_title2 = , leader_name2 = Walter Thurnherr , legislature = Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon Wafer
In electronics, a wafer (also called a slice or substrate) is a thin slice of semiconductor, such as a crystalline silicon (c-Si), used for the fabrication of integrated circuits and, in photovoltaics, to manufacture solar cells. The wafer serves as the substrate for microelectronic devices built in and upon the wafer. It undergoes many microfabrication processes, such as doping, ion implantation, etching, thin-film deposition of various materials, and photolithographic patterning. Finally, the individual microcircuits are separated by wafer dicing and packaged as an integrated circuit. History In the semiconductor or silicon wafer industry, the term wafer appeared in the 1950s to describe a thin round slice of semiconductor material, typically germanium or silicon. Round shape comes from single-crystal ingots usually produced using the Czochralski method. Silicon wafers were first introduced in the 1940s. By 1960, silicon wafers were being manufactured in the U.S. by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics Today
''Physics Today'' is the membership magazine of the American Institute of Physics. First published in May 1948, it is issued on a monthly schedule, and is provided to the members of ten physics societies, including the American Physical Society. It is also available to non-members as a paid annual subscription. The magazine informs readers about important developments in overview articles written by experts, shorter review articles written internally by staff, and also discusses issues and events of importance to the science community in politics, education, and other fields. The magazine provides a historical resource of events associated with physics. For example it discussed debunking the physics of the Star Wars program of the 1980s, and the state of physics in China and the Soviet Union during the 1950s and 1970s. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2017 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flat Panel Display
A flat-panel display (FPD) is an electronic display used to display visual content such as text or images. It is present in consumer, medical, transportation, and industrial equipment. Flat-panel displays are thin, lightweight, provide better linearity and are capable of higher resolution than typical consumer-grade TVs from earlier eras. They are usually less than thick. While the highest resolution for consumer-grade CRT televisions was 1080i, many flat-panel displays in the 2020s are capable of 1080p and 4K resolution. In the 2010s, portable consumer electronics such as laptops, mobile phones, and portable cameras have used flat-panel displays since they consume less power and are lightweight. As of 2016, flat-panel displays have almost completely replaced CRT displays. Most 2010s-era flat-panel displays use LCD or light-emitting diode (LED) technologies, sometimes combined. Most LCD screens are back-lit with color filters used to display colors. In many cases, flat-panel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
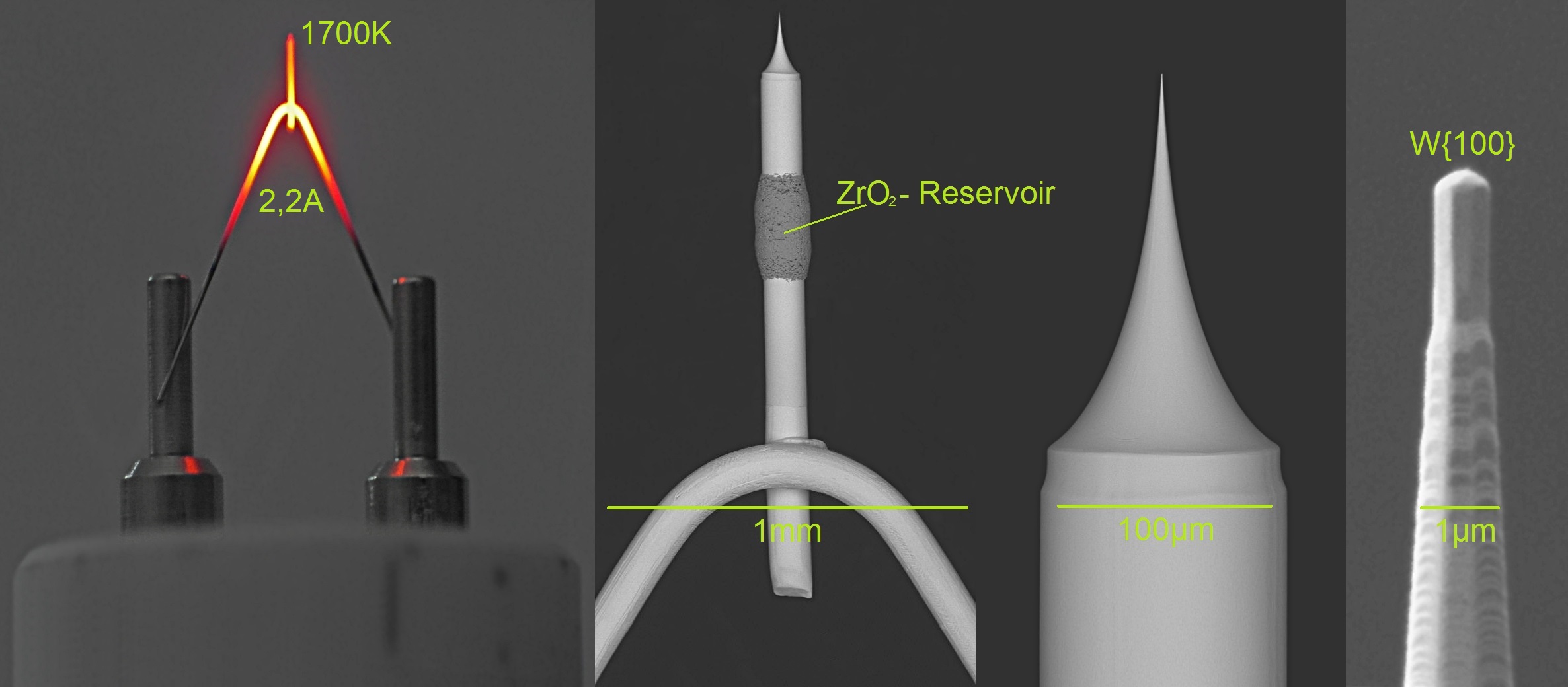
Field Emitter
Field electron emission, also known as field emission (FE) and electron field emission, is emission of electrons induced by an electrostatic field. The most common context is field emission from a solid surface into a vacuum. However, field emission can take place from solid or liquid surfaces, into a vacuum, a fluid (e.g. air), or any non-conducting or weakly conducting dielectric. The field-induced promotion of electrons from the valence to conduction band of semiconductors (the Zener effect) can also be regarded as a form of field emission. The terminology is historical because related phenomena of surface photoeffect, thermionic emission (or Richardson–Dushman effect) and "cold electronic emission", i.e. the emission of electrons in strong static (or quasi-static) electric fields, were discovered and studied independently from the 1880s to 1930s. When field emission is used without qualifiers it typically means "cold emission". Field emission in pure metals occurs in high ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_20.jpg)