|
Walker Pass
Walker Pass (el. ) is a mountain pass by Lake Isabella in the southern Sierra Nevada. It is located in northeastern Kern County, approximately 53 mi (85 km) ENE of Bakersfield and 10 mi (16 km) WNW of Ridgecrest. The pass provides a route between the Kern River Valley and San Joaquin Valley on the west, and the Mojave Desert on the east. Walker Pass is a National Historic Landmark, and is under the stewardship of the Bureau of Land Management. History Walker Pass was charted as a route through the Sierra in 1834 by Joseph Rutherford Walker, a member of the Bonneville Expedition who learned of it from Native Americans. Walker returned through the pass in 1843, leading an immigrant wagon train into California. In 1845 the military surveying expedition of John C. Fremont used the pass. He suggested it be named after Walker. The Walker Pass Lodge was built nearby in the 1930s and was a well-known rest stop before burning down around 1990. Aside from the pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sierra Crest
The Sierra Crest is a roughly generally north-to-south ridgeline that demarcates the broad west and narrow east slopes of the Sierra Nevada and that extends as far east as the Sierra's topographic front (e.g., Diamond Mountains and Sierran escarpment). The northern and central Sierra Crest sections coincide with over of the Great Basin Divide, and the southern crest demarcates Tulare and Inyo counties and extends through Kern County to meet the Tehachapi crest. The Sierra Crest also forms two paths (bifurcates) around endorheic cirques (e.g., Cup Lake) between the west and east Sierra slopes. Theodore Solomons made the first attempt to map a crest route along the Sierras. He was instrumental in envisioning, exploring, and establishing the route of what became the John Muir Trail from Yosemite Valley along the crest of the Sierra Nevada to Mount Whitney Mount Whitney (Paiute: Tumanguya; ''Too-man-i-goo-yah'') is the highest mountain in the contiguous United States and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph B
Joseph Ber Soloveitchik ( he, יוסף דב הלוי סולובייצ׳יק ''Yosef Dov ha-Levi Soloveychik''; February 27, 1903 – April 9, 1993) was a major American Orthodox rabbi, Talmudist, and modern Jewish philosopher. He was a scion of the Lithuanian Jewish Soloveitchik rabbinic dynasty. As a '' rosh yeshiva'' of Rabbi Isaac Elchanan Theological Seminary at Yeshiva University in New York City, The Rav, as he came to be known, ordained close to 2,000 rabbis over the course of almost half a century. Rabbinic literature sometimes refers to him as הגרי"ד, short for "The great Rabbi Yosef Dov". He served as an advisor, guide, mentor, and role-model for tens of thousands of Jews, both as a Talmudic scholar and as a religious leader. He is regarded as a seminal figure by Modern Orthodox Judaism. Heritage Joseph Ber Soloveitchik was born on February 27, 1903, in Pruzhany, Imperial Russia (later Poland, now Belarus). He came from a rabbinical dynasty dating back some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Crest Trail
The Pacific Crest Trail (PCT), officially designated as the Pacific Crest National Scenic Trail, is a long-distance hiking and equestrian trail closely aligned with the highest portion of the Cascade and Sierra Nevada mountain ranges, which lie east of the U.S. Pacific coast. The trail's southern terminus is next to the Mexico–United States border, just south of Campo, California, and its northern terminus is on the Canada–US border, upon which it continues unofficially to the Windy Joe Trail within Manning Park in British Columbia; it passes through the states of California, Oregon, and Washington. The Pacific Crest Trail is long and ranges in elevation from roughly above sea level near the Bridge of the Gods on the Oregon–Washington border to at Forester Pass in the Sierra Nevada. The route passes through 25 national forests and 7 national parks. Its midpoint is near Chester, California (near Mt. Lassen), where the Sierra and Cascade mountain ranges meet. It was d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California State Route 88
State Route 88 (SR 88), also known as the Carson Pass Highway, is a state highway in the U.S. state of California. It travels in an east–west direction from Stockton in the San Joaquin Valley, crossing the Sierra Nevada at Carson Pass, and ending at the Nevada state line, whereupon it becomes Nevada State Route 88, eventually terminating at U.S. Route 395. Unlike other two-lane California highways through the mountains (Routes 4, 108 and 120), Route 88 stays open through winter, except during the worst snowstorms, making it the third major route through the mountains, after Interstate 80 and U.S. Route 50. In fact, Route 88 over the Carson Pass is designated as Alternate U.S. 50, such that it may be used during floods of the American River Canyon. Route description SR 88 begins just outside Stockton as Waterloo Road, heading northeast towards Waterloo. The highway turns north at Waterloo, and SR 88 continues north to an intersection with SR 12, where the latter runs co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carson Pass
Carson Pass is a mountain pass on the crest of the central Sierra Nevada, in the Eldorado National Forest and Alpine County, eastern California. The pass is traversed by California State Route 88. It lies on the Great Basin Divide, with the West Fork Carson River on the east and the South Fork American River on the west. The historic pass was a point on the Carson Trail during the California Gold Rush and was used for American Civil War shipping to California until the completion of the First transcontinental railroad. The Pacific Crest Trail traverses the Carson Pass summit, which has California Historical Landmark #315 at CA 88 postmile 6.09 where Kit Carson carved his name into a tree. History The 1844 Frémont Expedition turned south from northern Nevada. When encamped at Nevada's Carson Valley on January 31, 1844, guide Kit Carson suggested the expedition detour west during the winter conditions to Sutter's Fort in California for supplies. Local Washoe Indians told them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sherman Pass (California)
Sherman Pass (elevation ) is a mountain pass in California on the Kern Plateau in the Sequoia National Forest near the southern tip of the Sierra Nevada. It is traversed by Sherman Pass Road (Forest Route 22S05), which runs from Kern River Highway (M-99) at the North Fork of the Kern River on the west to Kennedy Meadow Road ( County Route J41) on the east. Access from the east is via US 395 at 9-Mile Canyon Road north of Pearsonville, Kennedy Meadow Road to Kennedy Meadows, and Sherman Pass Road. One access route from the west is via SR 99 at Sierra Avenue ( County Route J22) in Earlimart to Ducor, Avenue 56 (County Route J22), Hot Springs Road (M-56) to California Hot Springs, Parker Pass Road (M-504 / Forest Route 23S03), Parker Pass Drive (M-50), Kern River Highway to Johnsondale, and Sherman Pass Road. Another access route from the south is via SR 99 at SR 58 in Bakersfield, SR 184, SR 178 to Lake Isabella Lake Isabella also called Isabella Lake, is a reser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Oceania in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), this largest division of the World Ocean—and, in turn, the hydrosphere—covers about 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of its total surface area, larger than Earth's entire land area combined .Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the |
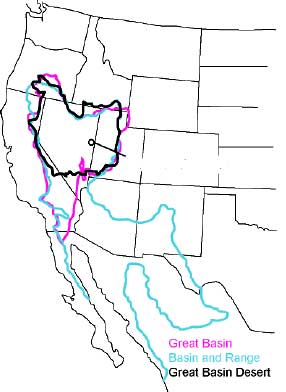
Great Basin
The Great Basin is the largest area of contiguous endorheic basin, endorheic watersheds, those with no outlets, in North America. It spans nearly all of Nevada, much of Utah, and portions of California, Idaho, Oregon, Wyoming, and Baja California. It is noted for both its arid climate and the basin and range topography that varies from the North American low point at Badwater Basin in Death Valley to the highest point of the contiguous United States, less than away at the summit of Mount Whitney. The region spans several physical geography, physiographic divisions, biomes, ecoregions, and deserts. Definition The term "Great Basin" is applied to hydrography, hydrographic, ecology, biological, floristic province, floristic, physiographic, topography, topographic, and Ethnography, ethnographic geographic areas. The name was originally coined by John C. Frémont, who, based on information gleaned from Joseph R. Walker as well as his own travels, recognized the hydrographic nature o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Wells Valley
Indian Wells Valley is an arid north-south basin in east-central California. In the geologic sense, it is a southern extension of Owens Valley to the north, with the recent volcanics of the Coso Range being the separator. It is defined by a major fault on the west side of the valley. Unlike Owens Valley, it is bound by a fault to the south, the Garlock Fault (within the El Paso Mountains). This valley is part of the northwesternmost Mojave Desert plant community and ecoregion. The largest city in the valley is Ridgecrest. Other locations include Inyokern, Indian Wells, and communities associated with the China Lake Naval Weapons Center, the primary industry in the valley. California State Route 14 and US Highway 395 are the main transportation corridors through the valley. See also * Tehachapi Wind Resource Area External links *Groundwater Quality in the Indian Wells Valley, CaliforniaUnited States Geological Survey The United States Geological Survey (USGS), former ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tioga Pass
Tioga Pass is a mountain pass in the Sierra Nevada mountain range of California. State Route 120 runs through it, and serves as the eastern entry point for Yosemite National Park, at the Tioga Pass Entrance Station. It is the highest elevation highway pass in California and in the Sierra Nevada at an elevation of . Mount Dana is to the east of the pass, and Gaylor Peak to the west. Etymology Tioga Pass is named after Tioga Mine, whose name came from the Tioga River in New York: ''Tioga'' is an Iroquois and Mohawk term meaning "where it forks". Description This pass, like many other passes in the Sierra Nevada, has a gradual approach from the west and drops off to the east dramatically, losing more than by the time the road reaches U.S. Route 395. The pass is subject to winter closure due to high snowfall, normally from around the end of October until the end of May the following year, though these dates are subject to considerable variation. In heavy snow years, the road has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tehachapi Mountains
The Tehachapi Mountains (; Kawaiisu: ''Tihachipia'', meaning "hard climb") are a mountain range in the Transverse Ranges system of California in the Western United States. The range extends for approximately in southern Kern County and northwestern Los Angeles County and form part of the boundary between the San Joaquin Valley and the Mojave Desert. Geography The Tehachapis form a geographic, watershed, habitat, and rain shadow divide separating the San Joaquin Valley to the northwest and the Mojave Desert to the southeast. The Tehachapis' crest varies in height from approximately . They are southeast of Bakersfield and the Central Valley, and west of Mojave and the Antelope Valley. The range runs southwest to northeast (SW-NE) connecting the Southern Sierra Nevada range on their northeast with the San Emigdio Mountains on the west and Sierra Pelona Mountains on the southwest. The Tehachapis are delineated from the San Emigdio Mountains by Tejon Pass at the range's weste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tehachapi Pass
Tehachapi Pass (Kawaiisu: ''Tihachipia'', meaning "hard climb") is a mountain pass crossing the Tehachapi Mountains in Kern County, California. Traditionally, the pass marks the northeast end of the Tehachapis and the south end of the Sierra Nevada range. The route is a principal connector between the San Joaquin Valley and the Mojave Desert. The Native American Kitanemuk people used the pass as a trade route before the American settlement of the region in the 19th century. The main line of the former Southern Pacific Railroad opened though the pass in 1876; the tracks are now owned by the Union Pacific Railroad and shared with BNSF Railway. U.S. Route 466 was built in the 1930s, and the road is now State Route 58. The Pass is also the route of the planned California High-Speed Rail line. The Tehachapi Mountains are also crossed by Tejon Pass at the southwest end of the range. Nomenclature The precise meaning of the name Tehachapi Pass is often a source of confusion. Technical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

.jpg)