|
Wakefulness-promoting Agent
Eugeroics (originally "eugrégorique" or "eugregoric"), also known as wakefulness-promoting agents and wakefulness-promoting drugs, are a class of drugs that promote wakefulness and alertness. They are medically indicated for the treatment of certain sleep disorders including excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS) in narcolepsy or obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Eugeroics are also often prescribed off-label for the treatment of EDS in idiopathic hypersomnia, a rare and often debilitating sleep disorder which currently has no official treatments approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). In contrast to classical psychostimulants, such as methylphenidate and amphetamine, which are also used in the treatment of these disorders, eugeroics typically do not produce euphoria, and, consequently, have a lower addictive potential. Modafinil and armodafinil are each thought to act as selective, weak, atypical dopamine reuptake inhibitors (DRI), whereas adrafinil acts as a prodrug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
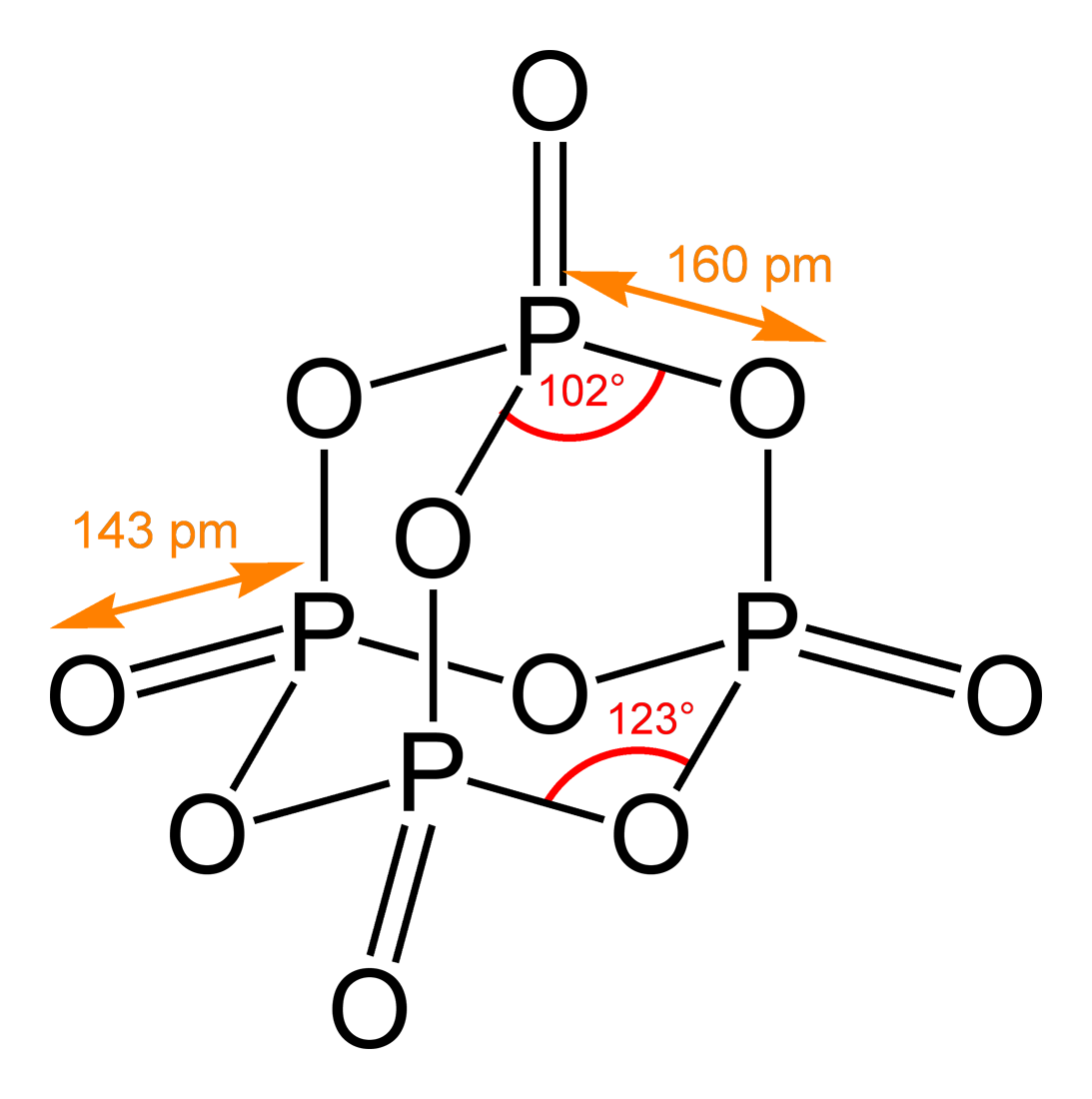
Chemical Structure
A chemical structure determination includes a chemist's specifying the molecular geometry and, when feasible and necessary, the electronic structure of the target molecule or other solid. Molecular geometry refers to the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together, and can be represented using structural formulae and by molecular models; complete electronic structure descriptions include specifying the occupation of a molecule's molecular orbitals. Structure determination can be applied to a range of targets from very simple molecules (e.g., diatomic oxygen or nitrogen), to very complex ones (e.g., such as protein or DNA). Background Theories of chemical structure were first developed by August Kekulé, Archibald Scott Couper, and Aleksandr Butlerov, among others, from about 1858. These theories were first to state that chemical compounds are not a random cluster of atoms and functional groups, but rather had a definite or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Addictive Potential
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to engage in certain behaviors, one of which is the usage of a drug, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use often alters brain function in ways that perpetuate craving, and weakens (but does not completely negate) self-control. This phenomenon – drugs reshaping brain function – has led to an understanding of addiction as a brain disorder with a complex variety of psychosocial as well as neurobiological (and thus involuntary) factors that are implicated in addiction's development. Classic signs of addiction include compulsive engagement in rewarding stimuli, ''preoccupation'' with substances or behavior, and continued use despite negative consequences. Habits and patterns associated with addiction are typically characterized by immediate gratification (short-term reward), coupled with delayed deleterious effects (long-term costs). Examples ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solriamfetol
Solriamfetol, sold under the brand name Sunosi, is a wakefulness-promoting medication used in the treatment of excessive sleepiness related to narcolepsy and sleep apnea. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects of solriamfetol include headache, nausea, anxiety, and trouble sleeping. It is a norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI) and is thought to work by increasing levels of the neurotransmitters norepinephrine and dopamine in the brain. The drug was discovered by a subsidiary of SK Group, which licensed rights outside of eleven countries in Asia to Aerial Pharma in 2011. Medical uses Solriamfetol is used to promote wakefulness in the treatment of excessive daytime sleepiness associated with narcolepsy or obstructive sleep apnea in adults. Available forms Solriamfetol is available in the form of 75 and 150mg oral tablets. Side effects Side effects of solriamfetol include headache, nausea, decreased appetite, insomnia, anxiety, irritability, feeling jitte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitolisant
Pitolisant, sold under the brand name Wakix among others, is a medication for the treatment of excessive daytime sleepiness in adults with narcolepsy. It is a histamine 3 (H3) receptor antagonist/ inverse agonist. It represents the first commercially available medication in its class. Pitolisant enhances the activity of histaminergic neurons in the brain that function to improve a person's wakefulness. The most common side effects include difficulty sleeping, nausea, and feeling worried. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers it to be a first-in-class medication. Medical uses Pitolisant (Wakix) is used in adults for the treatment of excessive daytime sleepiness and narcolepsy. Text was copied from this source which is © European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged. Narcolepsy is a sleep problem that is characterized by an irresistible urge to sleep and disturbed nighttime sleep, while cataplexy refers to attacks o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armodafinil
Armodafinil (trade name Nuvigil) is the enantiopure compound of the eugeroic modafinil (Provigil). It consists of only the (''R'')-(−)-enantiomer of the racemic modafinil. Armodafinil is produced by the pharmaceutical company Cephalon Inc. and was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in June 2007. In 2016, the FDA granted Mylan rights for the first generic version of Cephalon's Nuvigil to be marketed in the U.S. Because armodafinil has a longer half-life than modafinil does, it may be more effective at improving wakefulness in patients with excessive daytime sleepiness. Medical uses Armodafinil is currently FDA-approved to treat excessive daytime sleepiness associated with obstructive sleep apnea, narcolepsy, and shift work disorder. It is commonly used off-label to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, chronic fatigue syndrome, and major depressive disorder, and has been repurposed as an adjunctive treatment for bipolar disorder. It has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
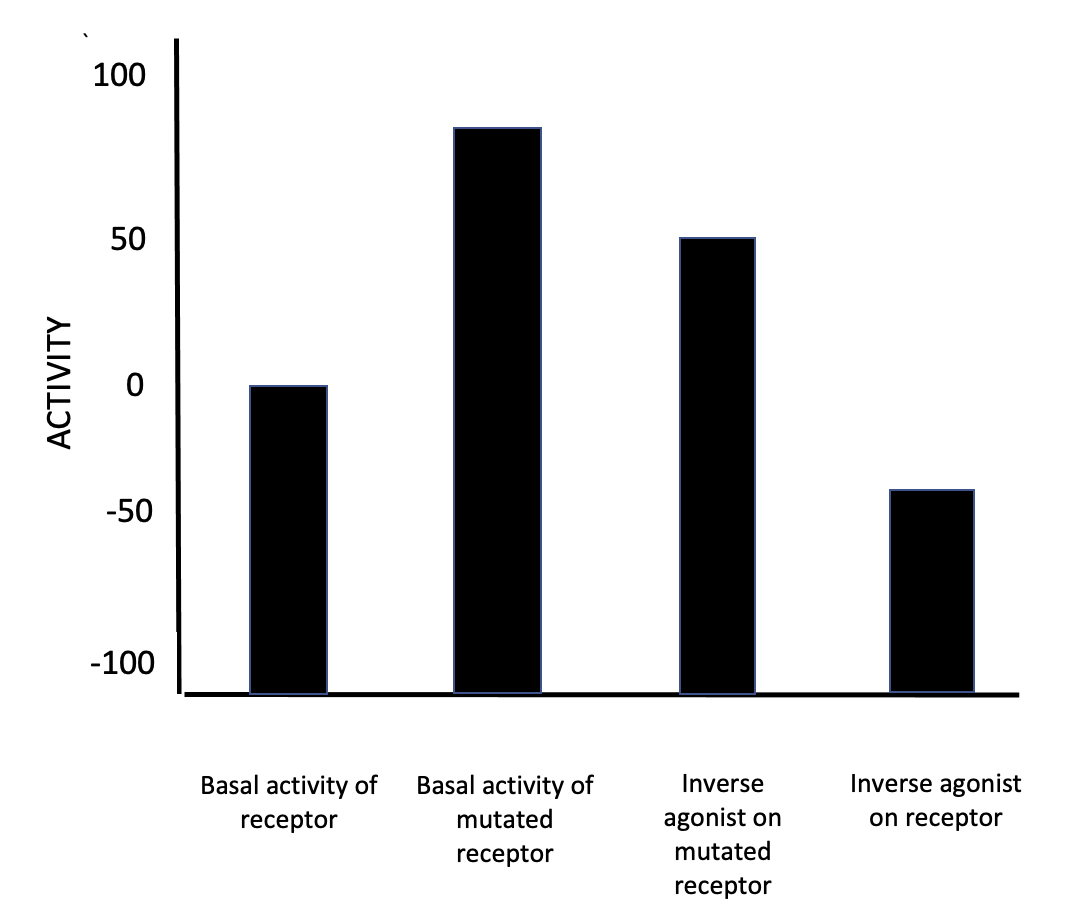
Inverse Agonist
In pharmacology, an inverse agonist is a drug that binds to the same receptor as an agonist but induces a pharmacological response opposite to that of the agonist. A neutral antagonist has no activity in the absence of an agonist or inverse agonist but can block the activity of either. Inverse agonists have opposite actions to those of agonists but the effects of both of these can be blocked by antagonists. A prerequisite for an inverse agonist response is that the receptor must have a constitutive (also known as intrinsic or basal) level of activity in the absence of any ligand. An agonist increases the activity of a receptor above its basal level, whereas an inverse agonist decreases the activity below the basal level. The efficacy of a full agonist is by definition 100%, a neutral antagonist has 0% efficacy, and an inverse agonist has < 0% (i.e., negative) efficacy. Examples Receptors for which inverse agonists have been identified include the[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H3 Receptor Antagonist
An H3 receptor antagonist is a classification of drugs used to block the action of histamine at the H3 receptor. Unlike the H1 and H2 receptors which have primarily peripheral actions, but cause sedation if they are blocked in the brain, H3 receptors are primarily found in the brain and are inhibitory autoreceptors located on histaminergic nerve terminals, which modulate the release of histamine. Histamine release in the brain triggers secondary release of excitatory neurotransmitters such as glutamate and acetylcholine via stimulation of H1 receptors in the cerebral cortex. Consequently, unlike the H1 antagonist antihistamines which are sedating, H3 antagonists have stimulant and nootropic effects, and are being researched as potential drugs for the treatment of neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer's disease. Examples of selective H3 antagonists include clobenpropit, ABT-239, ciproxifan, conessine, A-349,821, betahistine, and pitolisant. History The histamine H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitolisant
Pitolisant, sold under the brand name Wakix among others, is a medication for the treatment of excessive daytime sleepiness in adults with narcolepsy. It is a histamine 3 (H3) receptor antagonist/ inverse agonist. It represents the first commercially available medication in its class. Pitolisant enhances the activity of histaminergic neurons in the brain that function to improve a person's wakefulness. The most common side effects include difficulty sleeping, nausea, and feeling worried. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers it to be a first-in-class medication. Medical uses Pitolisant (Wakix) is used in adults for the treatment of excessive daytime sleepiness and narcolepsy. Text was copied from this source which is © European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged. Narcolepsy is a sleep problem that is characterized by an irresistible urge to sleep and disturbed nighttime sleep, while cataplexy refers to attacks o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solriamfetol
Solriamfetol, sold under the brand name Sunosi, is a wakefulness-promoting medication used in the treatment of excessive sleepiness related to narcolepsy and sleep apnea. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects of solriamfetol include headache, nausea, anxiety, and trouble sleeping. It is a norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI) and is thought to work by increasing levels of the neurotransmitters norepinephrine and dopamine in the brain. The drug was discovered by a subsidiary of SK Group, which licensed rights outside of eleven countries in Asia to Aerial Pharma in 2011. Medical uses Solriamfetol is used to promote wakefulness in the treatment of excessive daytime sleepiness associated with narcolepsy or obstructive sleep apnea in adults. Available forms Solriamfetol is available in the form of 75 and 150mg oral tablets. Side effects Side effects of solriamfetol include headache, nausea, decreased appetite, insomnia, anxiety, irritability, feeling jitte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prodrug
A prodrug is a medication or compound that, after intake, is metabolized (i.e., converted within the body) into a pharmacologically active drug. Instead of administering a drug directly, a corresponding prodrug can be used to improve how the drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted ( ADME). Prodrugs are often designed to improve bioavailability when a drug itself is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. A prodrug may be used to improve how selectively the drug interacts with cells or processes that are not its intended target. This reduces adverse or unintended effects of a drug, especially important in treatments like chemotherapy, which can have severe unintended and undesirable side effects. History Many herbal extracts historically used in medicine contain glycosides (sugar derivatives) of the active agent, which are hydrolyzed in the intestines to release the active and more bioavailable aglycone. For example, salicin is a β-D-glucopy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrafinil
Adrafinil, sold under the brand name Olmifon, is a wakefulness-promoting medication that was formerly used in France to improve alertness, attention, wakefulness, and mood, particularly in the elderly. It was also used off-label by individuals who wished to avoid fatigue, such as night workers or others who needed to stay awake and alert for long periods of time. Additionally, the medication has been used non-medically as a nootropic. Adrafinil is a prodrug; it is primarily metabolized ''in vivo'' to modafinil, resulting in very similar pharmacological effects. Unlike modafinil, however, it takes time for the metabolite to accumulate to active levels in the bloodstream. Effects usually are apparent within 45–60 minutes when taken orally on an empty stomach. Adrafinil was marketed in France until September 2011 when it was voluntarily discontinued due to an unfavorable risk–benefit ratio. Medical uses Adrafinil is a wakefulness-promoting agent and was used to promote al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |