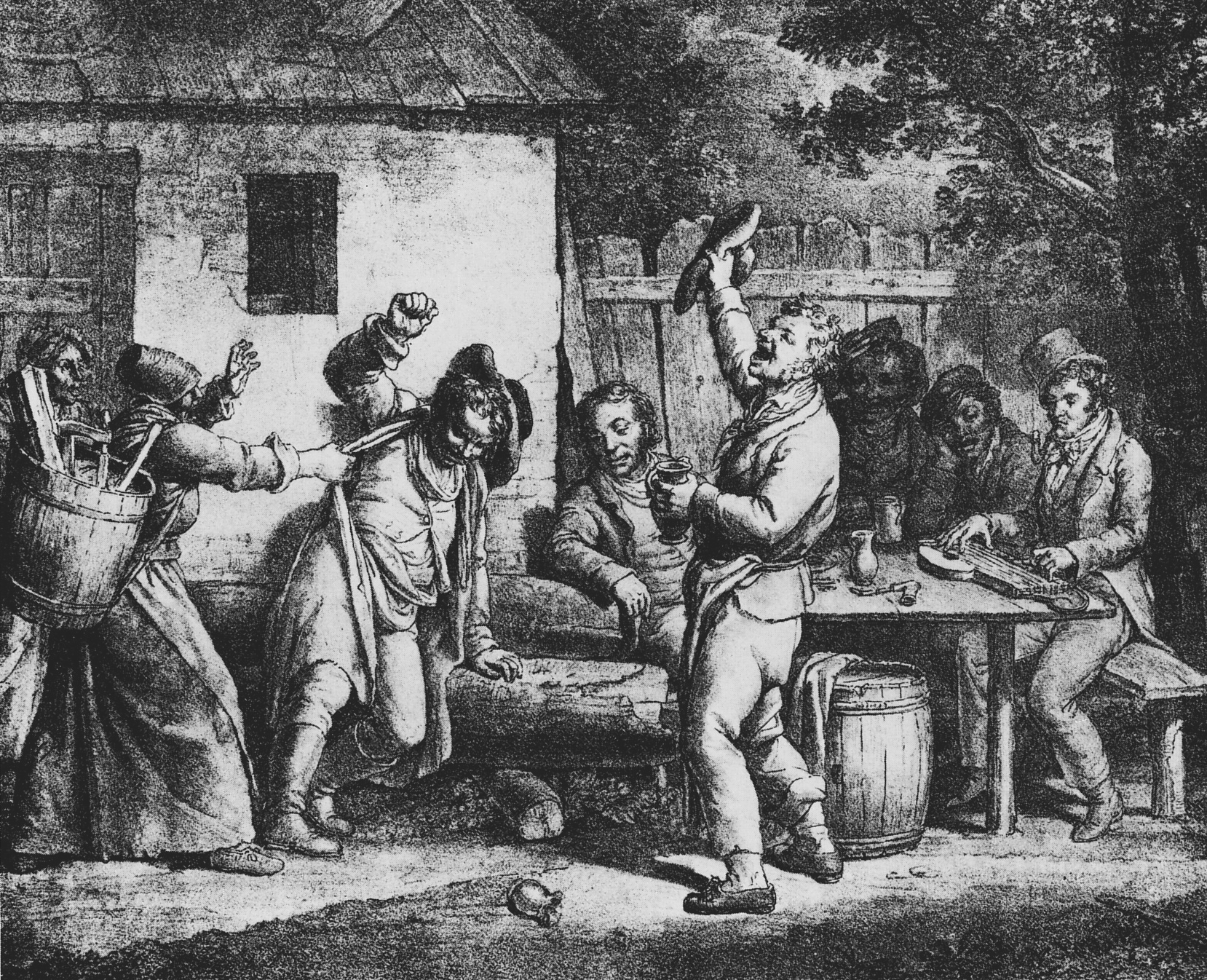|
Waiting For The Weekend
''Waiting for the Weekend'' is a book published in 1991 by Canadian architect, professor and writer Witold Rybczynski. In ''Waiting for the Weekend'', Rybczynski recounts the evolution of the seven-day week, which came into being with the Babylonian calendar, and the later, more modern, development of the two-day weekend. In so doing, he tells the history of leisure and time off; starting first with "taboo" days, market days, public festivals and holy days and how, with the coming of the Industrial Revolution the practice of "keeping Saint Monday Saint Monday is the tradition of absenteeism on a Monday. Saint Tuesday is the less common extension of this to a Tuesday. The tradition of taking Monday off has been common among craft workers since at least the seventeenth century, when the wor ...", that is, staying home from work, evolved into the modern weekend. Notes 1991 non-fiction books Books by Witold Rybczynski Working time {{hist-book-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their being ''Canadian''. Canada is a multilingual and Multiculturalism, multicultural society home to people of groups of many different ethnic, religious, and national origins, with the majority of the population made up of Old World Immigration to Canada, immigrants and their descendants. Following the initial period of New France, French and then the much larger British colonization of the Americas, British colonization, different waves (or peaks) of immigration and settlement of non-indigenous peoples took place over the course of nearly two centuries and continue today. Elements of Indigenous, French, British, and more recent immigrant customs, languages, and religions have combined to form the culture of Canada, and thus a Canadian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing buildings or other structures. The term comes ; ; . Architectural works, in the material form of buildings, are often perceived as cultural symbols and as works of art. Historical civilizations are often identified with their surviving architectural achievements. The practice, which began in the prehistoric era, has been used as a way of expressing culture for civilizations on all seven continents. For this reason, architecture is considered to be a form of art. Texts on architecture have been written since ancient times. The earliest surviving text on architectural theories is the 1st century AD treatise ''De architectura'' by the Roman architect Vitruvius, according to whom a good building embodies , and (durability, utility, and beauty) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Witold Rybczynski
Witold Rybczynski (born 1 March 1943) is a Canadian American architect, professor and writer. He is currently the Martin and Margy Meyerson Professor Emeritus of Urbanism at the University of Pennsylvania. Early life Rybczynski was born in Edinburgh of Polish parentage and raised in Surrey, England, before moving at a young age to Canada. He attended Loyola College in Montreal. He received Bachelor of Architecture (1966) and Master of Architecture (1972) degrees from McGill University in Montreal. Career Rybczynski has written around 300 articles and papers on the subjects of housing, architecture, and technology, many of which are aimed at a non-technical readership. His work has been published in a wide variety of magazines, including '' The Wilson Quarterly'', ''The Atlantic Monthly'', and ''The New Yorker''. From 2004 to 2010, he was architecture critic for ''Slate''. He taught at McGill University (1974–1993) and the University of Pennsylvania (1993–2012), and se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babylonian Calendar
The Babylonian calendar was a lunisolar calendar with years consisting of 12 lunar months, each beginning when a new lunar phase, crescent moon was first sighted low on the western horizon at sunset, plus an intercalary month inserted as needed by decree. The calendar is based on a Sumerian (Third Dynasty of Ur) predecessor preserved in the Umma calendar of Shulgi (c. 21st century BC). Months The year begins in spring, and is divided into ''reš šatti'' "beginning", ''mišil šatti'' "middle", and ''qīt šatti'' "end of the year". The word for "month" was ''arḫu'' (construct state ''araḫ''). The chief deity of the Assyrians is assigned the surplus intercalary month, showing that the calendar originates in Babylonian, and not later Assyrian times. During the 6th century BC Babylonian captivity of the Jews, the Babylonian month names were adopted into the Hebrew calendar. In Iraq and the Levant the Gregorian solar calendar is used with these names replacing the Latin ones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Workweek
The weekdays and weekend are the complementary parts of the week devoted to labour and rest, respectively. The legal weekdays (British English), or workweek (American English), is the part of the seven-day week devoted to working. In most of the world, the workweek is from Monday to Friday and the weekend is Saturday and Sunday. A weekday or workday is any day of the working week. Other institutions often follow this pattern, such as places of education. The constituted weekend has varying definitions, based on determined calendar days, designated period of time, and/or regional definition of the working week (e.g., commencing after 5:00 p.m. on Friday and lasting until 6:00 p.m. on Sunday). Sometimes the term "weekend" is expanded to include the time after work hours on the last workday of the week (e.g., Friday evening is often referred to as the start of the weekend). In some Christian traditions, Sunday is the " day of rest and worship". The Jewish '' Shabbat'' o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leisure
Leisure has often been defined as a quality of experience or as free time. Free time is time spent away from business, work, job hunting, domestic chores, and education, as well as necessary activities such as eating and sleeping. Leisure as an experience usually emphasizes dimensions of perceived freedom and choice. It is done for "its own sake", for the quality of experience and involvement. Other classic definitions include Thorsten Veblen's (1899) of "nonproductive consumption of time." Free time is not easy to define due to the multiplicity of approaches used to determine its essence. Different disciplines have definitions reflecting their common issues: for example, sociology on social forces and contexts and psychology as mental and emotional states and conditions. From a research perspective, these approaches have an advantage of being quantifiable and comparable over time and place. Leisure studies and sociology of leisure are the academic disciplines concer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taboo
A taboo or tabu is a social group's ban, prohibition, or avoidance of something (usually an utterance or behavior) based on the group's sense that it is excessively repulsive, sacred, or allowed only for certain persons.''Encyclopædia Britannica Online''.Taboo. Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 2012. Retrieved 21 Mar. 2012 Such prohibitions are present in virtually all societies. Taboos may be prohibited explicitly, for example within a legal system or religion, or implicitly, for example by social norms or conventions followed by a particular culture or organization. Taboos are often meant to protect the individual, but there are other reasons for their development. An ecological or medical background is apparent in many, including some that are seen as religious or spiritual in origin. Taboos can help use a resource more efficiently, but when applied to only a subsection of the community they can also serve to suppress said subsection of the community. A taboo acknowledged by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Day
A business day means any day except any Saturday, any Sunday, or any day which is a legal holiday or any day on which banking institutions are authorized or required by law or other governmental action to close. The definition of a business day varies by region. It depends on the local workweek which is dictated by local customs, religions, and business operations. For example, in the United States and much of the Western world, they are typically Monday through Friday from 9a.m. to 5p.m. By contrast, for many eastern countries such as Japan, the normal business day is Monday through Friday from 8:30a.m. to 7p.m. The length of a business day varies by era, by region, by industry, and by company. Prevalent norms have included the 8-hour day and the 10-hour day, but various lengths, from 4 to 16 hours, have been normal in certain times and places. Business days are commonly used by couriers when determining the arrival date of a package. If a courier ships a parcel on a Thursday ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Festival
A festival is an event ordinarily celebrated by a community and centering on some characteristic aspect or aspects of that community and its religion or cultures. It is often marked as a local or national holiday, mela, or eid. A festival constitutes typical cases of glocalization, as well as the high culture-low culture interrelationship. Next to religion and folklore, a significant origin is agricultural. Food is such a vital resource that many festivals are associated with harvest time. Religious commemoration and thanksgiving for good harvests are blended in events that take place in autumn, such as Halloween in the northern hemisphere and Easter in the southern. Festivals often serve to fulfill specific communal purposes, especially in regard to commemoration or thanking to the gods, goddesses or saints: they are called patronal festivals. They may also provide entertainment, which was particularly important to local communities before the advent of mass-produced ente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liturgical Year
The liturgical year, also called the church year, Christian year or kalendar, consists of the cycle of liturgical seasons in Christian churches that determines when feast days, including celebrations of saints, are to be observed, and which portions of Scripture are to be read either in an annual cycle or in a cycle of several years. Distinct liturgical colours may be used in connection with different seasons of the liturgical year. The dates of the festivals vary somewhat among the different churches, although the sequence and logic is largely the same. Liturgical cycle The liturgical cycle divides the year into a series of seasons, each with their own mood, theological emphases, and modes of prayer, which can be signified by different ways of decorating churches, colours of paraments and vestments for clergy, scriptural readings, themes for preaching and even different traditions and practices often observed personally or in the home. In churches that follow the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going from hand production methods to machines, new chemical manufacturing and iron production processes, the increasing use of steam power and water power, the development of machine tools and the rise of the mechanized factory system. Output greatly increased, and a result was an unprecedented rise in population and in the rate of population growth. Textiles were the dominant industry of the Industrial Revolution in terms of employment, value of output and capital invested. The textile industry was also the first to use modern production methods. The Industrial Revolution began in Great Britain, and many of the technological and architectural innovations were of British origin. By the mid-18th century, Britain was the world's leadin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Monday
Saint Monday is the tradition of absenteeism on a Monday. Saint Tuesday is the less common extension of this to a Tuesday. The tradition of taking Monday off has been common among craft workers since at least the seventeenth century, when the workweek ran from Monday to Saturday as had been the custom and expectation for centuries. In his autobiography, Benjamin Franklin refers to the practice, saying of his youthful employment in a London printing house, "My constant attendance (I never making a St. Monday) recommended me to the master". Later writers often ascribed Saint Monday to the organisation and improvement of working class life which occurred with industrialisation. Pay day was typically Saturday, and therefore workers often had spare money on Monday. Business owners in some industries had become accustomed to workers not arriving on Monday, and were willing to tolerate it. Food would commonly be left over from the weekend, thus workers did not need to visit the wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |