|
Waite's Pipefish
Waite's pipefish (''Corythoichthys waitei'') is a species of Indo-Pacific pipefish from the family Syngnathidae which is found from the Philippines east to Samoa, south to Papua New Guinea. It was previously considered to be a synonym of ''Corythoichthys intestinalis'' but is now considered to be a valid species by many authorities. The specific name honours the English ichthyologist Edgar Ravenswood Waite Edgar Ravenswood Waite (5 May 1866 – 19 January 1928) was a British/Australian zoologist, ichthyologist, herpetologist, and ornithologist. Waite was born in Leeds, Yorkshire, England, the second son of John Waite, a bank clerk, and his wife J ... (1866-1928). References waitei Fish described in 1906 {{Syngnathiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Starr Jordan
David Starr Jordan (January 19, 1851 – September 19, 1931) was the founding president of Stanford University, serving from 1891 to 1913. He was an ichthyologist during his research career. Prior to serving as president of Stanford University, he had served as president of Indiana University from 1884 to 1891. Starr was also a strong supporter of eugenics, and his published views expressed a fear of "race-degeneration" and asserted that cattle and human beings are "governed by the same laws of selection". He was an antimilitarist since he believed that war killed off the best members of the gene pool, and he initially opposed American involvement in World War I. Early life and career Jordan was born in Gainesville, New York, and grew up on a farm in upstate New York. His parents made the unorthodox decision to educate him at a local girls' high school. His middle name, Starr, does not appear in early census records, and was apparently self-selected; he had begun using ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alvin Seale
Alvin Seale (July 8, 1871 – July 28, 1958) was a naturalist known for his aquarium design and as an ichthyologist. Early life Alvin Seale was born on July 8, 1871, in Fairmount, Indiana, to a family of Quakers. In 1892, he attended Stanford University, and was tutored by David Starr Jordan. Education In 1896, the year that Seale would have graduated from Stanford in zoology, he was picked by Professor Jordan, along with fellow student Norman B. Scofield, to go to Point Barrow in Alaska. His mission was to look for salmon in the Mackenzie River. Travels Before returning to Stanford Seale collected sea birds along the Alaskan coast on behalf of the British Museum. He also went with his roommate to the Klondike to join the gold rush there. According to Seale, his companion “struck it rich.” Seale, however, was too busy exploring the native wildlife to waste his time searching for gold. In his unpublished diary Seale writes that he spent “an exciting year." Polynesian c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Pacific
The Indo-Pacific is a vast biogeographic region of Earth. In a narrow sense, sometimes known as the Indo-West Pacific or Indo-Pacific Asia, it comprises the tropical waters of the Indian Ocean, the western and central Pacific Ocean, and the seas connecting the two in the general area of Indonesia. It does not include the temperate and polar regions of the Indian and Pacific oceans, nor the Tropical Eastern Pacific, along the Pacific coast of the Americas, which is also a distinct marine realm. The term is especially useful in marine biology, ichthyology, and similar fields, since many marine habitats are continuously connected from Madagascar to Japan and Oceania, and a number of species occur over that range, but are not found in the Atlantic Ocean. The region has an exceptionally high species richness, with the world's highest species richness being found in at its heart in the Coral Triangle, and a remarkable gradient of decreasing species richness radiating outward in al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
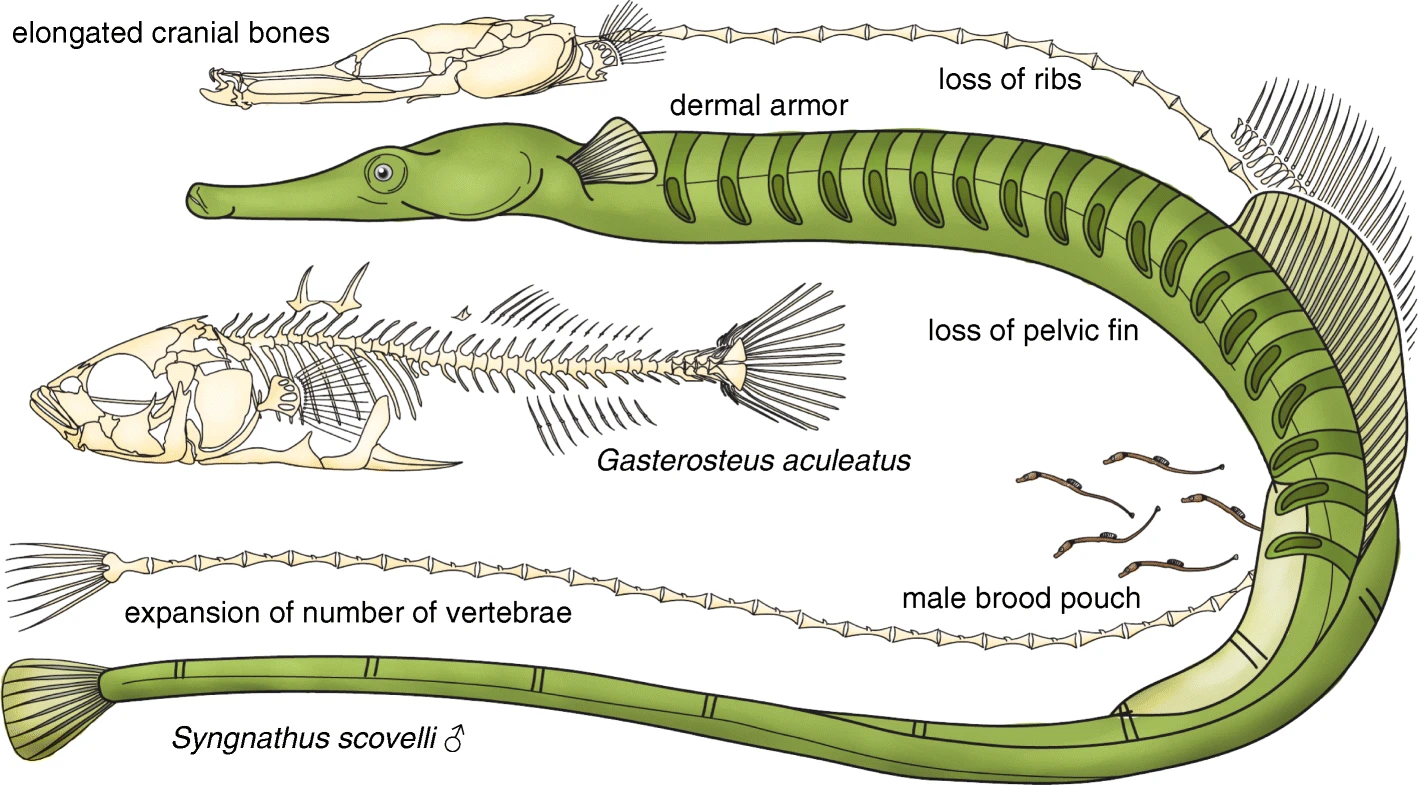
Pipefish
Pipefishes or pipe-fishes (Syngnathinae) are a subfamily of small fishes, which, together with the seahorses and seadragons (''Phycodurus'' and ''Phyllopteryx''), form the family Syngnathidae. Description Pipefish look like straight-bodied seahorses with tiny mouths. The name is derived from the peculiar form of the snout, which is like a long tube, ending in a narrow and small mouth which opens upwards and is toothless. The body and tail are long, thin, and snake-like. They each have a highly modified skeleton formed into armored plating. This dermal skeleton has several longitudinal ridges, so a vertical section through the body looks angular, not round or oval as in the majority of other fishes. A dorsal fin is always present, and is the principal (in some species, the only) organ of locomotion. The ventral fins are consistently absent, and the other fins may or may not be developed. The gill openings are extremely small and placed near the upper posterior angle of the gill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syngnathidae
The Syngnathidae is a family of fish which includes seahorses, pipefishes, and seadragons (''Phycodurus'' and ''Phyllopteryx''). The name is derived from grc, σύν (), meaning "together", and (), meaning "jaw". The fused jaw is one of the traits that the entire family have in common. Description and biology Syngnathids are found in temperate and tropical seas across the world. Most species inhabit shallow, coastal waters, but a few are known from the open ocean, especially in association with sargassum mats. They are characterised by their elongated snouts, fused jaws, the absence of pelvic fins, and by thick plates of bony armour covering their bodies. The armour gives them a rigid body, so they swim by rapidly fanning their fins. As a result, they are relatively slow compared with other fish but are able to control their movements with great precision, including hovering in place for extended periods. Uniquely, after syngnathid females lay their eggs, the male then fertiliz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synonym (taxonomy)
The Botanical and Zoological Codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that (now) goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called ''Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, ''Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved for two names at the same rank that refers to a taxon at that rank - for example, the name ''Papilio prorsa'' Linnaeus, 1758 is a junior synonym of ''Papilio levana'' Linnaeus, 1758, being names for different seasonal forms of the species now referred to as ''Araschnia le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corythoichthys Intestinalis
''Corythoichthys intestinalis'', known commonly as the scribbled pipefish, is a species of marine fish in the family Syngnathidae.Lieske & Myers,''Coral reef fishes'',Princeton University Press, 2009, Other common names used include banded pipefish, Australian banded pipefish, Australian messmate pipefish and messmate pipefish. The Scribbled pipefish is widespread throughout the tropical waters of the central Indo-Pacific region. The Scribbled pipefish is a small fish and can reach a maximum size of total length. Biology Adults occur in shallow sandy or mixed sand, rubble, or coral areas of reef flats and lagoons, also sometimes on seaward reefs, to depths of . The Scribbled pipefish is ovoviviparous Ovoviviparity, ovovivipary, ovivipary, or aplacental viviparity is a term used as a "bridging" form of reproduction between egg-laying oviparous and live-bearing viviparous reproduction. Ovoviviparous animals possess embryos that develop insi .... The male carries the eggs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Name (zoology)
In zoological nomenclature, the specific name (also specific epithet or species epithet) is the second part (the second name) within the scientific name of a species (a binomen). The first part of the name of a species is the name of the genus or the generic name. The rules and regulations governing the giving of a new species name are explained in the article species description. For example, the scientific name for humans is ''Homo sapiens'', which is the species name, consisting of two names: ''Homo'' is the " generic name" (the name of the genus) and ''sapiens'' is the "specific name". Historically, ''specific name'' referred to the combination of what are now called the generic and specific names. Carl Linnaeus, who formalized binomial nomenclature, made explicit distinctions between specific, generic, and trivial names. The generic name was that of the genus, the first in the binomial, the trivial name was the second name in the binomial, and the specific the proper term for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe by the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south. The country covers five-eighths of the island of Great Britain, which lies in the North Atlantic, and includes over 100 smaller islands, such as the Isles of Scilly and the Isle of Wight. The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic period, but takes its name from the Angles, a Germanic tribe deriving its name from the Anglia peninsula, who settled during the 5th and 6th centuries. England became a unified state in the 10th century and has had a significant cultural and legal impact on the wider world since the Age of Discovery, which began during the 15th century. The English language, the Anglican Church, and Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyology
Ichthyology is the branch of zoology devoted to the study of fish, including bony fish ( Osteichthyes), cartilaginous fish (Chondrichthyes), and jawless fish (Agnatha). According to FishBase, 33,400 species of fish had been described as of October 2016, with approximately 250 new species described each year. Etymology The word is derived from the Greek words ἰχθύς, ''ikhthus'', meaning "fish"; and λογία, ''logia'', meaning "to study". History The study of fish dates from the Upper Paleolithic Revolution (with the advent of "high culture"). The science of ichthyology was developed in several interconnecting epochs, each with various significant advancements. The study of fish receives its origins from humans' desire to feed, clothe, and equip themselves with useful implements. According to Michael Barton, a prominent ichthyologist and professor at Centre College, "the earliest ichthyologists were ''hunters and gatherers'' who had learned how to obtain the most use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edgar Ravenswood Waite
Edgar Ravenswood Waite (5 May 1866 – 19 January 1928) was a British/Australian zoologist, ichthyologist, herpetologist, and ornithologist. Waite was born in Leeds, Yorkshire, England, the second son of John Waite, a bank clerk, and his wife Jane, ''née'' Vause. Waite was educated at Leeds Parish Church Middle Class School and at the Victoria University of Manchester. In 1888 he was appointed sub-curator of the Leeds Museum and three years later was made curator. On 7 April 1892 Waite married Rose Edith Green at St. Matthew's parish church, Leeds. In 1893 Waite became zoologist at the Australian Museum, Sydney, he was the Fish Curator there from 1893 to 1906. Waite accompanied Charles Hedley of the Australian Museum on the 1896 ''Funafuti Coral Reef Boring Expedition of the Royal Society'' under Professor William Sollas and Professor Edgeworth David. Following the expedition to Funafuti in the Ellice Islands (now known as Tuvalu) Waite published an account of ''The mammals, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |