|
Wadagam State
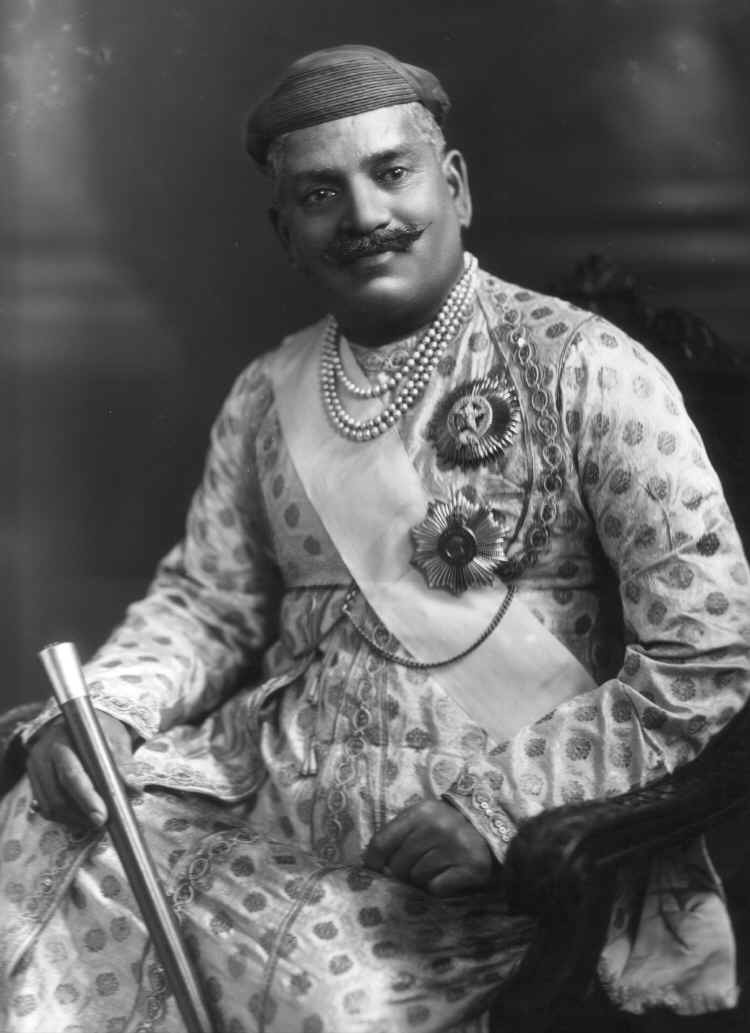
The Vadagam State ( gu, વડગામ; hi, वड़ागाम) was a 5th Class princely state belonging to the Mahi Kantha Agency of the Bombay Presidency during the era of the British Raj. It had its capital in Vadgam taluk, Banaskantha district of present-day Gujarat State. Wadagam State's last ruler signed the accession to join the Indian Union in 1948. History Wadagam state was founded by Kumar Shri Keshavdasji Rajsinhji of Ranasan, a scion of the family of Ranasan and the former Raos of Chandravati. Rulers The rulers of Wadagam State bore the title 'Thakur'. *.... – .... Keshavdasji Rajsinhji *.... – .... *.... – .... Umedsinhji *.... – .... Gulabsimhji Umedsinhji *.... – .... *.... – .... Rajsinhi *.... – .... *9 Feb 1848 – .... Kesrisinhji Pahadji (b. 1821 – d. ....) *12 Feb 1920 – .... Gopalsinhji Kesrisinhji *14 Jan 1929 – 1947 Vakhatsimhji ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another, they existed between 1612 and 1947, conventionally divided into three historical periods: *Between 1612 and 1757 the East India Company set up Factory (trading post), factories (trading posts) in several locations, mostly in coastal India, with the consent of the Mughal emperors, Maratha Empire or local rulers. Its rivals were the merchant trading companies of Portugal, Denmark, the Netherlands, and France. By the mid-18th century, three ''presidency towns'': Madras, Bombay and Calcutta, had grown in size. *During the period of Company rule in India (1757–1858), the company gradually acquired sovereignty over large parts of India, now called "presidencies". However, it also increasingly came under British government over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banaskantha District
Banaskantha district is one of the thirty-three districts of the Gujarat state of India. The administrative headquarters of the district is at Palanpur which is also its largest city. The district is located in the Northeast of Gujarat and is presumably named after the West Banas River which runs through the valley between Mount Abu and Aravalli Range, flowing to the plains of Gujarat in this region and towards the Rann of Kutch. The district is famous for the Ambaji temple which draws many tourists. It covers an area of 12703 km2 and is the second largest district in the state. Geography Banaskantha shares its borders with Rajasthan state in the North, Sabarkantha district in East, Kutch district in West and Patan district and Mehsana district in the South. Economy The economy of the district is based on agro & food Processing, tourism, textile, and mineral based industries (ceramics). The food processing industry in the district has attracted 57% of the total investmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princely States Of Gujarat
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. The female equivalent is a princess. The English word derives, via the French word ''prince'', from the Latin noun , from (first) and (head), meaning "the first, foremost, the chief, most distinguished, noble ruler, prince". Historical background The Latin word (older Latin *prīsmo-kaps, literally "the one who takes the first lace/position), became the usual title of the informal leader of the Roman senate some centuries before the transition to empire, the ''princeps senatus''. Emperor Augustus established the formal position of monarch on the basis of principate, not dominion. He also tasked his grandsons as summer rulers of the city when most of the government were on holiday in the country or attending religious rituals, and, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Rajput Dynasties And States
During the medieval and later feudal/colonial periods, many parts of the Indian subcontinent were ruled as sovereign or princely states by various dynasties of Rajputs. The Rajputs rose to political prominence after the large empires of ancient India broke into smaller ones. The Rajputs became prominent in the early medieval period in about seventh century and dominated in regions now known as Rajasthan, Delhi, Haryana, Western Gangetic plains and Bundelkhand. However, the term "Rajput" has been used as an anachronistic designation for Hindu dynasties before the 16th century because the Rajput identity for a lineage did not exist before this time, and these lineages were classified as aristocratic Rajput clans in the later times. Thus, the term "Rajput" does not occur in Muslim sources before the 16th century. List Following is the list of those ruling Rajput dynasties of the Indian Subcontinent: * Kachhwahas of Jaipur, Alwar, Lawa and Maihar * Sisodias of Mewar * Ratho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
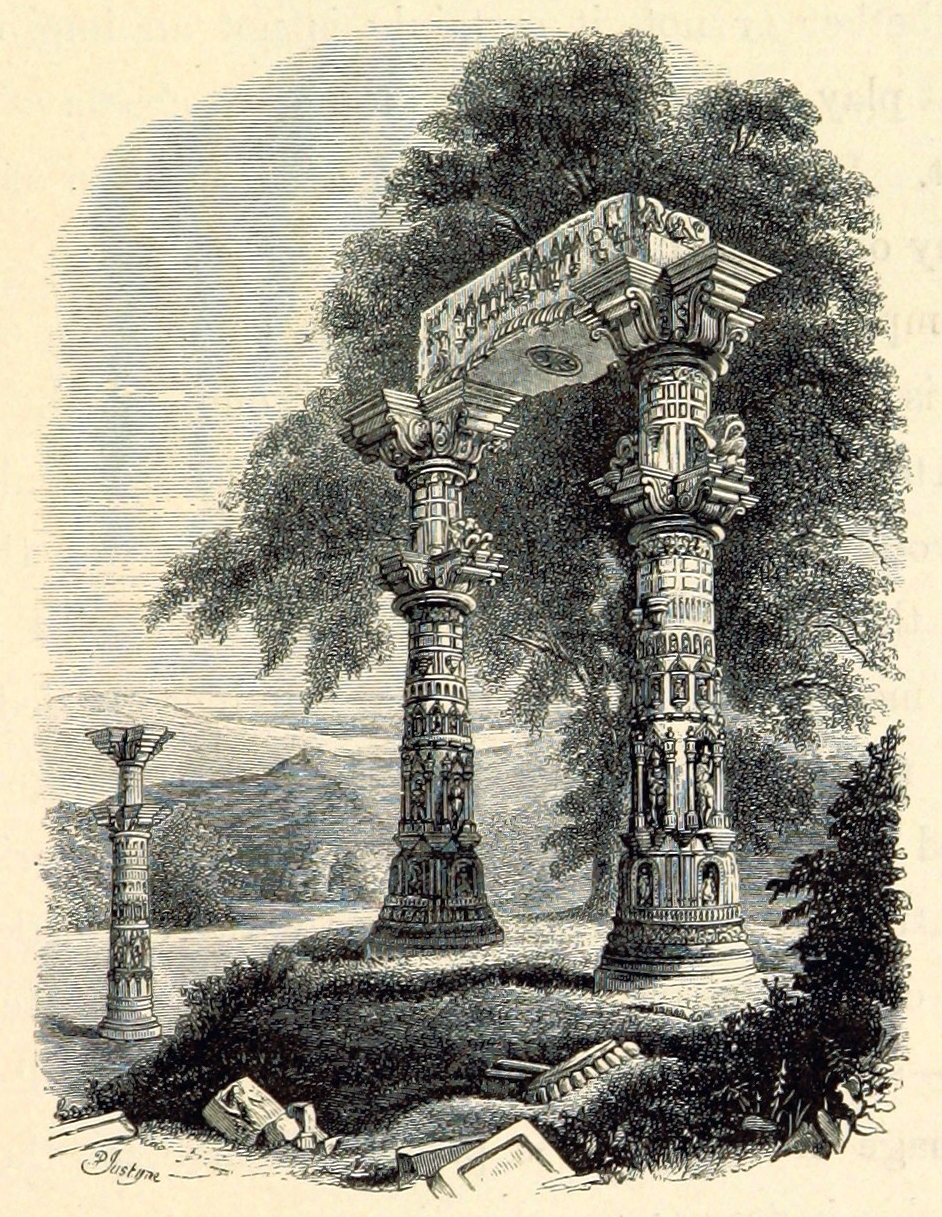
Chandravati
Chandravati, popularly known as Chandroti, is a village situated near Abu Road on the bank of the West Banas River in the Indian state of Rajasthan. In ancient times it was an extensive town, and present villages such as Dattani, Kiverli, Kharadi and Santpura were its suburbs. The old ruins, such as temples, torans and images scattered over the large area, bear testimony to its past glory. History Archeological excavations suggested that there was a large settlement at the place before the establishment of Chandravati by Paramaras. Chandravati was ruled by the Paramaras of Abu. The first Paramara ruler of the area was Sindhuraja in the early tenth century.Mathur, Vijayendra Kumar: Aitihasik Sthanavali (Hindi), Vaigyanik tatha Takaniki Shabdawali Ayog, Government of India, 1990, p.319 Chandravati was the major city in past said to once been eighteen miles in circuit. Its prosperity seems to have lasted from the seventh to the beginning of the fifteenth century. Tradition g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranasan State
The Ranasan State was a small princely state belonging to the Mahi Kantha Agency of the Bombay Presidency during the era of the British Raj. It had its capital in Ranasan village, Talod municipality, Sabarkantha district of present-day Gujarat State. History The state was ruled by the Rehvar clan of the Hindu Parmar dynasty of Rajputs. Ranasan State was merged with Baroda State under the Attachment Scheme on 10 July 1943. Finally, Baroda State instrument of accession, acceded to the Dominion of India, Indian Union on 1 May 1949. Rulers The rulers of Ranasan State bore the title 'Thakur'. *.... – .... Rajsinhji *.... – .... Sursinhji Rajsinhji *.... – .... Garibdasji Surinhji *.... – .... Adesinhji Garibdasji *.... – 1768 Bharatsinhji Adesinhji *1768 – 1802 Khumansinhji Bharatsinhji (d. 1802) *1802 – 1828 Makansinhji Khumansinhji (d. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominion Of India
The Dominion of India, officially the Union of India,* Quote: “The first collective use (of the word "dominion") occurred at the Colonial Conference (April to May 1907) when the title was conferred upon Canada and Australia. New Zealand and Newfoundland were afforded the designation in September of that same year, followed by South Africa in 1910. These were the only British possessions recognized as Dominions at the outbreak of war. In 1922, the Irish Free State was given Dominion status, followed by the short-lived inclusion of India and Pakistan in 1947 (although India was officially recognized as the Union of India). The Union of India became the Republic of India in 1950, while the became the Islamic Republic of Pakistan in 1956.” was an independent dominion in the British Commonwealth of Nations existing between 15 August 1947 and 26 January 1950. Until its independence, India had been ruled as an informal empire by the United Kingdom. The empire, also called the Britis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarat State
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth-most populous state, with a population of 60.4 million. It is bordered by Rajasthan to the northeast, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the south, Maharashtra to the southeast, Madhya Pradesh to the east, and the Arabian Sea and the Pakistani province of Sindh to the west. Gujarat's capital city is Gandhinagar, while its largest city is Ahmedabad. The Gujaratis are indigenous to the state and their language, Gujarati, is the state's official language. The state encompasses 23 sites of the ancient Indus Valley civilisation (more than any other state). The most important sites are Lothal (the world's first dry dock), Dholavira (the fifth largest site), and Gola Dhoro (where 5 uncommon seals were found). Lothal is believed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taluk
A tehsil (, also known as tahsil, taluka, or taluk) is a local unit of administrative division in some countries of South Asia. It is a subdistrict of the area within a district including the designated populated place that serves as its administrative centre, with possible additional towns, and usually a number of villages. The terms in India have replaced earlier terms, such as '' pargana'' (''pergunnah'') and ''thana''. In Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, a newer unit called mandal (circle) has come to replace the system of tehsils. It is generally smaller than a tehsil, and is meant for facilitating local self-government in the panchayat system. In West Bengal, Bihar, Jharkhand, community development blocks are the empowered grassroots administrative unit, replacing tehsils. As an entity of local government, the tehsil office (panchayat samiti) exercises certain fiscal and administrative power over the villages and municipalities within its jurisdiction. It is the ultimate execu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princely State
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Raj, British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, subject to a subsidiary alliance and the suzerainty or paramountcy of the the Crown, British crown. There were officially 565 princely states when India and Pakistan became independent in 1947, but the great majority had contracted with the viceroy to provide public services and tax collection. Only 21 had actual state governments, and only four were large (Hyderabad State, Mysore State, Kashmir and Jammu (princely state), Jammu and Kashmir State, and Baroda State). They Instrument of accession, acceded to one of the two new independent nations between 1947 and 1949. All the princes were eventually pensioned off. At the time of the British withdrawal, 565 princely states were officially recognised in the Indian subcontinent, apart from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vadgam
Vadgam is located in India, situated in Banaskantha district in northern Gujarat. Administratively, it is a Taluka. There are 110 villages under this Taluka. Vadgam region also known as a Dhandhar. Geography Vadgam is situated between Kheralu and Palanpur, 15 km away from Palanpur the main city of the Banaskantha District. It is a commercial place for the surrounding the villages Memadpur, Kodaram, Pilucha, Rupal, Gola, Parakhadi, Magarwada, Nandotra, Majadar, Gidasan and Nanosana. average raindrop in vadgam region is 706mm. History During the British Raj Vadgam was the capital of Wadagam State, one of the princely states of the Mahi Kantha Agency ruled by Rajputs. Nearby places of interest * Ambaji: 50 km *Palanpur Palanpur is a city and a municipality of Banaskantha district in the Indian state of Gujarat. Palanpur is the administrative headquarters of Banaskantha district. Palanpur is the ancestral home to an industry of Indian diamond merchants. Ety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent; * * it is also called Crown rule in India, * * * * or Direct rule in India, * Quote: "Mill, who was himself employed by the British East India company from the age of seventeen until the British government assumed direct rule over India in 1858." * * and lasted from 1858 to 1947. * * The region under British control was commonly called India in contemporaneous usage and included areas directly administered by the United Kingdom, which were collectively called British India, and areas ruled by indigenous rulers, but under British paramountcy, called the princely states. The region was sometimes called the Indian Empire, though not officially. As ''India'', it was a founding member of the League of Nations, a participating nation in the Summer Olympics in 1900, 1920, 1928, 1932, and 1936, and a founding member of the United Nations in San F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |