|
WEAC-CD
WEAC-CD, virtual channel 24 (UHF digital channel 35), is a low-power, Class A The Walk TV, and AMGTV-affiliated television station licensed to Anniston, Alabama, United States. The station is owned by Alabama Heritage Communications. WEAC maintains studio facilities on Highway 78 in Anniston, and its transmitter is located atop Coldwater Mountain in Oxford. The station is also currently available on 12 cable television systems, primarily across seven-county service area in eastern Alabama. History The station first signed on the air on December 29, 1994 as W24CB, which broadcast information for students, staff and visitors of Jacksonville State University Jacksonville State University (JSU) is a public university in Jacksonville, Alabama. Founded in 1883, Jacksonville State offers programs of study in six academic schools leading to bachelor's, master's, education specialist, and doctorate degrees .... The station changed its call letters to WJXS-CA in 2002, as an affiliat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Walk TV
The Walk TV (stylized as the WALK TV) is an American Christian specialty television network in the United States. The network consists primarily of 263 low-powered television stations across the United States, and is also available on C-band free-to-air satellite services. In addition, The Walk TV is also available to users of the Roku Digital media receiver. History The network was launched as LegacyTV on January 11, 2010. The purpose of this channel is to provide programming that helps people appreciate the Judeo-Christian legacy. The name of the channel was changed to its current name in 2013. The network was run by James L. West, who also ran the Doctor TV channel. In February 2020, WGGS-TV acquired The Walk TV. Programming General programming The Walk TV programming lineup consists primarily of religious programming, family movies, off-network syndicated public domain episodes of ''Bonanza'', and some Christian music programming. The Walk TV also features a program pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
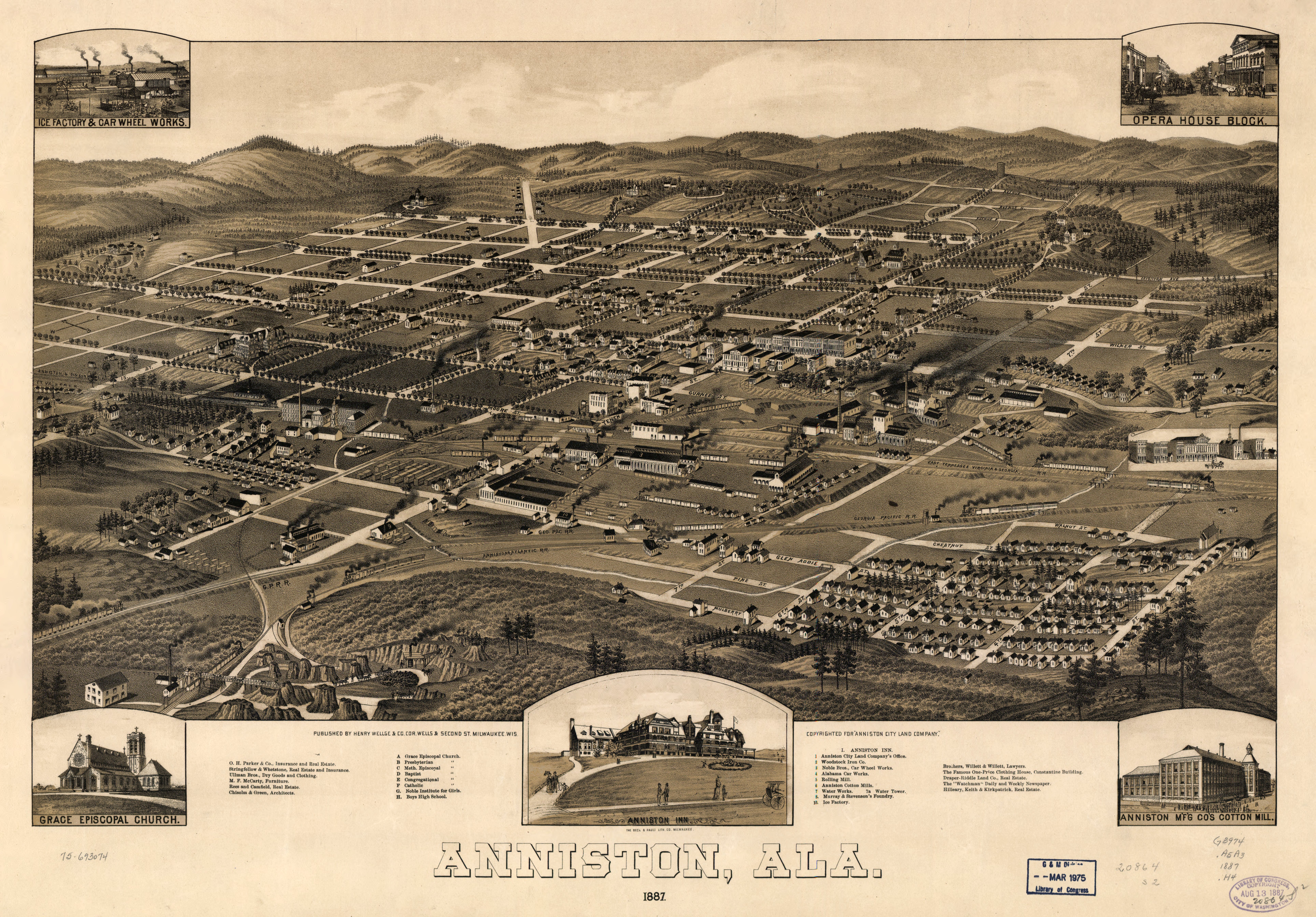
Anniston, Alabama
Anniston is the county seat of Calhoun County in Alabama and is one of two urban centers/principal cities of and included in the Anniston-Oxford Metropolitan Statistical Area. As of the 2010 census, the population of the city was 23,106. According to 2019 Census estimates, the city had a population of 21,287. Named "The Model City" by Atlanta newspaperman Henry W. Grady for its careful planning in the late 19th century, the city is situated on the slope of Blue Mountain. History Civil War Though the surrounding area was settled much earlier, the mineral resources in the area of Anniston were not exploited until the Civil War. The Confederate States of America then operated an iron furnace near present-day downtown Anniston, until it was finally destroyed by raiding Union cavalry in early 1865. Later, cast iron for sewer systems became the focus of Anniston's industrial output. Cast iron pipe, also called soil pipe, was popular until the advent of plastic pipe in the 1960s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford, Alabama
Oxford is a city in Calhoun, Talladega, and Cleburne counties in the State of Alabama. The population was 22,069 at the 2020 census,. Oxford is one of two principal cities of and included in the Anniston-Oxford Metropolitan Statistical Area, and it is the largest city in Calhoun County by population. History Founded in the early 1850s, Oxford was the first city in Calhoun County to be incorporated, in 1852. The name "Oxford" was due to the presence of a narrow crossing of Chocolocco Creek that allowed farmers to ford cattle from one side of the creek to the other. Since 1970, Oxford has annexed large amounts of land to the south and west, including the communities of Coldwater and Bynum. In 1970, it was all in Calhoun County, but today it includes areas in Talladega County and Cleburne County. A smaller municipality, Hobson City, was once a part of Oxford. The area, then known as the Mooree Quarter, is one square mile, and is located north and west of Oxford, and south and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultra High Frequency
Ultra high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies in the range between 300 megahertz (MHz) and 3 gigahertz (GHz), also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one tenth of a meter (one decimeter). Radio waves with frequencies above the UHF band fall into the super-high frequency (SHF) or microwave frequency range. Lower frequency signals fall into the VHF ( very high frequency) or lower bands. UHF radio waves propagate mainly by line of sight; they are blocked by hills and large buildings although the transmission through building walls is strong enough for indoor reception. They are used for television broadcasting, cell phones, satellite communication including GPS, personal radio services including Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, walkie-talkies, cordless phones, satellite phones, and numerous other applications. The IEEE defines the UHF radar band as frequencies between 300 MHz and 1 GHz. Two other IE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Television Stations In Alabama
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, entertainment, news, and sports. Television became available in crude experimental forms in the late 1920s, but only after several years of further development was the new technology marketed to consumers. After World War II, an improved form of black-and-white television broadcasting became popular in the United Kingdom and the United States, and television sets became commonplace in homes, businesses, and institutions. During the 1950s, television was the primary medium for influencing public opinion.Diggs-Brown, Barbara (2011''Strategic Public Relations: Audience Focused Practice''p. 48 In the mid-1960s, color broadcasting was introduced in the U.S. and most other developed countries. The availability of various types of archival storag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pigskin Roundup
Pigskin may refer to: * Ball (gridiron football) In Canada and the United States, a football (also called a pigskin) is a ball, roughly in the form of a prolate spheroid, used in the context of playing gridiron football. Footballs are often made of cowhide leather, as such a material is requir ... (also a pigskin), a ball, roughly in the form of a prolate spheroid, used in the context of playing gridiron football * ''Pigskin'' (video game), a 1979 video game by Acorn Software Products for the TRS-80 * '' Pigskin 621 A.D.'', an arcade game released in 1990 by Midway Manufacturing * "Pigskin", the sixth song from the 2013 Hollywood Undead album ''Notes from the Underground'' {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Affairs (broadcasting)
In broadcasting, public affairs radio or television programs focus on matters of politics and public policy. Among commercial broadcasters, such programs are often only to satisfy Federal Communications Commission (FCC) regulatory expectations and are not scheduled in prime time. Public affairs television programs are often broadcast at times when few listeners or viewers are tuned in (or even awake) in the U.S., in time slots known as graveyard slots; such programs can be frequently encountered at times such as 5-6 a.m. on a Sunday. Sunday morning talk shows are a notable exception to this obscure scheduling. Harvard University claims that the public affairs genre has been losing popularity since the beginning of the digital era. References See also * Public service announcement (PSA) * Sunday morning talk show Radio broadcasting Television genres Television terminology Affairs An affair is a sexual relationship, romantic friendship, or passionate attac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
480i
480i is the video mode used for standard-definition digital television in the Caribbean, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, Philippines, Laos, Western Sahara, and most of the Americas (with the exception of Argentina, Paraguay, and Uruguay). The ''480'' identifies a vertical resolution of 480 lines, and the ''i'' identifies it as an interlaced resolution. The field rate, which is 60 Hz (or 59.94 Hz when used with NTSC color), is sometimes included when identifying the video mode, i.e. 480i60; another notation, endorsed by both the International Telecommunication Union in BT.601 and SMPTE in SMPTE 259M, includes the frame rate, as in 480i/30. The other common standard definition digital standard, used in the rest of the world, is 576i. It originated from the need for a standard to digitize analog TV (defined in BT.601) and is now used for digital TV broadcasts and home appliances such as game consoles and DVD disc players. Although related, it should not be confused w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspect Ratio (image)
The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of its width to its height, and is expressed with two numbers separated by a colon, such as ''16:9'', sixteen-to-nine. For the ''x'':''y'' aspect ratio, the image is ''x'' units wide and ''y'' units high. Common aspect ratios are 1.85:1 and 2.39:1 in cinematography, 4:3 and 16:9 in television photography, and 3:2 in still photography. Some common examples The common film aspect ratios used in cinemas are 1.85:1 and 2.39:1.The 2.39:1 ratio is commonly labeled 2.40:1, e.g., in the American Society of Cinematographers' ''American Cinematographer Manual'' (Many widescreen films before the 1970 SMPTE revision used 2.35:1). Two common videographic aspect ratios are 4:3 (1.:1), the universal video format of the 20th century, and 16:9 (1.:1), universal for high-definition television and European digital television. Other cinema and video aspect ratios exist, but are used infrequently. In still camera photography, the most common aspec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Display Resolution
The display resolution or display modes of a digital television, computer monitor or display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by different factors in cathode ray tube (CRT) displays, flat-panel displays (including liquid-crystal displays) and projection displays using fixed picture-element (pixel) arrays. It is usually quoted as ', with the units in pixels: for example, ' means the width is 1024 pixels and the height is 768 pixels. This example would normally be spoken as "ten twenty-four by seven sixty-eight" or "ten twenty-four by seven six eight". One use of the term ''display resolution'' applies to fixed-pixel-array displays such as plasma display panels (PDP), liquid-crystal displays (LCD), Digital Light Processing (DLP) projectors, OLED displays, and similar technologies, and is simply the physical number of columns and rows of pixels cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Subchannel
In broadcasting, digital subchannels are a method of transmitting more than one independent program stream simultaneously from the same digital radio or television station on the same radio frequency channel. This is done by using data compression techniques to reduce the size of each individual program stream, and multiplexing to combine them into a single signal. The practice is sometimes called "multicasting". ATSC television United States The ATSC digital television standard used in the United States supports multiple program streams over-the-air, allowing television stations to transmit one or more subchannels over a single digital signal. A virtual channel numbering scheme distinguishes broadcast subchannels by appending the television channel number with a period digit (".xx"). Simultaneously, the suffix indicates that a television station offers additional programming streams. By convention, the suffix position ".1" is normally used to refer to the station's main digita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacksonville State University
Jacksonville State University (JSU) is a public university in Jacksonville, Alabama. Founded in 1883, Jacksonville State offers programs of study in six academic schools leading to bachelor's, master's, education specialist, and doctorate degrees in addition to certificate programs and continuing education opportunities. In the Fall semester of 2011, JSU began offering the school's first doctoral degree, Doctor of Science in Emergency Management. In 2016, the university gained approval to offer its second doctorate, a Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP) degree. The university was founded as Jacksonville State Normal School, and in 1930, the name changed to Jacksonville State Teachers College, and again in 1957, to Jacksonville State College. The university began operating as Jacksonville State University in 1966. JSU currently has an enrollment of more than 9,000 students, with nearly 500 faculty members (more than 320 of whom are full-time). Jacksonville State's Business School was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |