|
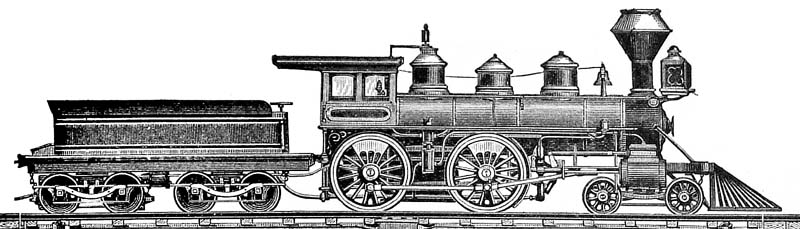
WAGR R Class
The WAGR R class was a class of 4-4-0 steam locomotives used by the Western Australian Government Railways (WAGR) between 1897 and 1953. All members of the class were built by Dübs & Co. Gunzburg 1984, p. 63. See also * Rail transport in Western Australia * List of Western Australian locomotive classes * WAGR R class (diesel) The R Class are diesel locomotives built by English Electric, Rocklea for the Western Australian Government Railways in 1968. They were followed by the revised RA class. Description The R class were a hood type general purpose diesel-electric ... – a class of diesel-electric locomotives also designated as the WAGR R class References Notes Cited works * External links {{WAGR Locomotives Dübs locomotives Railway locomotives introduced in 1897 R WAGR class 4-4-0 locomotives 3 ft 6 in gauge locomotives of Australia Scrapped locomotives Passenger locomotives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boorabbin, Western Australia
Boorabbin was a location on the narrow gauge Eastern Goldfields Railway in Western Australia. It was half way between Southern Cross and Coolgardie. It was the location of a water tank used during the era of steam power on the railways. Construction of the tank began in 1896; it had a capacity of five and a quarter million gallons. The townsite was gazetted in 1898. It was named by C.C. Hunt in 1865. It is in the area of the Boorabbin National Park, and Boorabbin Rocks. The locality was identified as the nearest to a tragedy on the Great Eastern Highway Great Eastern Highway is a road that links the Western Australian capital of Perth with the city of Kalgoorlie. A key route for road vehicles accessing the eastern Wheatbelt and the Goldfields, it is the western portion of the main road link ... when three truck drivers were killed by bushfire across the highway in 2007. Notes {{authority control Towns in Western Australia Goldfields-Esperance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-4-0
4-4-0 is a locomotive type with a classification that uses the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement and represents the arrangement: four leading wheels on two axles (usually in a leading bogie), four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles, and a lack of trailing wheels. Due to the large number of the type that were produced and used in the United States, the 4-4-0 is most commonly known as the American type, but the type subsequently also became popular in the United Kingdom, where large numbers were produced.White, John H., Jr. (1968). ''A history of the American locomotive; its development: 1830-1880''. New York: Dover Publications, pp. 46-. Almost every major railroad that operated in North America in the first half of the 19th century owned and operated locomotives of this type. The first use of the name ''American'' to describe locomotives of this wheel arrangement was made by ''Railroad Gazette'' in April 1872. Prior to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
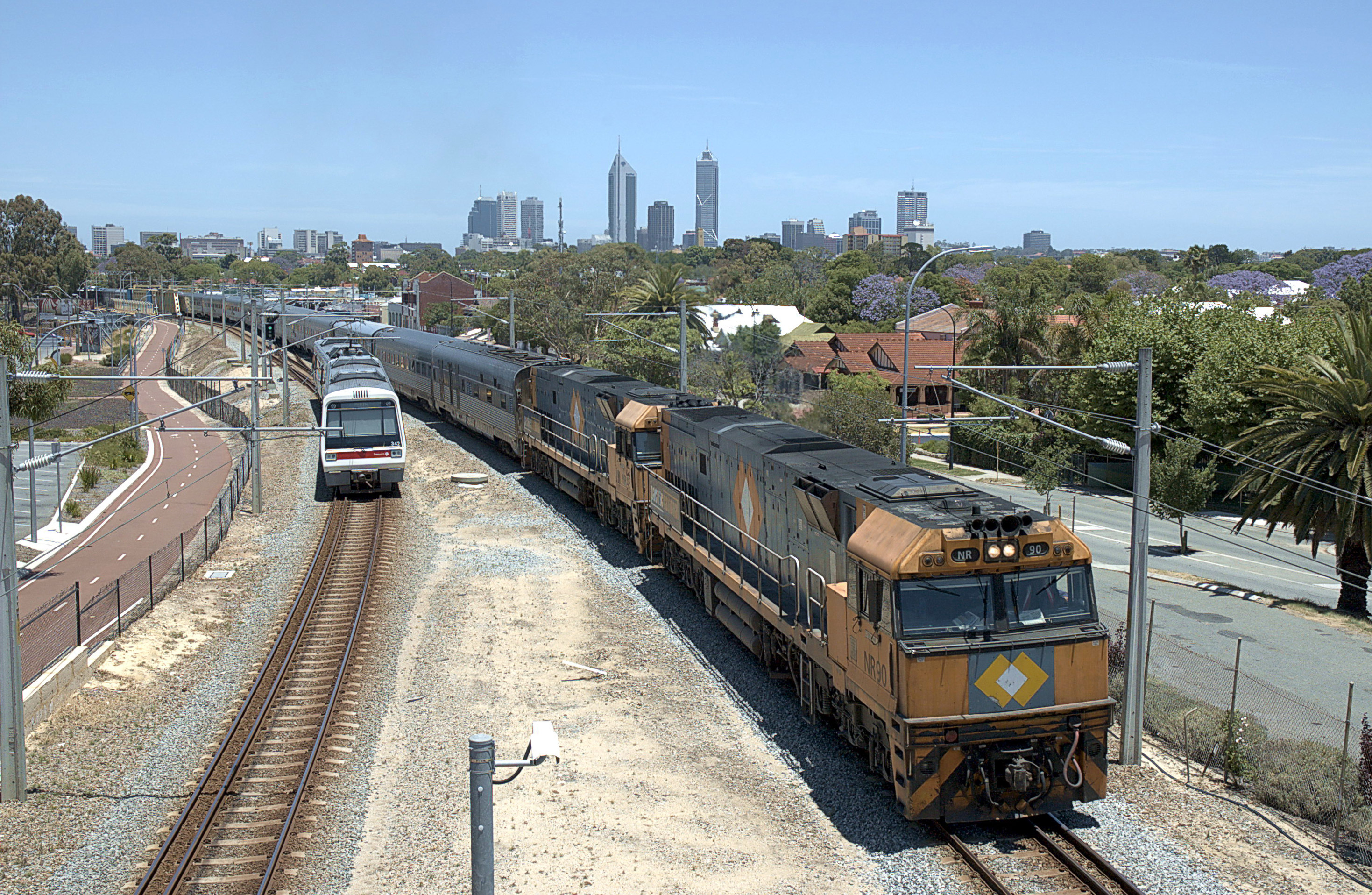
Western Australian Government Railways
Western Australian Government Railways (WAGR) was the operator of railway services in the state of Western Australia between October 1890 and June 2003. Owned by the state government, it was renamed a number of times to reflect extra responsibility for tram and ferry operations that it assumed and later relinquished. Westrail was the trading name of WAGR from September 1975 until December 2000, when the WAGR's freight division and the Westrail name and logo were privatised. Its freight operations were privatised in December 2000 with the remaining passenger operations transferred to the Public Transport Authority in July 2003. History of operations The WAGR had its origins in 1879, when the Department of Works & Railways was established. The first WAGR line opened on 26 July 1879 between Geraldton and Northampton. It was followed by the Eastern Railway from Fremantle to Guildford via Perth on 1 March 1881. The WAGR adopted the narrow gauge of to reduce construction co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomotive's boiler to the point where it becomes gaseous and its volume increases 1,700 times. Functionally, it is a steam engine on wheels. In most locomotives, the steam is admitted alternately to each end of its cylinders, in which pistons are mechanically connected to the locomotive's main wheels. Fuel and water supplies are usually carried with the locomotive, either on the locomotive itself or in a tender coupled to it. Variations in this general design include electrically-powered boilers, turbines in place of pistons, and using steam generated externally. Steam locomotives were first developed in the United Kingdom during the early 19th century and used for railway transport until the middle of the 20th century. Richard Trevithick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dübs And Company
Dübs & Co. was a locomotive manufacturer in Glasgow, Scotland, founded by Henry Dübs in 1863 and based at the Queens Park Works in Polmadie. In 1903 it amalgamated with two other Glasgow locomotive manufacturers to create the North British Locomotive Company. Preserved locomotives Eleven locomotives built for the New Zealand Railways Department, numerous others in South Africa and the Isle of Man. Preserved locomotives in New Zealand Four members of the 0-4-0 A class built in 1873 have been preserved. A 64 and A 67 are in full operational condition on vintage railways; A 64 resides at The Plains Vintage Railway & Historical Museum in Ashburton. A 67 is owned and operated by the Ocean Beach Railway / Otago Railway & Locomotive Society Inc, while A 62 is in private ownership and it is understood that the smokebox has been snapped from the boiler. A 66 (also owned by the Ocean Beach Railway) was damaged by fire when the building in which it was kept on static display was burnt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport In Western Australia
Railways in Western Australia were developed in the 19th century both by the Government of Western Australia and a number of private companies. Today passenger rail services are controlled by the Public Transport Authority (a department of the Government of Western Australia) through Transperth, which operates public transport in Perth, and Transwa, which operates country passenger services. Great Southern Rail operates the ''Indian Pacific''. The interstate standard gauge line east from Kalgoorlie is owned by the Australian Rail Track Corporation, with most other lines leased by the state to Arc Infrastructure. Freight rail was privatised in 2000. General intrastate freight is mainly operated by Aurizon, while grain traffic is also operated by Aurizon under contract to the CBH Group. Interstate traffic is operated by Pacific National and SCT Logistics. Aurizon also operate an interstate mineral sands service to Kwinana from Broken Hill for Tronox. A number of private iron or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Western Australian Locomotive Classes
This is a list of Western Australian locomotive classes, being classes of locomotive that have worked on railways in Western Australia. The majority of Western Australian steam locomotive classes were operated by the Western Australian Government Railways (WAGR). Regularly scheduled steam working ceased on WAGR mainline operations after 1971 - with only special excursion or enthusiasts trains being hauled by steam after that time. Other significant operators include the Commonwealth Railways, the Midland Railway Company of Western Australia and State Saw Mills. Many private organisations also operated steam locomotives in Western Australia. Locomotives Western Australian Government Railway Midland Railway Company of Western Australia (In order of introduction on the Midland railway.) Commonwealth Railways Other Diesel locomotives BHP (In order of introduction on the Goldsworthy and Mount Newman railways.) * CM39-8 * CM40-8M * CM40-8 * GE AC6000CW * EMD S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WAGR R Class (diesel)
The R Class are diesel locomotives built by English Electric, Rocklea for the Western Australian Government Railways in 1968. They were followed by the revised RA class. Description The R class were a hood type general purpose diesel-electric locomotive. They were similar to the Queensland Railways 1300 class. All equipment, except traction motors, were interchangeable with the standard gauge K class. The bogies are an English Electric design with low weight transfer characteristics. They feature fully equalised primary spring gear, all traction motors in each bogie mounted with the nose-suspension facing inwards, traction thrust at near axle level and long pivot centres to reduce inter-bogie transfer. Adhesion loss at maximum tractive effort is limited to 4.5 per cent allowing trailing load to be hauled up a 1 in 100 grade. History In 1968 the Western Australian Government Railways took delivery of five narrow gauge versions of the K class for use on bauxite traffic, the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Locomotives Introduced In 1897
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer facili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |