|
W54
The W54 (also known as the Mark 54 or B54) was a tactical nuclear warhead developed by the United States in the late 1950s. The weapon is notable for being the smallest nuclear weapon in both weight and yield to have entered US service. It was a compact implosion device containing plutonium-239 as its fissile material, and in its various versions and mods it had a yield of . The weapon had two distinct versions: a warhead used in the AIM-26 Falcon air-to-air missile and in the Davy Crockett recoilless gun, and another used in the Special Atomic Demolition Munition (SADM) system, along with several mods (modifications) for each version. The two types are distinct in that much of the design between them was different, to the point that during the development of the SADM it was proposed that it be given its own unique mark designation. A later development was the W72, which was a rebuilt W54 used with the AGM-62 Walleye guided bomb. The W72 was in service until 1979. Developmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
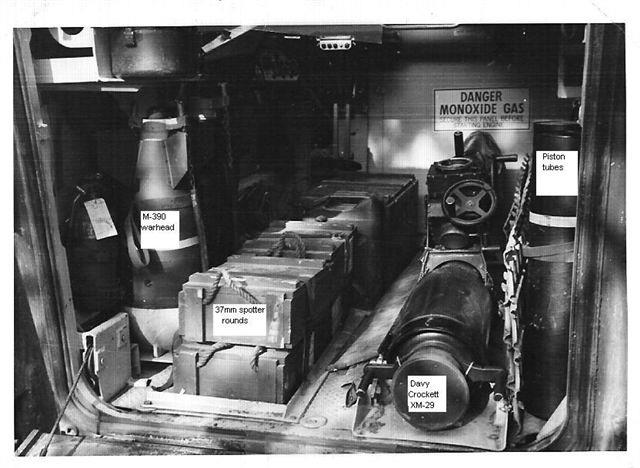
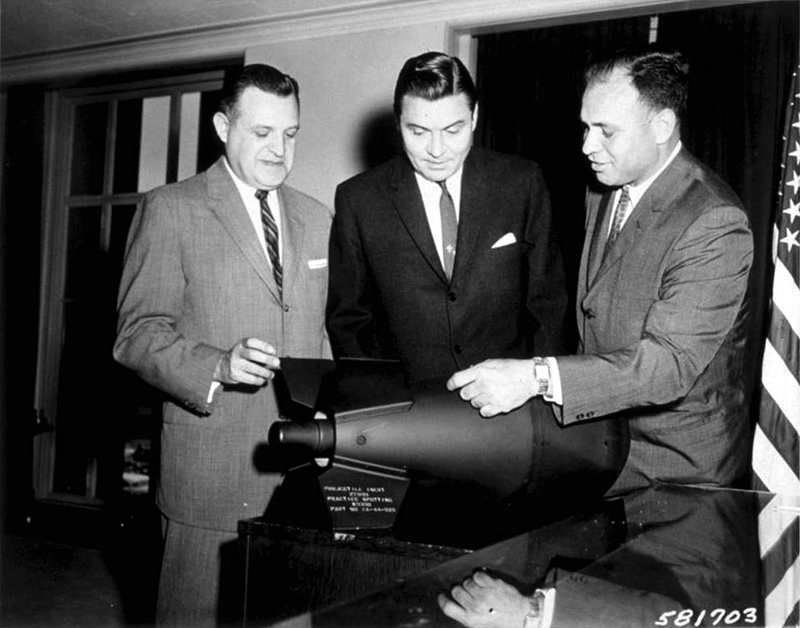
Davy Crockett (nuclear Device)
The M-28 or M-29 Davy Crockett Weapon System was a tactical nuclear recoilless smoothbore gun for firing the M388 nuclear projectile, armed with the W54 nuclear warhead, that was deployed by the United States during the Cold War. It was the first project assigned to the United States Army Weapon Command in Rock Island, Illinois. It remains one of the smallest nuclear weapon systems ever built, with a yield of . It is named after American folk hero, soldier, and congressman Davy Crockett. History By the year 1950, there had been rapid developments made in the use of nuclear weapons after the detonation of "Little Boy" and "Fat Man" in 1945. These developments paved the way for nuclear warheads to be created at a smaller size. By the 1950s, advances in nuclear weapons technology, spurred on by the first detonation of the Soviet nuclear bomb in 1949, led to great reductions in the size of nuclear weapons. By 1957, the Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) declared that it had created a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Davy Crockett (nuclear Device)
The M-28 or M-29 Davy Crockett Weapon System was a tactical nuclear recoilless smoothbore gun for firing the M388 nuclear projectile, armed with the W54 nuclear warhead, that was deployed by the United States during the Cold War. It was the first project assigned to the United States Army Weapon Command in Rock Island, Illinois. It remains one of the smallest nuclear weapon systems ever built, with a yield of . It is named after American folk hero, soldier, and congressman Davy Crockett. History By the year 1950, there had been rapid developments made in the use of nuclear weapons after the detonation of "Little Boy" and "Fat Man" in 1945. These developments paved the way for nuclear warheads to be created at a smaller size. By the 1950s, advances in nuclear weapons technology, spurred on by the first detonation of the Soviet nuclear bomb in 1949, led to great reductions in the size of nuclear weapons. By 1957, the Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) declared that it had created a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
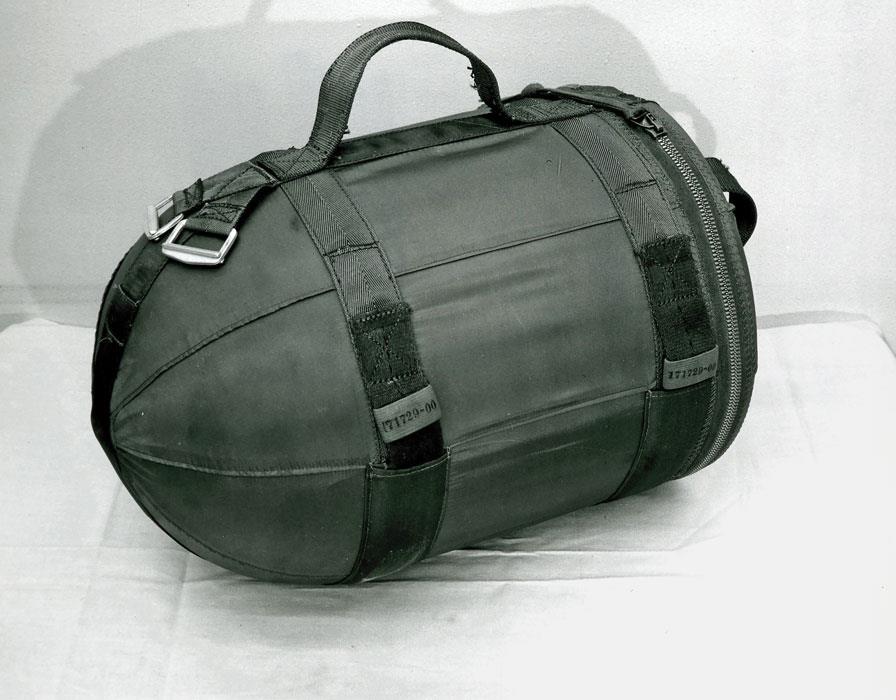
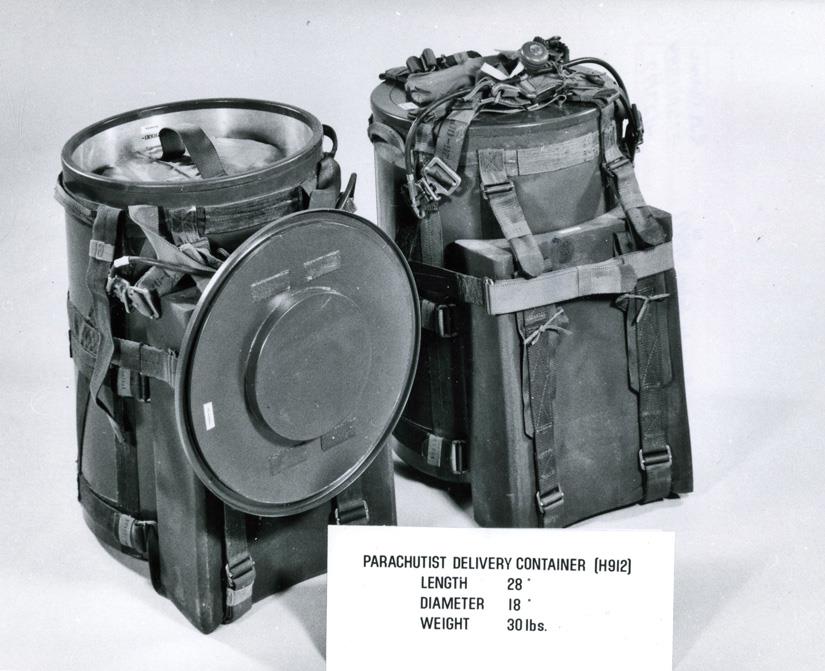
Special Atomic Demolition Munition
The Special Atomic Demolition Munition (SADM), also known as the XM129 and XM159 Atomic Demolition Charges, and the B54 bomb was a nuclear man-portable atomic demolition munition (ADM) system fielded by the US military from the 1960s to 1980s but never used in combat. History and design At the time of the weapon's development, the existing Atomic Demolition Munition (ADM) was the T-4 Atomic Demolition Munition. Its transport required 4 men, each carrying a section of the weapon. Development began in June 1960 and an interim Mark 54 Mod 0 (now called the B54-0) weapon was put into production in April 1963. Production of the B54 Mod 1 SADM began in August 1964. The weapon was in diameter, long, and weighed . It included the warhead, a fuzing and firing system with a mechanical timer, a ferroelectric firing set and a sealed housing. The body was constructed with aluminum forgings and molded fiberglass, and foam-rubber insulation was used between the warhead and case. Dials w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
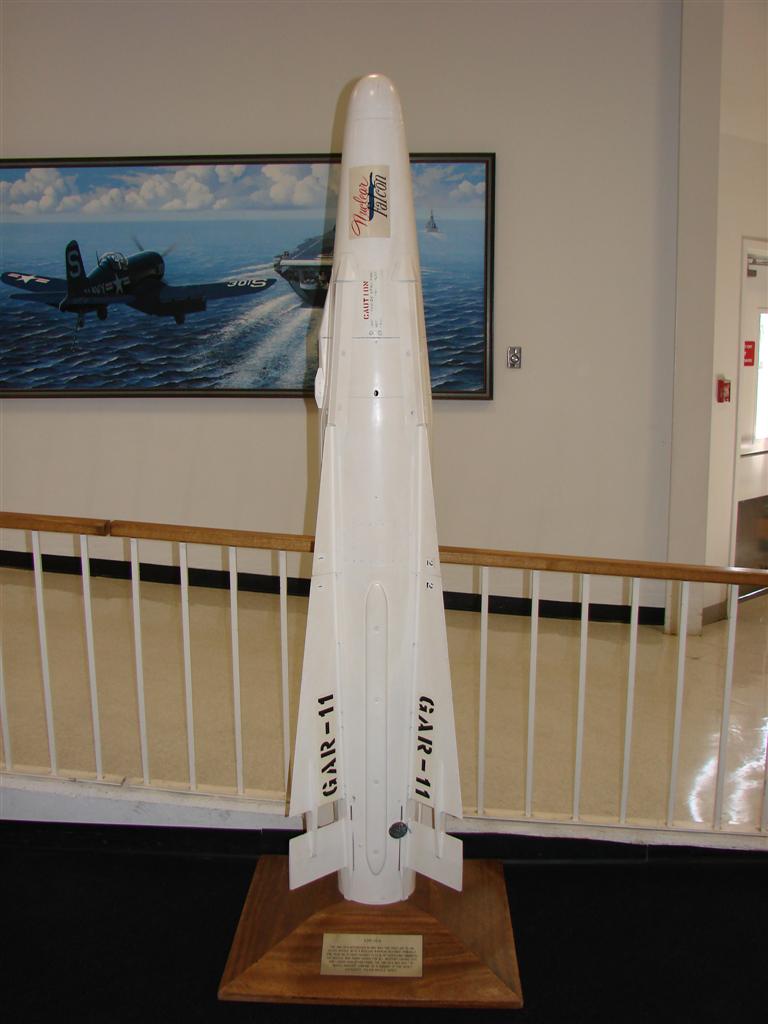
AIM-26 Falcon
The AIM-26 Falcon was a larger, more powerful version of the AIM-4 Falcon air-to-air missile built by Hughes. It is the only guided American air-to-air missile with a nuclear warhead to be produced; the unguided AIR-2 Genie rocket was also nuclear-armed. Development Starting in 1956 Hughes Electronics began the development of an enlarged version of the GAR-1D Falcon that would carry a nuclear warhead. It was intended to provide a sure kill in attacks on Soviet heavy bomber aircraft, at a time when guided missiles were not accurate enough to produce high-probability kills with small conventional warheads. The original development was for semi-active radar homing and heat-seeking versions based on the conventional GAR-1/GAR-2 weapons, under the designations GAR-5 and GAR-6, respectively. The original program was cancelled. The program was revived in 1959, now under the name GAR-11. It entered service in 1961, carried by Air Defense Command F-102 Delta Dagger interceptors. It u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-4 Atomic Demolition Munition
The T4 Atomic Demolition Munition (ADM) was a nuclear weapon derived from the American W9 nuclear artillery shell. History The T4 was produced in 1957 from recycled W9 fissile components and was in service until 1963, when it was replaced with W30 Tactical Atomic Demolition Munitions and W45 Medium Atomic Demolition Munitions. The weapon weighed and could be broken down into four sections for transport by a four-man crew. Media coverage An article in the mid-1990s in '' Soldier of Fortune'' magazine by a former US Navy Underwater Demolition Team member described the T4 ADM without naming it. The description was moderately detailed, including that the T4 was assembled out of a number of separate components: *A gun barrel assembly, with the fission “bullet” and propellant and detonator preloaded *A base assembly, which the gun barrel screwed into, which was normally handled empty *Three heavy HEU rings, which were added to the base assembly and came in separate carrying c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Nuclear Weapons
This is a list of nuclear weapons listed according to country of origin, and then by type within the states. United States US nuclear weapons of all types – bombs, warheads, shells, and others – are numbered in the same sequence starting with the Mark 1 and () ending with the W-91 (which was canceled prior to introduction into service). All designs which were formally intended to be weapons at some point received a number designation. Pure test units which were experiments (and not intended to be weapons) are not numbered in this sequence. Early weapons were very large and could only be used as free fall bombs. These were known by "Mark" designators, like the Mark 4 which was a development of the Fat Man weapon. As weapons became more sophisticated they also became much smaller and lighter, allowing them to be used in many roles. At this time the weapons began to receive designations based on their role; bombs were given the prefix "B", while the same warhead used in other r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tactical Nuclear Weapon
A tactical nuclear weapon (TNW) or non-strategic nuclear weapon (NSNW) is a nuclear weapon that is designed to be used on a battlefield in military situations, mostly with friendly forces in proximity and perhaps even on contested friendly territory. Generally smaller in explosive power, they are defined in contrast to strategic nuclear weapons, which are designed mostly to be targeted at the enemy interior far away from the war front against military bases, cities, towns, arms industries, and other hardened or larger-area targets to damage the enemy's ability to wage war. No tactical nuclear weapon has ever been used in a combat situation. Tactical nuclear weapons include gravity bombs, short-range missiles, artillery shells, land mines, depth charges, and torpedoes which are equipped with nuclear warheads. Also in this category are nuclear armed ground-based or shipborne surface-to-air missiles (SAMs) and air-to-air missiles. Small, two-man portable or truck-portable tactical w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb types release large quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. The first test of a fission ("atomic") bomb released an amount of energy approximately equal to . The first thermonuclear ("hydrogen") bomb test released energy approximately equal to . Nuclear bombs have had yields between 10 tons TNT (the W54) and 50 megatons for the Tsar Bomba (see TNT equivalent). A thermonuclear weapon weighing as little as can release energy equal to more than . A nuclear device no larger than a conventional bomb can devastate an entire city by blast, fire, and radiation. Since they are weapons of mass destruction, the proliferation of nuclear weapons is a focus of international relations policy. Nuclear weapons have been d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Feller I
Little Feller II and Little Feller I were code names for a set of nuclear tests undertaken by the United States at the Nevada Test Site on July 7 and 17, 1962 as part of Operation Sunbeam. They were both tests of stockpiled W54 warheads, the smallest nuclear warheads known to have been produced by the United States, used in both the Davy Crockett warhead and the Special Atomic Demolition Munition. In Little Feller II (July 7), the warhead was suspended only three feet above the ground and had a yield equivalent to . In Little Feller I (July 17), the warhead was launched as a Davy Crockett device from a stationary 155 millimeter launcher and set to detonate between above the ground around from the launch point, with a yield of . This test was performed in conjunction with Operation Ivy Flats, a simulated military environment, and was observed by Attorney General Robert F. Kennedy and presidential adviser General Maxwell D. Taylor. Little Feller I was the last near-ground at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AGM-62 Walleye
The AGM-62 Walleye is a television-guided glide bomb which was produced by Martin Marietta and used by the United States Armed Forces from the 1960s-1990s. Most had a 250 lb (113 kg) high-explosive warhead; some had a nuclear warhead. The designation of the ''Walleye'' as an "air-to-ground missile" is a misnomer, as it is an unpowered bomb with guidance avionics, similar to the more modern GBU-15. The Walleye was superseded by the AGM-65 Maverick. History The Walleye was the first of a family of precision-guided munitions designed to hit targets with minimal collateral damage. This "smart bomb" had no propulsion system, but it could be maneuvered via a television assisted guidance system during its glide from an aircraft to the target. As a pilot dived towards a target, a television camera in the nose of the bomb transmitted images to a monitor in the cockpit. Once the pilot acquired a sharp image of the target on his screen, he designated an aim point and released t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Feller II
Little Feller II and Little Feller I were code names for a set of nuclear tests undertaken by the United States at the Nevada Test Site on July 7 and 17, 1962 as part of Operation Sunbeam. They were both tests of stockpiled W54 warheads, the smallest nuclear warheads known to have been produced by the United States, used in both the Davy Crockett warhead and the Special Atomic Demolition Munition. In Little Feller II (July 7), the warhead was suspended only three feet above the ground and had a yield equivalent to . In Little Feller I (July 17), the warhead was launched as a Davy Crockett device from a stationary 155 millimeter launcher and set to detonate between above the ground around from the launch point, with a yield of . This test was performed in conjunction with Operation Ivy Flats, a simulated military environment, and was observed by Attorney General Robert F. Kennedy and presidential adviser General Maxwell D. Taylor. Little Feller I was the last near-ground at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert F
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown" and '' berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe it entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including English, German, Dutch, Norwegian, Swedish, Scots, Danish, and Icelandic. It c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |