|
Volodymyr (city)
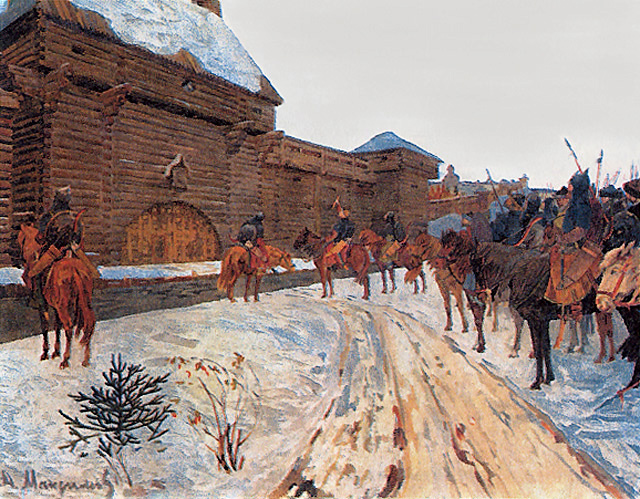
Volodymyr ( uk, Володи́мир, from 1944 to 2021 Volodymyr-Volynskyi ( uk, Володи́мир-Воли́нський)) is a small city located in Volyn Oblast, in north-western Ukraine. It is the administrative centre of the Volodymyr Raion and the center of Volodymyr hromada. The city is the historic centre of the region of Volhynia and the historic capital of the Principality of Volhynia and one of the capital cities of the Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia. It is one of the oldest cities of Ukraine and Kyiv Rus'. Population: The medieval Latin name of the town "Lodomeria" became the namesake of the 19th century Austro-Hungarian Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria, of which the town itself was not a part. south from Volodymyr is Zymne, the oldest Orthodox Monastery in Volynia is located. Name The city was named ''Volodymyr'', after Prince Volodymyr the Great (born in the village of Budiatychi, about 20 km from Volodymyr), and later also abbreviated ''Lodomeria'','' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
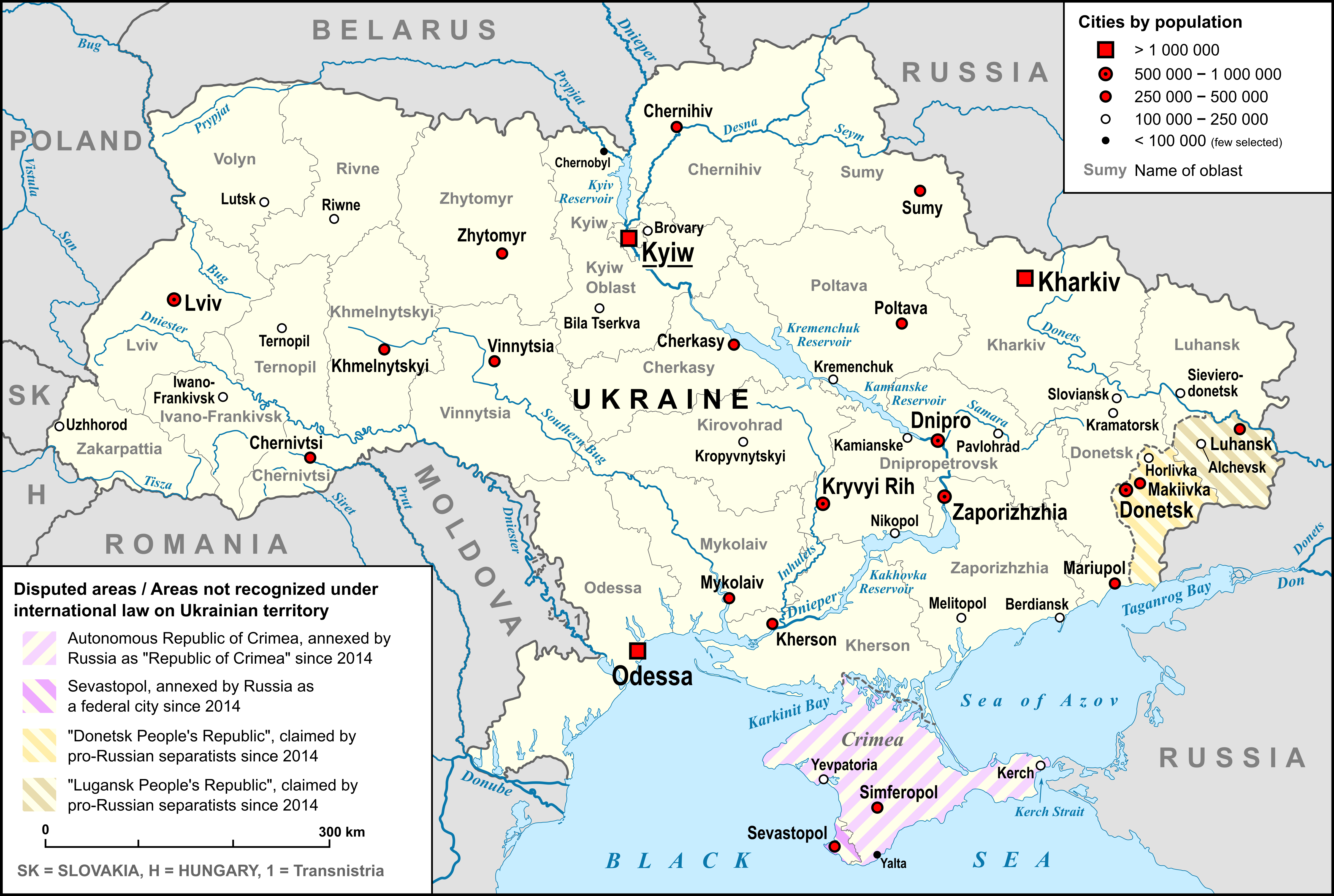
List Of Cities In Ukraine
This is a complete list of cities in Ukraine. On 1 January 2022, there were 461 cities ( uk, місто, ''misto'') in Ukraine. City status is granted by the Verkhovna Rada, the Ukrainian parliament. The city status is only partially related to the size of a populated place in Ukraine. Smaller settlements are urban-type settlements (comparable to towns in English-speaking countries) and villages ( uk, село, ''selo''). Historically, there were systems of city rights, granted by the territorial lords, which defined the status of a place as a ''misto'' or ''selo''. Cities were self-governing and had several privileges. The list of cities is ordered by 2021 estimates of population and compared to the 2001 Ukrainian Census, except for Chernobyl for which population is an unofficial estimate. The cities with special status are shown in ''italic''. Cities in Ukraine Jump to table of cities See also * Geography ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Galicia And Lodomeria
The Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria,, ; pl, Królestwo Galicji i Lodomerii, ; uk, Королівство Галичини та Володимирії, Korolivstvo Halychyny ta Volodymyrii; la, Rēgnum Galiciae et Lodomeriae also known as Austrian Galicia or colloquially Austrian Poland, was a constituent possession of the Habsburg monarchy in the historical region of Galicia in Eastern Europe. The crownland was established in 1772. The lands were annexed from the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth as part of the First Partition of Poland. In 1804 it became a crownland of the newly proclaimed Austrian Empire. From 1867 it was a crownland within the Cisleithanian or Austrian half of the dual monarchy of Austria-Hungary. It maintained a degree of provincial autonomy. Its status remained unchanged until the dissolution of the monarchy in 1918. The domain was initially carved in 1772 from the south-western part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. During the following pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lendians
The Lendians ( pl, Lędzianie) were a Lechitic tribe who lived in the area of East Lesser Poland and Cherven Cities between the 7th and 11th centuries. Since they were documented primarily by foreign authors whose knowledge of Central and East Europe geography was often vague, they were recorded by different names, which include ''Lendzanenoi'', ''Lendzaninoi'', ''Lz’njn'', ''Lachy'', ''Lyakhs'', ''Landzaneh'', ''Lendizi'', ''Licicaviki'' and ''Litziki''. Name The name "Lędzianie" (*lęd-jan-inъ) derives from the Proto-Slavic and Old Polish word "lęda", meaning "field". In modern Polish, the word "ląd" means "land". The Lędzianie tribe's name comes from their use of slash-and-burn agriculture, which involved cutting and burning of forests or woodlands to create fields. Accordingly, in this meaning Lendians were woodland-burning farmers, or "inhabitants of fields". Several European nations source their ethnonym for Poles, and hence Poland, from the name of Lendians: Lit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruthenia
Ruthenia or , uk, Рутенія, translit=Rutenia or uk, Русь, translit=Rus, label=none, pl, Ruś, be, Рутэнія, Русь, russian: Рутения, Русь is an exonym, originally used in Medieval Latin as one of several terms for Kievan Rus', the Kingdom of Galicia-Volhynia and, after their collapse, for East Slavs, East Slavic and Eastern Orthodox regions of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland, corresponding to what is now Ukraine and Belarus. During the early modern period, the term ''Ruthenia'' started to be mostly associated with the Ruthenian Voivodeship, Ruthenian lands of the Polish Crown and the Cossack Hetmanate. Bohdan Khmelnytsky declared himself the ruler of ''the Ruthenian state'' to the Polish representative Adam Kysil in February 1649. Grand Principality of Rus' (1658), Grand Principality of Ruthenia was the project name of the Cossack Hetmanate integrated into the Polish–Lithuanian–Ruthenian Commonwealth. Lands inhabited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruthenian Language
Ruthenian ( Belarusian: руская мова; Ukrainian: руська мова; Ruthenian: руска(ѧ) мова; also see other names) is an exonymic linguonym for a closely-related group of East Slavic linguistic varieties, particularly those spoken from the 15th to 18th centuries in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and in East Slavic regions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Regional distribution of those varieties, both in their literary and vernacular forms, corresponded approximately to the territories of the modern states of Belarus and Ukraine. By the end of the 18th century, they gradually diverged into regional variants, which subsequently developed into the modern Belarusian, Ukrainian, and Rusyn languages. In the Austrian and Austro-Hungarian Empires, the same term (german: ruthenische Sprache, hu, Rutén nyelv) was employed continuously (up to 1918) as an official exonym for the entire East Slavic linguistic body within the borders of the Monarchy. Severa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old East Slavic Language
Old East Slavic (traditionally also Old Russian; be, старажытнаруская мова; russian: древнерусский язык; uk, давньоруська мова) was a language used during the 9th–15th centuries by East Slavs in Kievan Rus' and its successor states, from which the Belarusian, Russian, Rusyn, and Ukrainian languages later evolved. Terminology The name of the language is known as ''Old East Slavic'', in reference to the modern family of East Slavic languages. Its original speakers were the Slavic tribes inhabiting territories of today's Belarus, the western edge of Russia, and western and central Ukraine. However, the term ''Old East Slavic'' is not universally applied. The language is traditionally also known as ''Old Russian'', (; russian: древнерусский язык, translit=drevnerusskij jazyk), however the term has been described as a misnomer, because the initial stages of the language which it denotes predate the dialecta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrayinska Pravda
''Ukrainska Pravda'' ( uk, Українська правда, lit=Ukrainian Truth) is a Ukrainian online newspaper founded by Georgiy Gongadze on 16 April 2000 (the day of the Ukrainian constitutional referendum). Published mainly in Ukrainian with selected articles published in or translated to Russian and English, the newspaper is tailored for a general readership with an emphasis on the politics of Ukraine. In May 2021, owner Olena Prytula sold 100% of the corporate rights of ''Ukrainska Pravda'' to Dragon Capital. The parties agreed that the editorial policy of the publication would remain unchanged. Along with Hromadske and the Center for United Action, ''Ukrainska Pravda'' is part of the Kyiv MediaHub. History In December 2002, ''Ukrainska Pravda'' was refused a press accreditation by the Prosecutor General of Ukraine Svyatoslav Piskun (an offence against the Criminal Code of Ukraine). According to the Ukrainian Helsinki Human Rights Union, after ''Ukrainska Pra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verkhovna Rada
The Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine ( uk, Верхо́вна Ра́да Украї́ни, translit=, Verkhovna Rada Ukrainy, translation=Supreme Council of Ukraine, Ukrainian abbreviation ''ВРУ''), often simply Verkhovna Rada or just Rada, is the Wikt:Unicameralism, unicameral parliament of Ukraine. The Verkhovna Rada is composed of 450 Deputy (legislator), deputies, who are presided over by a Chairman of the Verkhovna Rada, chairman (speaker). The Verkhovna Rada meets in the Verkhovna Rada building in Ukraine's capital Kyiv. The deputies elected in the 21 July 2019 Ukrainian parliamentary election were inaugurated on 29 August 2019. The Verkhovna Rada developed out of the systems of the republican representative body known in the Soviet Union as Supreme Soviet (Supreme Council) that was first established 26 June 1938 as a type of legislature of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, Ukrainian SSR after the dissolution of the All-Ukrainian Congress of Soviets, Congress of Soviet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir-na-Kliazme
Vladimir ( rus, Влади́мир, p=vlɐ'dʲimʲɪr, a=Ru-Владимир.ogg) is a city and the administrative center of Vladimir Oblast, Russia, located on the Klyazma River, east of Moscow. It is served by a railway and the M7 motorway. Population: History Vladimir was one of the medieval capitals of Russia, with significant buildings surviving from the 12th century. Two of its Russian Orthodox cathedrals, a monastery, and associated buildings have been designated as among the White Monuments of Vladimir and Suzdal, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. In the past, the city was also known as Vladimir-on-Klyazma () and Vladimir-Zalessky (), to distinguish it from another Vladimir in Volhynia (modern Ukraine). Foundation The founding date of Vladimir is disputed between 990 and 1108. In the ''Novgorod First Chronicle'', Vladimir is mentioned under the year 1108, and during the Soviet period, this year was decreed to be its foundation year with the view that attributes the foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Russia
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the List of Russian monarchs, Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. The rise of the Russian Empire coincided with the decline of neighbouring rival powers: the Swedish Empire, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Qajar Iran, the Ottoman Empire, and Qing dynasty, Qing China. It also held colonies in North America between 1799 and 1867. Covering an area of approximately , it remains the list of largest empires, third-largest empire in history, surpassed only by the British Empire and the Mongol Empire; it ruled over a population of 125.6 million people per the Russian Empire Census, 1897 Russian census, which was the only census carried out during the entire imperial period. Owing to its geographic extent across three continents at its peak, it featured great ethnic, linguistic, re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partition Of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place toward the end of the 18th century and ended the existence of the state, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland and Lithuania for 123 years. The partitions were conducted by the Habsburg monarchy, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Russian Empire, which divided up the Commonwealth lands among themselves progressively in the process of territorial seizures and annexations. The First Partition was decided on August 5, 1772 after the Bar Confederation lost the war with Russia. The Second Partition occurred in the aftermath of the Polish–Russian War of 1792 and the Targowica Confederation of 1792 when Russian and Prussian troops entered the Commonwealth and the partition treaty was signed during the Grodno Sejm on January 23, 1793 (without Austria). The Third Partition took place on October 24, 1795, in reaction to the unsuccessful Polish Kościuszko Uprising the previo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Budiatychi
Budiatychi ( uk, Будятичі) is a village in the Volodymyr Raion (district) of the Volyn Oblast (province) in western Ukraine near Novovolynsk. History Budiatychi is a possible birthplace of Volodymyr the Great, Grand Prince of Kiev, ruler of Rus'. Notable People Saints * Volodymyr the Great Vladimir I Sviatoslavich or Volodymyr I Sviatoslavych ( orv, Володимѣръ Свѧтославичь, ''Volodiměrъ Svętoslavičь'';, ''Uladzimir'', russian: Владимир, ''Vladimir'', uk, Володимир, ''Volodymyr''. Se ... References Sources * * . — P. 259. External links Budyatychi, google maps {{Volyn-geo-stub Villages in Volodymyr Raion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)