Lendians on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Lendians ( pl, Lędzianie) were a Lechitic tribe who lived in the area of East
The Lendians ( pl, Lędzianie) were a Lechitic tribe who lived in the area of East

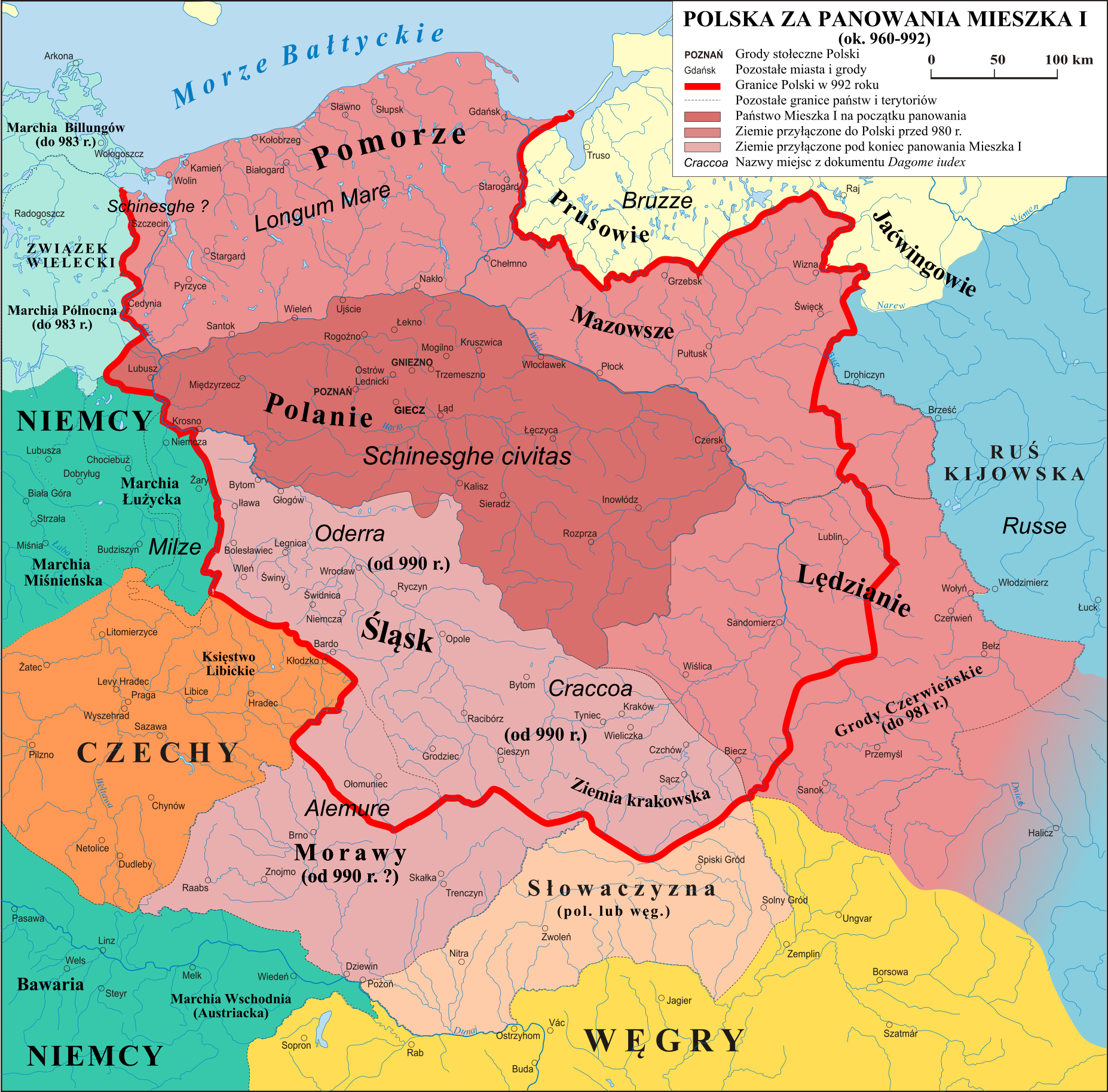 In pre- Slavic times the region was populated by the
In pre- Slavic times the region was populated by the
The Lendians: new variations on ancient motives
, Proc. Inst. Archaeol. Lviv. Univ, Vol. 10, 2015, pages 126–137 The region again fell under the Polish sphere of influence in 1018, when Bolesław I of Poland took the Cherven Cities Kiev Expedition (1018), on his way to Kiev. Yaroslav I the Wise, Yaroslav I the Grand Prince of Rus' reconquered the borderland in 1031. Around the year 1069, the region again returned to Poland, after Bolesław II the Generous retook the area and the city of Przemyśl, making it his temporary residence. Then in 1085, the region became a principality under Rus', and it remained part of Kievan Rus' and its successor state of Halych-Volhynia until 1340 when it was once again taken over by Kingdom of Poland (1320–1385), Kingdom of Poland under Casimir III of Poland. It is presumed that most of the Lendians were assimilated by the East Slavs, with a small portion remaining tied to West Slavs and Poland. The most important factors contributing to their fate were linguistic and ethnic similarity, influence of Kievan Rus' and Orthodox Christianity, deportations to central Ukraine by Yaroslav I the Wise after 1031 and colonization of their lands by Ruthenians fleeing west during Mongol assaults on Ruthenia during reign of Danylo of Halych.
Croats in Manuscripts: Problem of Ethno-tribal Belonging and Political Dependence (Historical Aspects)
, РОЗДІЛ ІІІ. Історіографія. Джерелознавство. Архівознавство. Памʼяткознавство. Етнологія. 7, 2015, pages 141–143, quote: Нарешті стосовно політичного підпорядкування хорватів археолог В. Гупало зазначає, що всередині VII ст. після поразки аварів, які до того тримали у сфері свого впливу слов’янські племена Волині й Прикарпаття, відбуваються кардинальні зміни в житті слов’ян. Зокрема, у VIII–IX ст., починають формуватися територіально-політичні структури на зразок «племінних» княжінь. Прикарпаття, на думку дослідниці, увійшло до складу Хорватського князівства. Вона зауважує, що на території східних хорватів у цей час існували потужні городища, які виконували функції центрів «племінних» княжінь: у Побужжі – Пліснеськ, у Верхньому Подністров’ї – Галич, у Надсянні – Перемишль [4, с. 73–75]. Висловлені вище думки прямо чи опосередковано пов’язуються з проблемою «хорвати чи лендзяни». У світлі новітніх досліджень факт існування племені або союзу племен під назвою «лендзяни» нині вже мало в кого викликає заперечення. Однак щодо території їхнього розселення, то знаний медієвіст Л. Войтович найбільш імовірним ареалом їх проживання вважає Сандомирсько�Люблінську землю [3, с. 26–27]. Janusz Kotlarczyk considered that Red Ruthenia extended over a vast territory between Carpathian Mountains and Przemyśl on the south (inhabited by White Croats) and Volhinia on the north (partly inhabited by Lendians).Kotlarczyk J. ''Siedziby Chorwatów wschodnich''. // Acta Archaeologica Carpathica. T. 12. Krakow, 1971. Pages 161–186. Alexander Nazarenko considers that uncertainty of extant 10th-century descriptions of the upper Dniester and Bug River region makes it plausible to infer that the Lendians, White Croats and probably some other peoples shared this vast territory along the border of modern-day Ukraine and Poland. According to Mykhailo Kuchynko, archaeological sources conclude that Prykarpattian region of Western Ukraine was not settled by West Slavic Lendians but East Slavic Croats, while the elements of material culture in early medieval sites alongside Upper San River in present-day Subcarpathian Voivodeship in Southeastern Poland show they belonged to East Slavic ethno-tribal affiliation. The early medieval sites near Dukla Pass, and villages Trzcinica, Subcarpathian Voivodeship, Trzcinica and Przeczyca indicate that West Slavic material tradition started only at river Wisłoka, the right tributary of Upper Vistula.
 The Lendians ( pl, Lędzianie) were a Lechitic tribe who lived in the area of East
The Lendians ( pl, Lędzianie) were a Lechitic tribe who lived in the area of East Lesser Poland
Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name Małopolska ( la, Polonia Minor), is a historical region situated in southern and south-eastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Kraków. Throughout centuries, Lesser Poland developed a s ...
and Cherven Cities
The Cherven Cities or Cherven Gords ( pl, Grody Czerwieńskie, uk, Червенські городи), often literally translated as Red Cities, Red Forts or Red Boroughs, was a point of dispute between the Kingdom of Poland and Kievan Rus' at th ...
between the 7th and 11th centuries. Since they were documented primarily by foreign authors whose knowledge of Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
and East Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whic ...
geography was often vague, they were recorded by different names, which include ''Lendzanenoi'', ''Lendzaninoi'', ''Lz’njn'', ''Lachy'', ''Lyakhs'', ''Landzaneh'', ''Lendizi'', ''Licicaviki'' and ''Litziki''.
Name
The name "Lędzianie" (*lęd-jan-inъ) derives from the Proto-Slavic andOld Polish
The Old Polish language ( pl, język staropolski, staropolszczyzna) was a period in the history of the Polish language between the 10th and the 16th centuries. It was followed by the Middle Polish language.
The sources for the study of the Old ...
word "lęda", meaning "field". In modern Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
*Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin screenwr ...
, the word "ląd" means "land". The Lędzianie tribe's name comes from their use of slash-and-burn agriculture, which involved cutting and burning of forests or woodlands to create fields. Accordingly, in this meaning Lendians were woodland-burning farmers, or "inhabitants of fields". Several European nations source their ethnonym for Poles, and hence Poland, from the name of Lendians: Lithuanians (''lenkai'', ''Lenkija'') and Hungarians (''Lengyelország'').
Gerard Labuda
Gerard Labuda ( csb, Gerard Labùda; 28 December 1916 – 1 October 2010) was a Polish historian whose main fields of interest were the Middle Ages and the Western Slavs. He was born in Kashubia. He lived and died in Poznań, Poland.
Life
Lab ...
notes that the Rus' originally called a specific tribal group settled around the Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
river as the Lendians and only later in the 11th and 12th century started to apply the name of the tribe to the entire populous of the " Piast realm" because of the their common language.
Sources
In Latin historiography the Bavarian Geographer (generally dated to the mid-9th century) attests that ''Lendizi habent civitates XCVIII'', that is, that the "Lendizi" had 98 gords, or settlements. The Lendians are mentioned, among others, by ''De administrando imperio
''De Administrando Imperio'' ("On the Governance of the Empire") is the Latin title of a Greek-language work written by the 10th-century Eastern Roman Emperor Constantine VII. The Greek title of the work is ("To yown son Romanos"). It is a domes ...
'' (c. 959, as Λενζανηνοί), by Josippon (c. 953, as ''Lz’njn''), by the ''Primary Chronicle
The ''Tale of Bygone Years'' ( orv, Повѣсть времѧньныхъ лѣтъ, translit=Pověstĭ vremęnĭnyxŭ lětŭ; ; ; ; ), often known in English as the ''Rus' Primary Chronicle'', the ''Russian Primary Chronicle'', or simply the ...
'' (c. 981, as ляхи), by Ali al-Masudi
Al-Mas'udi ( ar, أَبُو ٱلْحَسَن عَلِيّ ٱبْن ٱلْحُسَيْن ٱبْن عَلِيّ ٱلْمَسْعُودِيّ, '; –956) was an Arab historian, geographer and traveler. He is sometimes referred to as the "Herodotus ...
(c. 940, as ''Landzaneh'').
They are also identified to the ''Licicaviki'' from the 10th-century chronicle ''Res gestae saxonicae sive annalium libri tres
The ''Deeds of the Saxons, or Three Books of Annals'' ( la, Res gestae Saxonicae sive annalium libri tres) is a three-volume chronicle of 10th century Germany written by Widukind of Corvey. Widukind, proud of his people and history, begins his chr ...
'' by Widukind of Corvey, who recorded that Mieszko I of Poland
Mieszko I (; – 25 May 992) was the first ruler of Poland and the founder of the first independent Polish state, the Duchy of Poland. His reign stretched from 960 to his death and he was a member of the Piast dynasty, a son of Siemomysł and ...
(960–992) ruled over the ''Sclavi'' tribe. The same name is additionally considered to be related to the oral tradition of Michael of Zahumlje from ''DAI'' that his family originates from the unbaptized inhabitants of the river Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
called as ''Litziki'', and the recount by Thomas the Archdeacon
Thomas the Archdeacon ( la, Thomas Archidiaconus; it, Tommaso Arcidiacono; hr, Toma Arhiđakon; c. 1200 – 8 May 1268), also known as Thomas of Spalato ( la, Thomas Spalatensis, hu, Spalatói Tamás), was a Roman Catholic cleric, historian and ...
in his ''Historia Salonitana
''Historia Salonitanorum atque Spalatinorum pontificum'' or the History of the Bishops of Salona and Split ( hr, Povijest biskupa Salone i Splita), commonly known simply as the ''Historia Salonitana'', is a chronicle by Thomas the Archdeacon from t ...
'' (13th century), where seven or eight tribes of nobles, who he called ''Lingones'', arrived from Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
and settled in Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
under Totila's leadership.
History

 In pre- Slavic times the region was populated by the
In pre- Slavic times the region was populated by the Lugii
The Lugii (or ''Lugi'', ''Lygii'', ''Ligii'', ''Lugiones'', ''Lygians'', ''Ligians'', ''Lugians'', or ''Lougoi'') were a large tribal confederation mentioned by Roman authors living in ca. 100 BC–300 AD in Central Europe, north of the Sude ...
and Anarti
The Anartes (or Anarti, Anartii or Anartoi)Jan Czarnecki (1975) 120 were Celtic tribes, or, in the case of those sub-groups of Anartes which penetrated the ancient region of Dacia (roughly modern Romania), Celts culturally assimilated by the Dacian ...
, associated with the Przeworsk and Puchov cultures. They were followed by East Germanic tribes
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and ear ...
, the Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe ...
, and Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic peoples, Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal Kingdom, Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The ...
. After these vacated the territory, the West Slavs (Lendians and Vistulans) moved in. Around 833 the land of the Lendians was incorporated into the Great Moravian state. Upon the invasion of the Magyars, Hungarian tribes into the heart of Central Europe around 899, the Lendians submitted to their authority (Masudi). In the first half of the 10th century, they alongside Krivichs and other Slavic people paid tribute to Igor I of Kiev (DAI).
From the mid-950s onward, the Lendians were politically anchored in the Bohemian sphere of influence. Cosmas of Prague relates that the land of Krakow was controlled by the Přemyslids of Bohemia until 999. His report is buttressed by the foundation charter of the Archdiocese of Prague (1086), which traces the eastern border of the archdiocese, as established in 973, along the Bug (river), Bug and Styr (or Stryi River, Stryi) rivers. Abraham ben Jacob, who travelled in Eastern Europe in 965, remarks that Boleslaus II of Bohemia ruled the country "stretching from the city of Prague to the city of Krakow".
In the 970s, it is assumed that Mieszko I of Poland
Mieszko I (; – 25 May 992) was the first ruler of Poland and the founder of the first independent Polish state, the Duchy of Poland. His reign stretched from 960 to his death and he was a member of the Piast dynasty, a son of Siemomysł and ...
took over the region: the ''Primary Chronicle
The ''Tale of Bygone Years'' ( orv, Повѣсть времѧньныхъ лѣтъ, translit=Pověstĭ vremęnĭnyxŭ lětŭ; ; ; ; ), often known in English as the ''Rus' Primary Chronicle'', the ''Russian Primary Chronicle'', or simply the ...
'' infers this when reporting that Volodymyr the Great conquered the Cherven Cities from the Lyakhs in 981: "Volodymyr marched upon the Lyakhs and took their cities: Peremyshl (Przemyśl), Cherven (Czermno, Lublin Voivodeship, Czermno), and other towns". Historian Leontii Voitovych speculates that if the lands were under control of the Duchy of Poland (c. 960–1025), Duchy of Poland then the Kievan Rus' conquest would have been an open call for war between the principalities with an inevitable long struggle, but such a thing did not happen according to Voitovych, possibly indicating in Voitovych's view that the lands and its population weren't Polish, but an independent political-tribal union with some vassalage to Bohemia.Leontii Voitovych,The Lendians: new variations on ancient motives
, Proc. Inst. Archaeol. Lviv. Univ, Vol. 10, 2015, pages 126–137 The region again fell under the Polish sphere of influence in 1018, when Bolesław I of Poland took the Cherven Cities Kiev Expedition (1018), on his way to Kiev. Yaroslav I the Wise, Yaroslav I the Grand Prince of Rus' reconquered the borderland in 1031. Around the year 1069, the region again returned to Poland, after Bolesław II the Generous retook the area and the city of Przemyśl, making it his temporary residence. Then in 1085, the region became a principality under Rus', and it remained part of Kievan Rus' and its successor state of Halych-Volhynia until 1340 when it was once again taken over by Kingdom of Poland (1320–1385), Kingdom of Poland under Casimir III of Poland. It is presumed that most of the Lendians were assimilated by the East Slavs, with a small portion remaining tied to West Slavs and Poland. The most important factors contributing to their fate were linguistic and ethnic similarity, influence of Kievan Rus' and Orthodox Christianity, deportations to central Ukraine by Yaroslav I the Wise after 1031 and colonization of their lands by Ruthenians fleeing west during Mongol assaults on Ruthenia during reign of Danylo of Halych.
Tribal area
Constantine VII reports that in the year 944 Lendians were tributaries to the Kievan Rus' and that their monoxylae sailed under prince Wlodzislav downstream to Kiev to take part in the Rus'-Byzantine Wars (disambiguation), naval expeditions against Byzantium. This may be taken as an indication that the Lendians had access to some waterways leading to the Dnieper, e.g., the Styr River.Alexander Nazarenko. Древняя Русь на международных путях: Междисциплинарные очерки культурных, торговых, политических связей IX-XII веков. Moscow, 2001. . Pages 401–404. According to Nestor the Chronicler and his account in ''Primary Chronicle
The ''Tale of Bygone Years'' ( orv, Повѣсть времѧньныхъ лѣтъ, translit=Pověstĭ vremęnĭnyxŭ lětŭ; ; ; ; ), often known in English as the ''Rus' Primary Chronicle'', the ''Russian Primary Chronicle'', or simply the ...
'', the Lendians (''Lyakhs'') inhabited the Cherven Cities
The Cherven Cities or Cherven Gords ( pl, Grody Czerwieńskie, uk, Червенські городи), often literally translated as Red Cities, Red Forts or Red Boroughs, was a point of dispute between the Kingdom of Poland and Kievan Rus' at th ...
, when in 981 they were conqured by Vladimir the Great. Based on Constantine's and Nestor's report, Gerard Labuda
Gerard Labuda ( csb, Gerard Labùda; 28 December 1916 – 1 October 2010) was a Polish historian whose main fields of interest were the Middle Ages and the Western Slavs. He was born in Kashubia. He lived and died in Poznań, Poland.
Life
Lab ...
concludes that the Lendians occupied the area between the Upper Bug (river), Bug, Styr, and Upper Dniestr rivers in the east and the Wisłoka river in the west. This would indicate that through their land crossed an important route that connected Prague, Krakow, Kiev and the Khazars.
Polish historians Wojciech Kętrzyński, Stefan Maria Kuczyński, Janusz Kotlarczyk, and Jerzy Nalepa, among others, generally locate the Lendians in Upper San and Upper Dniester. Krzysztof Fokt advanced a viewpoint which claims that Lendians inhabited the whole of Western Ukraine (partly shared by D. E. Alimov), moving White Croats much further to the East in the direction of Vyatichi.
Henryk Łowmiański argued that the Lendians lived between Sandomierz and Lublin, and that with Vistulans even were tribal groups of White Croats. Leontii Voitovych also argues that the Lendians lived east of Vistulans and south of Mazovians, more specifically, in the area between Sandomierz and Lublin.Kuchynko Mykhailo,Croats in Manuscripts: Problem of Ethno-tribal Belonging and Political Dependence (Historical Aspects)
, РОЗДІЛ ІІІ. Історіографія. Джерелознавство. Архівознавство. Памʼяткознавство. Етнологія. 7, 2015, pages 141–143, quote: Нарешті стосовно політичного підпорядкування хорватів археолог В. Гупало зазначає, що всередині VII ст. після поразки аварів, які до того тримали у сфері свого впливу слов’янські племена Волині й Прикарпаття, відбуваються кардинальні зміни в житті слов’ян. Зокрема, у VIII–IX ст., починають формуватися територіально-політичні структури на зразок «племінних» княжінь. Прикарпаття, на думку дослідниці, увійшло до складу Хорватського князівства. Вона зауважує, що на території східних хорватів у цей час існували потужні городища, які виконували функції центрів «племінних» княжінь: у Побужжі – Пліснеськ, у Верхньому Подністров’ї – Галич, у Надсянні – Перемишль [4, с. 73–75]. Висловлені вище думки прямо чи опосередковано пов’язуються з проблемою «хорвати чи лендзяни». У світлі новітніх досліджень факт існування племені або союзу племен під назвою «лендзяни» нині вже мало в кого викликає заперечення. Однак щодо території їхнього розселення, то знаний медієвіст Л. Войтович найбільш імовірним ареалом їх проживання вважає Сандомирсько�Люблінську землю [3, с. 26–27]. Janusz Kotlarczyk considered that Red Ruthenia extended over a vast territory between Carpathian Mountains and Przemyśl on the south (inhabited by White Croats) and Volhinia on the north (partly inhabited by Lendians).Kotlarczyk J. ''Siedziby Chorwatów wschodnich''. // Acta Archaeologica Carpathica. T. 12. Krakow, 1971. Pages 161–186. Alexander Nazarenko considers that uncertainty of extant 10th-century descriptions of the upper Dniester and Bug River region makes it plausible to infer that the Lendians, White Croats and probably some other peoples shared this vast territory along the border of modern-day Ukraine and Poland. According to Mykhailo Kuchynko, archaeological sources conclude that Prykarpattian region of Western Ukraine was not settled by West Slavic Lendians but East Slavic Croats, while the elements of material culture in early medieval sites alongside Upper San River in present-day Subcarpathian Voivodeship in Southeastern Poland show they belonged to East Slavic ethno-tribal affiliation. The early medieval sites near Dukla Pass, and villages Trzcinica, Subcarpathian Voivodeship, Trzcinica and Przeczyca indicate that West Slavic material tradition started only at river Wisłoka, the right tributary of Upper Vistula.
See also
*List of Medieval Slavic tribesReferences
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ledzianie Early medieval Poland Lechites History of Kievan Rus' History of Galicia (Eastern Europe) West Slavic tribes History of Lesser Poland History of Red Ruthenia