|
Volcanism Of Eastern Canada
The volcanology of Eastern Canada includes the hundreds of volcanic areas and extensive lava formations in Eastern Canada. The region's different volcano and lava types originate from different tectonic settings and types of volcanic eruptions, ranging from passive lava eruptions to violent explosive eruptions. Eastern Canada has very large volumes of magmatic rock called large igneous provinces. They are represented by deep-level plumbing systems consisting of giant dike swarms, sill provinces and layered intrusions. The most capable large igneous provinces in Eastern Canada are Archean (3,800-2,500 million years ago) age greenstone belts containing a rare volcanic rock called komatiite. Greenstone belts Abitibi greenstone belt The 2,677 million year old Abitibi greenstone belt in Ontario and Quebec is one of the largest Archean greenstone belts on Earth and one of the youngest parts of the Superior craton which sequentially forms part of the Canadian Shield. Komatii ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcano
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and most are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, deep in the Earth. This results in hotspot volcanism, of which the Hawaiian hotspot is an example. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Craton
The Superior Craton is a stable crustal block covering Quebec, Ontario, and southeast Manitoba in Canada, and northern Minnesota in the United States. It is the biggest craton among those formed during the Archean period. A craton is a large part of the Earth's crust that has been stable and subjected to very little geological changes over a long time. The size of Superior Craton is about 1,572,000 km2. The craton underwent a series of events from 4.3 to 2.57 Ga. These events included the growth, drifting and deformation of both oceanic and continental crusts. Researchers have divided the Superior Craton into many different domains based on rock types and deformation styles. These domains (grouped into western and eastern superior provinces), include the North Superior Superterrane and Wawa Terrane, among others (shown in the table below). Studies on the formation of the Superior Craton varied in progress between the western and the eastern part. For the western part, five ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nunavut
Nunavut ( , ; iu, ᓄᓇᕗᑦ , ; ) is the largest and northernmost Provinces and territories of Canada#Territories, territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the ''Nunavut Act'' and the ''Nunavut Land Claims Agreement, Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act'', which provided this territory to the Inuit for independent government. The boundaries had been drawn in 1993. The creation of Nunavut resulted in the territorial evolution of Canada, first major change to Canada's political map in half a century since the province of Newfoundland and Labrador, Newfoundland was admitted in 1949. Nunavut comprises a major portion of Northern Canada and most of the Arctic Archipelago. Its vast territory makes it the list of the largest country subdivisions by area, fifth-largest country subdivision in the world, as well as North America's second-largest (after Greenland). The capital Iqaluit (formerly Frobisher Bay), on Baffin Islan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belcher Islands
The Belcher Islands ( iu, script=latn, ᓴᓪᓚᔪᒐᐃᑦ, Sanikiluaq) are an archipelago in the southeast part of Hudson Bay near the centre of the Nastapoka arc. The Belcher Islands are spread out over almost . Administratively, they belong to the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. The hamlet of Sanikiluaq (where the majority of the archipelago's inhabitants live) is on the north coast of Flaherty Island and is the southernmost in Nunavut. Along with Flaherty Island, the other large islands are Kugong Island, Tukarak Island, and Innetalling Island. Other main islands in the 1,500–island archipelago are Moore Island, Wiegand Island, Split Island, Snape Island and Mavor Island, while island groups include the Sleeper Islands, King George Islands, and Bakers Dozen Islands. History The archaeological evidence present on the islands indicates that they were inhabited by the Dorset culture between 500 BCE and 1000 CE. Centuries later, from 1200 to 1500, the Thule pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labrador
, nickname = "The Big Land" , etymology = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Canada , subdivision_type1 = Province , subdivision_name1 = Newfoundland and Labrador , subdivision_type2 = , subdivision_name2 = , subdivision_type3 = , subdivision_name3 = , subdivision_type4 = , subdivision_name4 = , image_map = File:Labrador-Region.PNG , map_caption = Labrador (red) within Canada , pushpin_map = , pushpin_relief = , pushpin_map_caption = , coordinates = , coordinates_footnotes = , established_title = Founded , established_date = 1763 , area_footnotes = , area_total_km2 = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
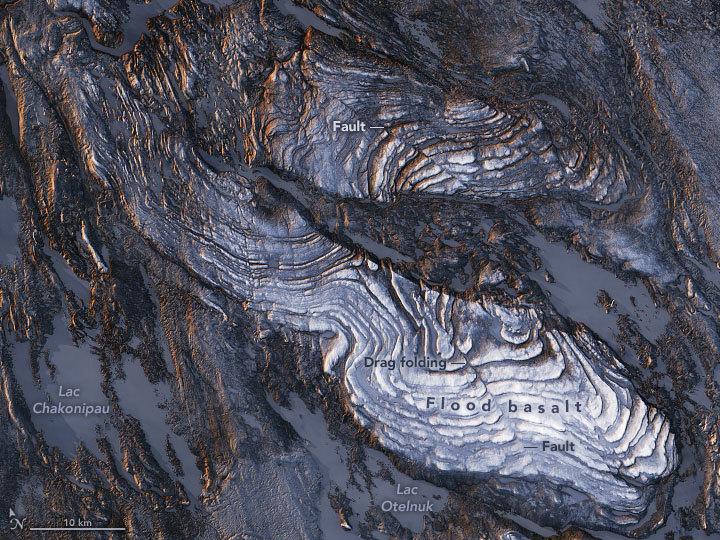
Labrador Trough
The Labrador Trough or the New Quebec Orogen is a long and wide geologic belt in Canada, extending south-southeast from Ungava Bay through Quebec and Labrador. The trough is a linear belt of sedimentary and volcanic rocks which developed in an Early Proterozoic rift basin. To the west is the Archean Superior Craton. To the east are the rocks of the Archean Rae Craton. The sedimentary rocks and volcanics of the Labrador Trough were intensely deformed and subjected to high grade metamorphism along with the Churchill terrain during the Trans-Hudson orogeny. It is a northeast extension of the Circum-Superior Belt and is terminated to the south by the Grenville Front Tectonic Zone. Radiometric dates of 1883-1870 Ma are reported for mafic, ultramafic, carbonatite and lamprophyre intrusions within the Trough. It is a large iron ore belt developed on banded iron formations and has had mining operations since 1954. At least two large magmatic events occurred in the Labrador Trough ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circum-Superior Belt
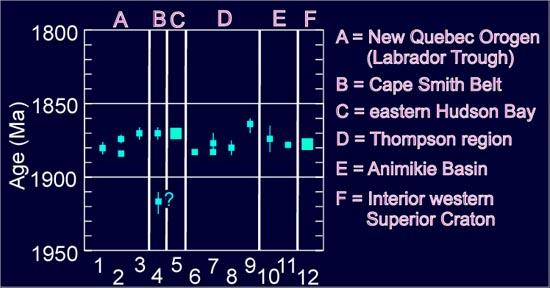
The Circum-Superior Belt is a widespread Paleoproterozoic large igneous province in the Canadian Shield of Northern, Western and Eastern Canada. It extends more than from northeastern Manitoba through northwestern Ontario, southern Nunavut to northern Quebec and into western Labrador. Igneous rocks of the Circum-Superior Belt are mafic-ultramafic in composition, deposited in the Labrador Trough near Ungava Bay, the Cape Smith Belt near the southern shore of Hudson Strait and along the eastern shore of Hudson Bay in its northern portion; the Thompson and Fox River belts in the northwest and the Marquette Range Supergroup in its southern portion. The Circum Superior Belt also hosts a rare example of Proterozoic Komatiite, in the Winnipegosis komatiite belt. A number of magmatic features are present in the Circum-Superior Belt, including dikes, sills and volcanics that comprise geologic formations. This geologic belt is considered to be a large igneous province because its m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uchi Subprovince
The Uchi Subprovince is a Neoarchean volcanic sequence in Manitoba, Canada. It is at the southern margin of the North Caribou terrane and comprises a number of greenstone belts, which contains volcanic rocks that record some 280 million years of volcanism. See also *Volcanism of Canada *Volcanism of Western Canada Volcanism of Western Canada has produced lava flows, lava plateaus, lava domes, cinder cones, stratovolcanoes, shield volcanoes, greenstone belts, submarine volcanoes, calderas, diatremes and maars, along with examples of more less common volcanic ... References Volcanism of Manitoba Greenstone belts Neoarchean volcanism {{Manitoba-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwestern Ontario
Northwestern Ontario is a secondary region of Northern Ontario in the Canadian province of Ontario which lies north and west of Lake Superior and west of Hudson Bay and James Bay. It includes most of subarctic Ontario. Its western boundary is the Canadian province of Manitoba, which disputed Ontario's claim to the western part of the region. Ontario's right to Northwestern Ontario was determined by the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council in 1884ONTARIO-MANITOBA BOUNDARY CASE and confirmed by the Canada (Ontario Boundary) Act, 1889, of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. In 1912, the Parliament of Canada by the ''Ontario Boundaries Extension Act'' gave jurisdiction over the District of Patricia to Ontario, thereby extending the northern boundary of the province to Hudson Bay. For some purposes, Northwestern Ontario and Northeastern Ontario are treated as separate regions, while for other purposes they are grouped together as Northern Ontario. Geographic subdivisions Northwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Lake Greenstone Belt
The Red Lake greenstone belt is an Archean greenstone belt at the town of Red Lake in Northwestern Ontario, Canada. It consists of basaltic and komatiitic volcanics ranging in age from 2,925 to 2,940 million years old and younger rhyolite-andesite volcanics ranging in age from 2,730 to 2,750 million years old. See also * |
The Distribution Of Ancient Volcanic Rocks Along The Eastern Border Of North America
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with pronouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of pronoun ''thee'') when followed by a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
.png)