|
Vladimir Braginsky
Vladimir Borisovich Braginsky (3 August 1931 – 29 March 2016) was a Russian experimental and theoretical physicist and a corresponding member of the Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS), and foreign member of the US National Academy of Sciences. He worked in the areas of precision and quantum measurements, the detection of gravitational waves, systems with low dissipation, and fundamental thermodynamic fluctuations. Biography Braginsky was born in Moscow and graduated from the Physics Department of Moscow State University in 1954, where he had been working since 1955. In 1959, he defended his thesis, and in 1967 his doctoral thesis. In 1969, he was appointed a professor. Scientific career In the 1970s, Braginsky headed the Physics Department of Moscow State University. In the 1987 to 2001 period, he headed the department of "Molecular Physics and Physical Measurements". From 2001 to 2002, he was the head of the department of "Physics of oscillations." Braginsky is the author ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million residents within the city limits, over 17 million residents in the urban area, and over 21.5 million residents in the metropolitan area. The city covers an area of , while the urban area covers , and the metropolitan area covers over . Moscow is among the world's largest cities; being the most populous city entirely in Europe, the largest urban and metropolitan area in Europe, and the largest city by land area on the European continent. First documented in 1147, Moscow grew to become a prosperous and powerful city that served as the capital of the Grand Duchy that bears its name. When the Grand Duchy of Moscow evolved into the Tsardom of Russia, Moscow remained the political and economic center for most of the Tsardom's history. When th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ponderomotive Force
In physics, a ponderomotive force is a nonlinear force that a charged particle experiences in an inhomogeneous oscillating electromagnetic field. It causes the particle to move towards the area of the weaker field strength, rather than oscillating around an initial point as happens in a homogeneous field. This occurs because the particle sees a greater magnitude of force during the half of the oscillation period while it is in the area with the stronger field. The net force during its period in the weaker area in the second half of the oscillation does not offset the net force of the first half, and so over a complete cycle this makes the particle move towards the area of lesser force. The ponderomotive force Fp is expressed by :\mathbf_= -\frac \nabla (E^2) which has units of newtons (in SI units) and where ''e'' is the electrical charge of the particle, ''m'' is its mass, ''ω'' is the angular frequency of oscillation of the field, and ''E'' is the amplitude of the electric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Physicists
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into Causality, cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs when a particular factor is manipulated. Experiments vary greatly in goal and scale but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results. There also exist natural experiment, natural experimental studies. A child may carry out basic experiments to understand how things fall to the ground, while teams of scientists may take years of systematic investigation to advance their understanding of a phenomenon. Experiments and other types of hands-on activities are very important to student learning in the science classroom. Experiments can raise test scores and help a student become more engaged and interested in the material they are learning, especially when used over time. Experiments can vary from personal and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Staff Of Moscow State University
An academy ( Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary or tertiary higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membership). The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 385 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and skill, north of Athens, Greece. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, '' Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philosopher Plato conversed with followers. Plato developed his sessions into a method of teaching philosophy and in 387 BC, established what is known today as the Old Academy. By extension, ''academia'' has come to mean the accumulatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow State University Alumni
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million residents within the city limits, over 17 million residents in the urban area, and over 21.5 million residents in the metropolitan area. The city covers an area of , while the urban area covers , and the metropolitan area covers over . Moscow is among the world's largest cities; being the most populous city entirely in Europe, the largest urban and metropolitan area in Europe, and the largest city by land area on the European continent. First documented in 1147, Moscow grew to become a prosperous and powerful city that served as the capital of the Grand Duchy that bears its name. When the Grand Duchy of Moscow evolved into the Tsardom of Russia, Moscow remained the political and economic center for most of the Tsardom's history. When th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Physicists
This list of Russian physicists includes the famous physicists from the Russian Empire, the Soviet Union and the Russian Federation. Alphabetical list __NOTOC__ A * Alexei Abrikosov, discovered how magnetic flux can penetrate a superconductor (the Abrikosov vortex), Nobel Prize winner *Franz Aepinus, related electricity and magnetism, proved the electric nature of pyroelectricity, explained electric polarization and electrostatic induction, invented achromatic microscope *Zhores Alferov, inventor of modern heterotransistor, Nobel Prize winner *Sergey Alekseenko, director of the Kutateladze Institute of Thermophysics, Global Energy Prize recipient *Artem Alikhanian, a prominent researcher of cosmic rays, inventor of wide-gap track spark chamber *Abram Alikhanov, nuclear physicist, a prominent researcher of cosmic rays, built the first nuclear reactors in the USSR, founder of Institute for Theoretical and Experimental Physics (ITEP) *Semen Altshuler, researched EPR and NMR, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2016 Deaths
This is a list of deaths of notable people, organised by year. New deaths articles are added to their respective month (e.g., Deaths in ) and then linked here. 2022 2021 2020 2019 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2004 2003 2002 2001 2000 1999 1998 1997 1996 1995 1994 1993 1992 1991 1990 1989 1988 1987 See also * Lists of deaths by day The following pages, corresponding to the Gregorian calendar, list the historical events, births, deaths, and holidays and observances of the specified day of the year: Footnotes See also * Leap year * List of calendars * List of non-standard ... * Deaths by year {{DEFAULTSORT:deaths by year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1931 Births
Events January * January 2 – South Dakota native Ernest Lawrence invents the cyclotron, used to accelerate particles to study nuclear physics. * January 4 – German pilot Elly Beinhorn begins her flight to Africa. * January 22 – Sir Isaac Isaacs is sworn in as the first Australian-born Governor-General of Australia. * January 25 – Mohandas Gandhi is again released from imprisonment in India. * January 27 – Pierre Laval forms a government in France. February * February 4 – Soviet leader Joseph Stalin gives a speech calling for rapid industrialization, arguing that only strong industrialized countries will win wars, while "weak" nations are "beaten". Stalin states: "We are fifty or a hundred years behind the advanced countries. We must make good this distance in ten years. Either we do it, or they will crush us." The first five-year plan in the Soviet Union is intensified, for the industrialization and collectivization of agriculture. * February 10 � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
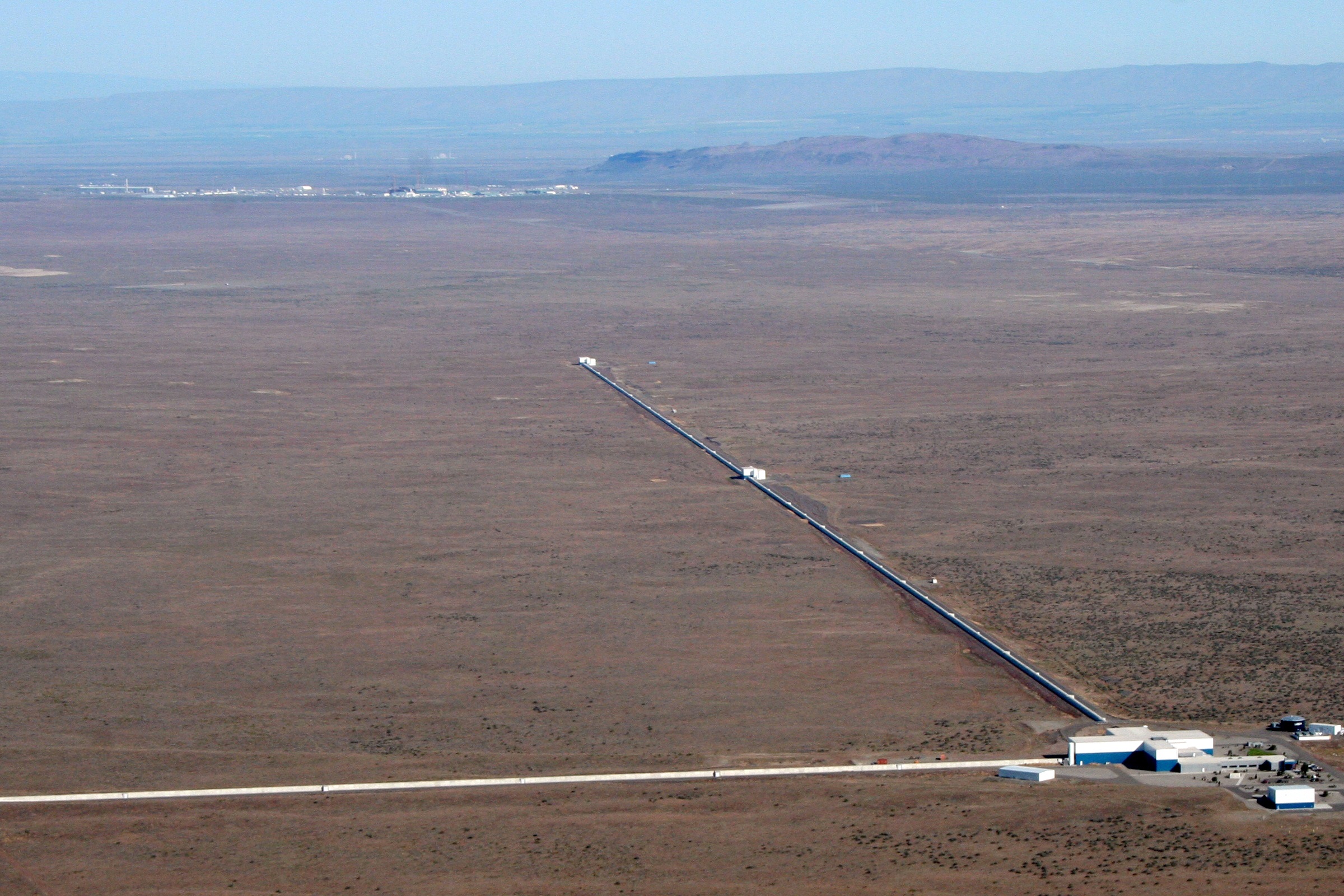
LIGO
The Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) is a large-scale physics experiment and observatory designed to detect cosmic gravitational waves and to develop gravitational-wave observations as an astronomical tool. Two large observatories were built in the United States with the aim of detecting gravitational waves by laser interferometry. These observatories use mirrors spaced four kilometers apart which are capable of detecting a change of less than one ten-thousandth the charge diameter of a proton. (that is, to Proxima Centauri at ). The initial LIGO observatories were funded by the United States National Science Foundation (NSF) and were conceived, built and are operated by Caltech and MIT. They collected data from 2002 to 2010 but no gravitational waves were detected. The Advanced LIGO Project to enhance the original LIGO detectors began in 2008 and continues to be supported by the NSF, with important contributions from the United Kingdom's Science ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational Wave
Gravitational waves are waves of the intensity of gravity generated by the accelerated masses of an orbital binary system that propagate as waves outward from their source at the speed of light. They were first proposed by Oliver Heaviside in 1893 and then later by Henri Poincaré in 1905 as waves similar to electromagnetic waves but the gravitational equivalent. Gravitational waves were later predicted in 1916 by Albert Einstein on the basis of his general theory of relativity as ripples in spacetime. Later he refused to accept gravitational waves. Gravitational waves transport energy as gravitational radiation, a form of radiant energy similar to electromagnetic radiation. Newton's law of universal gravitation, part of classical mechanics, does not provide for their existence, since that law is predicated on the assumption that physical interactions propagate instantaneously (at infinite speed)showing one of the ways the methods of Newtonian physics are unable to explain ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science (journal)
''Science'', also widely referred to as ''Science Magazine'', is the peer-reviewed academic journal of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) and one of the world's top academic journals. It was first published in 1880, is currently circulated weekly and has a subscriber base of around 130,000. Because institutional subscriptions and online access serve a larger audience, its estimated readership is over 400,000 people. ''Science'' is based in Washington, D.C., United States, with a second office in Cambridge, UK. Contents The major focus of the journal is publishing important original scientific research and research reviews, but ''Science'' also publishes science-related news, opinions on science policy and other matters of interest to scientists and others who are concerned with the wide implications of science and technology. Unlike most scientific journals, which focus on a specific field, ''Science'' and its rival ''Nature (journal), Nature'' c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Academy Of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the National Academy of Medicine (NAM). As a national academy, new members of the organization are elected annually by current members, based on their distinguished and continuing achievements in original research. Election to the National Academy is one of the highest honors in the scientific field. Members of the National Academy of Sciences serve '' pro bono'' as "advisers to the nation" on science, engineering, and medicine. The group holds a congressional charter under Title 36 of the United States Code. Founded in 1863 as a result of an Act of Congress that was approved by Abraham Lincoln, the NAS is charged with "providing independent, objective advice to the nation on matters related to science and technology. ... to provide scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |