|
Violin Concerto (Sessions)
Roger Sessions' Violin Concerto was composed between 1927 and 1935, and is scored for violin and orchestra (without violins). History The violin concerto was begun, at the suggestion of Serge Koussevitzky, in the summer of 1927—although the composer later postdated the beginning of this work to his years at the American Academy in Rome in 1928 and 1929,—and was completed in 1935. It was originally meant to have been premiered by the Boston Symphony Orchestra during their 1932–33 season, with Richard Burgin as soloist, but Sessions did not finish the finale—originally to have been the third movement—in time. Ultimately deciding on a four-movement form, Sessions delivered the violin part to Burgin in the fall of 1934, while still orchestrating the last movement, and Koussevitzky agreed to program the concerto during the first half of the 1935–36 season. When Sessions expressed a preference for a better-known violinist, Burgin graciously stepped aside and Joseph Szigeti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roger Sessions
Roger Huntington Sessions (December 28, 1896March 16, 1985) was an American composer, teacher and musicologist. He had initially started his career writing in a neoclassical style, but gradually moved further towards more complex harmonies and postromanticism, and finally the twelve-tone serialism of the Second Viennese School. Sessions' friendship with Arnold Schoenberg influenced this, but he would modify the technique to develop a unique style involving rows to supply melodic thematic material, while composing the subsidiary parts in a free and dissonant manner. Life Sessions was born in Brooklyn, New York, to a family that could trace its roots back to the American Revolution. His mother, Ruth Huntington Sessions, was a direct descendant of Samuel Huntington, a signatory of the Declaration of Independence. Roger studied music at Harvard University from the age of 14. There he wrote for and subsequently edited the ''Harvard Musical Review''. Graduating at age 18, he went on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tossy Spivakovsky
Nathan "Tossy" Spivakovsky ( – July 20, 1998), a Jewish, Russian Empire-born, German-trained violin virtuoso, was considered one of the greatest violinists of the 20th century. Biography Tossy Spivakovsky was born in Odessa, which in 1906 was still part of the Russian Empire. Under the increasing threat of pogroms his family moved to Berlin, where he studied with Arrigo Serato privately and later with Willy Hess at the Berliner Hochschule für Musik. A violin prodigy, he gave his first recital at age 10. Together with his elder brother Jacob "Jascha" (1896–1970), a renowned concert pianist, Tossy made his first European concert tour at age 13, performing as soloist with orchestras in a number of countries including Holland, England, Norway, Sweden, and Denmark, in 1919, where the brothers played for Danish royalty. At only 18, after being talent spotted by Wilhelm Furtwängler, Spivakovsky became the youngest concertmaster hired by the Berlin Philharmonic. Two years later h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
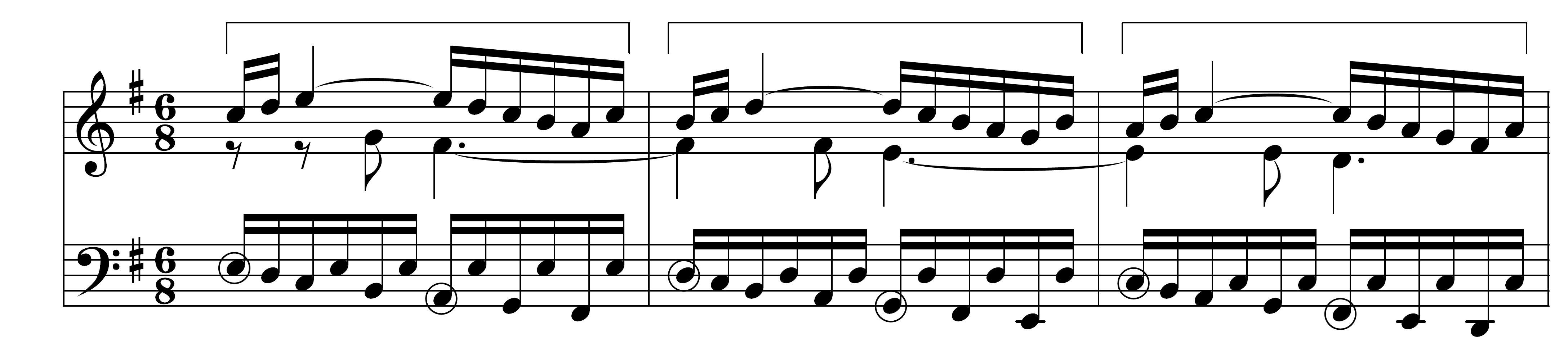
Tuplet
In music, a tuplet (also irrational rhythm or groupings, artificial division or groupings, abnormal divisions, irregular rhythm, gruppetto, extra-metric groupings, or, rarely, contrametric rhythm) is "any rhythm that involves dividing the beat into a different number of equal subdivisions from that usually permitted by the time-signature (e.g., triplets, duplets, etc.)" This is indicated by a number, or sometimes two indicating the fraction involved. The notes involved are also often grouped with a bracket or (in older notation) a slur. The most common type of tuplet is the triplet. Terminology The modern term 'tuplet' comes from a rebracketing of compound words like quintu(s)-(u)plet and sextu(s)-(u)plet, and from related mathematical terms such as "tuple", "-uplet" and "-plet", which are used to form terms denoting multiplets (''Oxford English Dictionary'', entries "multiplet", "-plet, ''comb. form''", "-let, ''suffix''", and "-et, ''suffix''1"). An alternative modern term, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridge (music)
In music, especially Western popular music, a bridge is a contrasting section that prepares for the return of the original material section. In a piece in which the original material or melody is referred to as the "A" section, the bridge may be the third eight-bar phrase in a thirty-two-bar form (the B in AABA), or may be used more loosely in verse-chorus form, or, in a compound AABA form, used as a contrast to a full AABA section. The bridge is often used to contrast with and prepare for the return of the verse and the chorus. "The b section of the popular song chorus is often called the ''bridge'' or ''release''." Etymology The term comes from a German word for bridge, ''Steg'', used by the Meistersingers of the 15th to the 18th century to describe a transitional section in medieval bar form. The German term became widely known in 1920s Germany through musicologist Alfred Lorenz and his exhaustive studies of Richard Wagner's adaptations of bar form in his popular 19th-cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirty-second Note
In music, a thirty-second note (American) or demisemiquaver (British) is a Musical note, note played for of the duration of a whole note (or ''semibreve''). It lasts half as long as a sixteenth note (or ''semiquaver'') and twice as long as a sixty-fourth note, sixty-fourth (or ''hemidemisemiquaver''). Thirty-second notes are notated with an oval, filled-in note head and a straight note stem with three flags or beam (music), beams. A single thirty-second note is always stemmed with flags, while two or more are usually beamed in groups.Gerou, Tom (1996). ''Essential Dictionary of Music Notation'', p.211. Alfred. As with all notes with stems, thirty-second notes are drawn with stems to the right of the notehead, extending up, when they are below the middle line of the musical staff. When they are on or above the middle line, they are drawn with stems on the left of the note head, extending down. Flags are always on the right side of the stem, and curve to the right. On stems e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metric Modulation
In music, metric modulation is a change in pulse rate (tempo) and/or pulse grouping (subdivision) which is derived from a note value or grouping heard before the change. Examples of metric modulation may include changes in time signature across an unchanging tempo, but the concept applies more specifically to shifts from one time signature/tempo (metre) to another, wherein a note value from the first is made equivalent to a note value in the second, like a pivot or bridge. The term "modulation" invokes the analogous and more familiar term in analyses of tonal harmony, wherein a pitch or pitch interval serves as a bridge between two keys. In both terms, the pivoting value functions differently before and after the change, but sounds the same, and acts as an audible common element between them. Metric modulation was first described by Richard Franko Goldman while reviewing the Cello Sonata of Elliott Carter, who prefers to call it tempo modulation. Another synonymous term is proporti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadenza
In music, a cadenza (from it, cadenza, link=no , meaning cadence; plural, ''cadenze'' ) is, generically, an improvisation, improvised or written-out ornament (music), ornamental passage (music), passage played or sung by a solo (music), soloist or soloists, usually in a "free" rhythmic style, and often allowing virtuoso, virtuosic display. During this time the accompaniment will rest, or sustain a note or chord. Thus an improvised cadenza is indicated in written notation by a fermata in all parts. A cadenza will usually occur over the final or penultimate note in a piece, the lead-in (german: Eingang, link=no) or over the final or penultimate note in an important subsection of a piece. It can also be found before a final coda (music), coda or ritornello. In concerti The term ''cadenza'' often refers to a portion of a concerto in which the orchestra stops playing, leaving the soloist to play alone in free time (music), free time (without a strict, regular pulse) and can be wr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B Minor
B minor is a minor scale based on B, consisting of the pitches B, C, D, E, F, G, and A. Its key signature has two sharps. Its relative major is D major and its parallel major is B major. The B natural minor scale is: : Changes needed for the melodic and harmonic versions of the scale are written in with accidentals as necessary. The B harmonic minor and melodic minor scales are: : : Christian Friedrich Daniel Schubart (1739–1791) regarded B minor as a key expressing a quiet acceptance of fate and very gentle complaint, something commentators find to be in line with Bach's use of the key in his ''St John Passion''. By the end of the Baroque era, however, conventional academic views of B minor had shifted: Composer-theorist Francesco Galeazzi (1758–1819) opined that B minor was not suitable for music in good taste. Beethoven labelled a B-minor melodic idea in one of his sketchbooks as a "black key". Notable compositions in B minor * Johann Sebastian Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motif (music)
In music, a motif IPA: ( /moʊˈtiːf/) (also motive) is a short musical phrase, a salient recurring figure, musical fragment or succession of notes that has some special importance in or is characteristic of a composition: "The motive is the smallest structural unit possessing thematic identity". The ''Encyclopédie de la Pléiade'' regards it as a "melodic, rhythmic, or harmonic cell", whereas the 1958 ''Encyclopédie Fasquelle'' maintains that it may contain one or more cells, though it remains the smallest analyzable element or phrase within a subject. It is commonly regarded as the shortest subdivision of a theme or phrase that still maintains its identity as a musical idea. "The smallest structural unit possessing thematic identity". Grove and Larousse also agree that the motif may have harmonic, melodic and/or rhythmic aspects, Grove adding that it "is most often thought of in melodic terms, and it is this aspect of the motif that is connoted by the term 'fig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Zukofsky
Paul Zukofsky (October 22, 1943 – June 6, 2017) was an American violinist and conductor known for his work in the field of contemporary classical music. Career Born in Brooklyn, New York, Paul Zukofsky was the only child of the American objectivist poet Louis Zukofsky and Celia Thaew Zukofsky, a musician and composer. Both parents were children of Yiddish-speaking immigrants from what was then the eastern Russian Empire (now Belarus). Revealing a precocious talent, he began taking music lessons at age three, soon concentrated on the violin, and at seven became a student of Ivan Galamian at the Juilliard School of Music. He made his first orchestral appearance in 1952 with the New Haven Symphony Orchestra, and a formal debut recital at Carnegie Hall in 1956.Slonimsky, Nicolas, ed. (2001). "Zukofsky, Paul", ''Baker's Biographical Dictionary of Musicians'' (9th edn.). New York: Schirmer Books. Vol. 6, p. 4044. . ''The New York Times'' praised his technique, noting he had gone through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoclassicism (music)
Neoclassicism in music was a twentieth-century trend, particularly current in the interwar period, in which composers sought to return to aesthetic precepts associated with the broadly defined concept of "classicism", namely order, balance, clarity, economy, and emotional restraint. As such, neoclassicism was a reaction against the unrestrained emotionalism and perceived formlessness of late Romanticism, as well as a "call to order" after the experimental ferment of the first two decades of the twentieth century. The neoclassical impulse found its expression in such features as the use of pared-down performing forces, an emphasis on rhythm and on contrapuntal texture, an updated or expanded tonal harmony, and a concentration on absolute music as opposed to Romantic program music. In form and thematic technique, neoclassical music often drew inspiration from music of the 18th century, though the inspiring canon belonged as frequently to the Baroque and even earlier periods as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ole Bøhn
Ole Bøhn (born 15 September 1945) is a Norwegian violinist. He was born in Oslo. He is regarded among Norway's leading violinists, and has toured in a large number of countries, in Europe, Asia and America. His repertoire includes both classical compositions and contemporary music. Among his recordings is the first performance of Elliott Carter's Violin Concerto, which won the 1994 Grammy Award for Best Classical Contemporary Composition. Among composers who have dedicated their works to Bøhn are Elliott Carter, Johan Kvandal, Niels Viggo Bentzon and Noël Lee Noël Lee (December 25, 1924 – July 15, 2013) was an American classical pianist and composer. Born in 1924 in Nanjing, China, Lee studied music in Lafayette, Indiana, then attended Harvard University, studying with Walter Piston, Irving Fine, .... Ole Bøhn was concertmaster of the Norwegian Opera from 1978 to 2012 and is professor at Sydney Conservatorium of Music since 2009. He is awarded King Harald's medal of me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |