|
Video Gaming In The United Kingdom
The United Kingdom has the largest video game sector in Europe. It has the second largest video game market in Europe after Germany and the sixth largest globally. The UK video game market was worth () in 2021, a 2% increase over the previous year. Many major video game franchises are developed in the UK, including '' Grand Theft Auto'', ''Tomb Raider'', ''Burnout'', ''LittleBigPlanet'', '' Wipeout'' and '' Dirt'', making Britain the third largest producer of video game series behind Japan and the United States. The best-selling video game series made in the UK is '' Grand Theft Auto'' (primary developed by Rockstar North in Edinburgh, Scotland), which has sold over 150 million copies as of September 2013; the most recent instalment '' Grand Theft Auto V'' became the fastest-selling video game of all time by making $815.7 million (£511.8 million) in sales worldwide during the first 24 hours of the game's sale. Another major British contribution to the game industry was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of England (which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guinness World Records
''Guinness World Records'', known from its inception in 1955 until 1999 as ''The Guinness Book of Records'' and in previous United States editions as ''The Guinness Book of World Records'', is a reference book published annually, listing world records both of human achievements and the extremes of the natural world. The brainchild of Sir Hugh Beaver, the book was co-founded by twin brothers Norris McWhirter, Norris and Ross McWhirter in Fleet Street, London, in August 1955. The first edition topped the best-seller list in the United Kingdom by Christmas 1955. The following year the book was launched internationally, and as of the 2022 edition, it is now in its 67th year of publication, published in 100 countries and 23 languages, and maintains over 53,000 records in its database. The international Franchising, franchise has extended beyond print to include television series and museums. The popularity of the franchise has resulted in ''Guinness World Records'' becoming the prim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alan Turing
Alan Mathison Turing (; 23 June 1912 – 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher, and theoretical biologist. Turing was highly influential in the development of theoretical computer science, providing a formalisation of the concepts of algorithm and computation with the Turing machine, which can be considered a model of a general-purpose computer. He is widely considered to be the father of theoretical computer science and artificial intelligence. Born in Maida Vale, London, Turing was raised in southern England. He graduated at King's College, Cambridge, with a degree in mathematics. Whilst he was a fellow at Cambridge, he published a proof demonstrating that some purely mathematical yes–no questions can never be answered by computation and defined a Turing machine, and went on to prove that the halting problem for Turing machines is undecidable. In 1938, he obtained his PhD from the Department ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
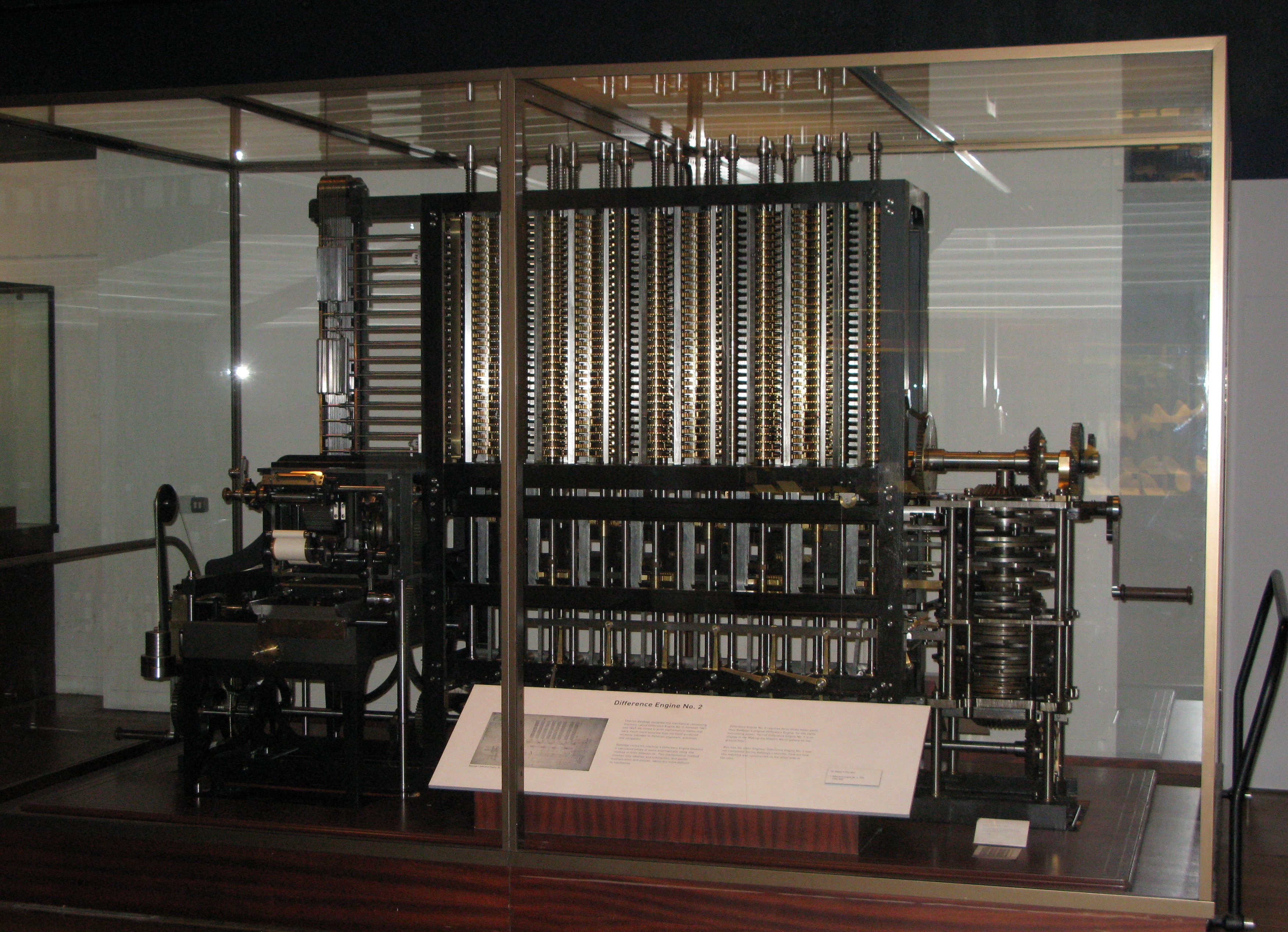
Difference Engine
A difference engine is an automatic mechanical calculator designed to tabulate polynomial functions. It was designed in the 1820s, and was first created by Charles Babbage. The name, the difference engine, is derived from the method of divided differences, a way to interpolate or tabulate functions by using a small set of polynomial co-efficients. Some of the most common mathematical functions used in engineering, science and navigation, were, and still are computable with the use of the difference engine's capability of computing logarithmic and trigonometric functions, which can be approximated by polynomials, so a difference engine can compute many useful tables of numbers. History The notion of a mechanical calculator for mathematical functions can be traced back to the Antikythera mechanism of the 2nd century BC, while early modern examples are attributed to Pascal and Leibniz in the 17th century. In 1784 J. H. Müller, an engineer in the Hessian army, devised a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ada Lovelace
Augusta Ada King, Countess of Lovelace (''née'' Byron; 10 December 1815 – 27 November 1852) was an English mathematician and writer, chiefly known for her work on Charles Babbage's proposed mechanical general-purpose computer, the Analytical Engine. She was the first to recognise that the machine had applications beyond pure calculation, and to have published the first algorithm intended to be carried out by such a machine. As a result, she is often regarded as the first computer programmer. Ada Byron was the only legitimate child of poet Lord Byron and Lady Byron. All of Byron's other children were born out of wedlock to other women. Byron separated from his wife a month after Ada was born and left England forever. Four months later, he commemorated the parting in a poem that begins, "Is thy face like thy mother's my fair child! ADA! sole daughter of my house and heart?" He died in Greece when Ada was eight. Her mother remained bitter and promoted Ada's interest in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Babbage
Charles Babbage (; 26 December 1791 – 18 October 1871) was an English polymath. A mathematician, philosopher, inventor and mechanical engineer, Babbage originated the concept of a digital programmable computer. Babbage is considered by some to be " father of the computer". Babbage is credited with inventing the first mechanical computer, the Difference Engine, that eventually led to more complex electronic designs, though all the essential ideas of modern computers are to be found in Babbage's Analytical Engine, programmed using a principle openly borrowed from the Jacquard loom. Babbage had a broad range of interests in addition to his work on computers covered in his book ''Economy of Manufactures and Machinery''. His varied work in other fields has led him to be described as "pre-eminent" among the many polymaths of his century. Babbage, who died before the complete successful engineering of many of his designs, including his Difference Engine and Analytical En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boolean Algebra
In mathematics and mathematical logic, Boolean algebra is a branch of algebra. It differs from elementary algebra in two ways. First, the values of the variables are the truth values ''true'' and ''false'', usually denoted 1 and 0, whereas in elementary algebra the values of the variables are numbers. Second, Boolean algebra uses logical operators such as conjunction (''and'') denoted as ∧, disjunction (''or'') denoted as ∨, and the negation (''not'') denoted as ¬. Elementary algebra, on the other hand, uses arithmetic operators such as addition, multiplication, subtraction and division. So Boolean algebra is a formal way of describing logical operations, in the same way that elementary algebra describes numerical operations. Boolean algebra was introduced by George Boole in his first book ''The Mathematical Analysis of Logic'' (1847), and set forth more fully in his '' An Investigation of the Laws of Thought'' (1854). According to Huntington, the term "Boolean alg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Boole
George Boole (; 2 November 1815 – 8 December 1864) was a largely self-taught English mathematician, philosopher, and logician, most of whose short career was spent as the first professor of mathematics at Queen's College, Cork in Ireland. He worked in the fields of differential equations and algebraic logic, and is best known as the author of '' The Laws of Thought'' (1854) which contains Boolean algebra. Boolean logic is credited with laying the foundations for the Information Age. Early life Boole was born in 1815 in Lincoln, Lincolnshire, England, the son of John Boole senior (1779–1848), a shoemaker and Mary Ann Joyce. He had a primary school education, and received lessons from his father, but due to a serious decline in business, he had little further formal and academic teaching. William Brooke, a bookseller in Lincoln, may have helped him with Latin, which he may also have learned at the school of Thomas Bainbridge. He was self-taught in modern langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Computing
The history of computing is longer than the history of computing hardware and modern computing technology and includes the history of methods intended for pen and paper or for chalk and slate, with or without the aid of tables. Concrete devices Digital computing is intimately tied to the representation of numbers. But long before abstractions like ''the number'' arose, there were mathematical concepts to serve the purposes of civilization. These concepts are implicit in concrete practices such as: *''One-to-one correspondence'', a rule to count ''how many'' items, e.g. on a tally stick, eventually abstracted into ''numbers''. *''Comparison to a standard'', a method for assuming ''reproducibility'' in a measurement, for example, the number of coins. *The ''3-4-5'' right triangle was a device for assuring a ''right angle'', using ropes with 12 evenly spaced knots, for example. Numbers Eventually, the concept of numbers became concrete and familiar enough for counting to arise, at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strachey Draughts Ferranti
Strachey is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: Strachey family of Sutton Court, Somerset *John Strachey (d. 1674), friend of John Locke ** John Strachey (geologist) (1671–1743), British geologist ***Henry Strachey of Sutton Court, Somerset **** Sir Henry Strachey, 1st Baronet (1737–1810), British politician and civil servant; son of Henry Strachey and grandson of the geologist John Strachey. He had at least two sons: *****Sir Henry Strachey, 2nd Baronet (1772–1858), eldest son of the 1st baronet *****Edward Strachey (1774–1832), second son of the 1st baronet; he was in the service of the East India Company. He had at least five sons, including: ******Sir Edward Strachey, 3rd Baronet (1812–1901), eldest son of Edward Strachey (1774–1832) and nephew of the second baronet. He had three sons: *******Edward Strachey, 1st Baron Strachie (1858–1936), Liberal politician; eldest son of the third baronet ********Edward Strachey, 2nd Baron Strachie (1882–197 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department For Culture, Media And Sport
, type = Department , logo = Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport logo.svg , logo_width = , logo_caption = , seal = , seal_width = , seal_caption = , picture = Government Offices Great George Street.jpg , picture_width = 200px , picture_caption = 100 Parliament Street – partly occupied by DCMS on the windowless fourth floor , formed = , preceding1 = Department for National Heritage , dissolved = , superseding = , jurisdiction = Government of the United Kingdom , headquarters = 100 Parliament Street,London SW1A 2BQ,England , employees = 3,020 , budget = £1.4 billion (current) & £1.3 billion (capital) for 2011–12 , minister1_name = Rt Hon Michelle Donelan MP , minister1_pfo = Secretary of State for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport , minister2_name = Matt Warman MP , minister2_pfo = Minister of State for Media, Data, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Association For UK Interactive Entertainment
The Association for UK Interactive Entertainment (Ukie) is a non-profit trade association for the video game industry in the United Kingdom (UK). Ukie was originally founded as the European Leisure Software Publishers Association (ELSPA), and then later Entertainment and Leisure Software Publishers Association (ELSPA), before changing to Ukie in 2010. History The association was founded in 1989, though then named as the European Leisure Software Publishers Association (ELSPA). Around 2002, the organisation changed its name to Entertainment and Leisure Software Publishers Association, reflecting that their primary concerns were video game development on the United Kingdom islands and not mainland Europe. In March 2010, members of the ELSPA voted to rename the association as Ukie, reflecting "the evolving and expanding nature of the industry, which the association exists to represent, and to encompass the new areas of activity that will be undertaken". The name was fully changed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


_School_-_Charles_Babbage_(1792–1871)_-_814168_-_National_Trust.jpg)
