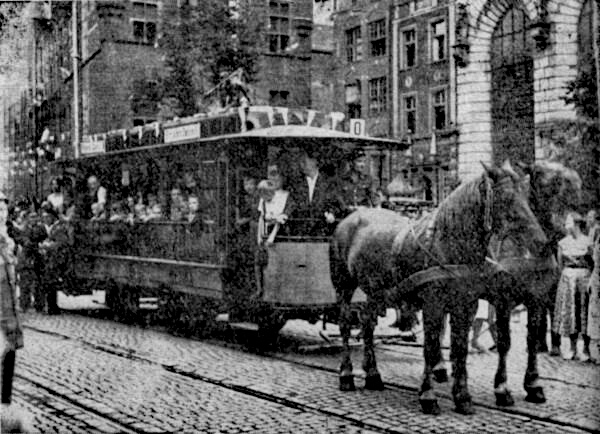|
Victorian Farm
''Victorian Farm'' is a British historical documentary TV series in six parts, first shown on BBC Two in January 2009, and followed by three Christmas-themed parts in December of the same year. The series, the second in the BBC historic farm series, recreates everyday life on a farm in Shropshire in the 1880s, using authentic replica equipment and clothing, original recipes and reconstructed building techniques. It was made for the BBC by independent production company Lion Television and filmed at a preserved Victorian era living museum farm, Acton Scott Historic Working Farm, Shropshire. The farming team was historian Ruth Goodman, and archaeologists Alex Langlands and Peter Ginn. Much use was made of period sources such as ''The Book of the Farm: Detailing the Labours of the Farmer, Farm-steward, Ploughman, Shepherd, Hedger, Cattle-man, Field-worker, and Dairy-maid'' by Dr Henry Stephens, first published in London in 1844. The series was one of BBC Two's biggest hits of 200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Upshal
David Upshal is a British television producer. His work includes ''Victorian Farm'', ''Victorian Pharmacy'', ''Edwardian Farm'', ''Wartime Farm'', ''Tales from the Green Valley'', ''Tudor Monastery Farm'', ''The True Face of War'', '' Days That Shook The World'', ''Outbreak Investigation'', ''Tony Benn: Free at Last'', ''Gordon Brown's Missing Billions'', ''Summer of Noise'', ''The Gospel of Gospel'', '' Pilgrimage with Simon Reeve'', ''On Tour with the Queen'', ''Lulu: Something to Shout About'', ''Secrets of the Castle'', ''The Hunt for the Arctic Ghost Ship'' and the historical skills game show ''Escape in Time'', for which he is also credited as format devisor. He previously directed the Channel 4 series ''The Hip Hop Years'' (short-listed for a BAFTA) and the landmark BBC series '' Windrush'' (winner of the 1999 Royal Television Society Award for Best Documentary Series). He began his television career at the BBC where his credits included ''The Late Show'', ''Reportage'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tudor Monastery Farm
''Tudor Monastery Farm'' is a British factual television series, first broadcast on BBC Two on 13 November 2013. The series, the fifth in the historic farm series, following the original, Tales from the Green Valley, stars archaeologists Peter Ginn and Tom Pinfold, and historian Ruth Goodman. The team discover what farming was like during the Tudor period at the Weald and Downland Open Air Museum. The program also recurringly features other historians, such as Colin Richards (an expert on rural crafts), and Professor Ronald Hutton (who specializes in folklore and religious beliefs). Production On 8 August 2013, the BBC announced the series. David Upshal, the executive producer of Lion Television, said: "We are delighted to be continuing with a new Farm series for BBC Two, taking us back to the earliest point in history we have tackled yet. Following the huge success of the Victorian, Edwardian and Wartime Farms, the new series will see us produce our 50th episode in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cider
Cider ( ) is an alcoholic beverage made from the fermented juice of apples. Cider is widely available in the United Kingdom (particularly in the West Country) and the Republic of Ireland. The UK has the world's highest per capita consumption, as well as the largest cider-producing companies. Ciders from the South West of England are generally higher in alcoholic content. Cider is also popular in many Commonwealth countries, such as India, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand. As well as the UK and its former colonies, cider is popular in Portugal (mainly in Minho and Madeira), France (particularly Normandy and Brittany), Friuli, and northern Spain (specifically Asturias). Central Europe also has its own types of cider with Rhineland-Palatinate and Hesse producing a particularly tart version known as Apfelwein. In the U.S., varieties of fermented cider are often called ''hard cider'' to distinguish alcoholic cider from non-alcoholic apple cider or "sweet cider", also made from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse-drawn Vehicle
A horse-drawn vehicle is a mechanized piece of equipment pulled by one horse or by a team of horses. These vehicles typically had two or four wheels and were used to carry passengers and/or a load. They were once common worldwide, but they have mostly been replaced by automobiles and other forms of self-propelled transport. General Horses were domesticated circa 3500 BCE. Prior to that oxen were used. Historically a wide variety of arrangements of horses and vehicles have been used, from chariot racing, which involved a small vehicle and four horses abreast, to horsecars or trollies, which used two horses to pull a car that was used in cities before electric trams were developed. A two-wheeled horse-drawn vehicle is a cart (see various types below, both for carrying people and for goods). Four-wheeled vehicles have many names – one for heavy loads is most commonly called a wagon. Very light carts and wagons can also be pulled by donkeys (much smaller than horses), pony, po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
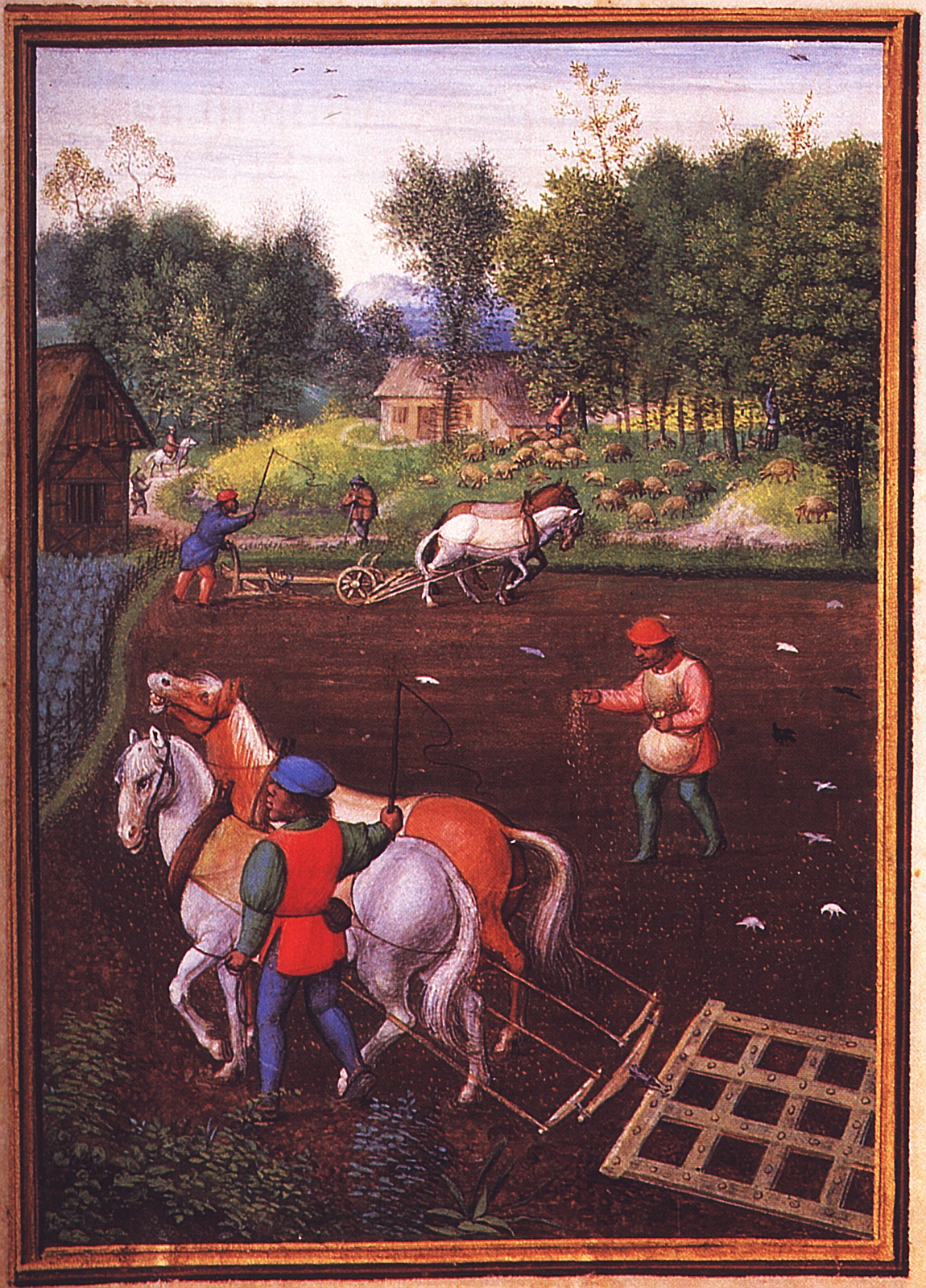
Sown
Sowing is the process of planting seeds. An area or object that has had seeds planted in it will be described as a sowed or sown area. Plants which are usually sown Among the major field crops, oats, wheat, and rye are sown, grasses and legumes are seeded and maize and soybeans are planted. In planting, wider rows (generally 75 cm (30 in) or more) are used, and the intent is to have precise; even spacing between individual seeds in the row, various mechanisms have been devised to count out individual seeds at exact intervals. Depth of sowing In sowing, little if any soil is placed over the seeds, as seeds can be generally sown into the soil by maintaining a planting depth of about 2-3 times the size of the seed. Sowing types and patterns For hand sowing, several sowing types exist; these include: * Flat sowing * Ridge sowing * Wide bed sowing Several patterns for sowing may be used together with these types; these include: * Regular rows * Rows that are ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harrowed
In agriculture, a harrow is a farm implement used for surface tillage. It is used after ploughing for breaking up and smoothing out the surface of the soil. The purpose of harrowing is to break up clods and to provide a soil structure, called tilth, that is suitable for planting seeds. Coarser harrowing may also be used to remove weeds and to cover seed after sowing. Harrows differ from ploughs, which cut the upper 12 to 25 centimetre (5 to 10 in) layer of soil, and leave furrows, parallel trenches. Harrows differ from cultivators in that they disturb the whole surface of the soil, while a cultivator instead disturbs only narrow tracks between the crop rows to kill weeds. There are four general types of harrows: disc harrows, tine harrows (including spring-tooth harrows, drag harrows, and spike harrows), chain harrows, and chain-disk harrows. Harrows were originally drawn by draft animals, such as horses, mules, or oxen, or in some times and places by manual labourers. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plough
A plough or plow ( US; both ) is a farm tool for loosening or turning the soil before sowing seed or planting. Ploughs were traditionally drawn by oxen and horses, but in modern farms are drawn by tractors. A plough may have a wooden, iron or steel frame, with a blade attached to cut and loosen the soil. It has been fundamental to farming for most of history. The earliest ploughs had no wheels; such a plough was known to the Romans as an ''aratrum''. Celtic peoples first came to use wheeled ploughs in the Roman era. The prime purpose of ploughing is to turn over the uppermost soil, bringing fresh nutrients to the surface while burying weeds and crop remains to decay. Trenches cut by the plough are called furrows. In modern use, a ploughed field is normally left to dry and then harrowed before planting. Ploughing and cultivating soil evens the content of the upper layer of soil, where most plant-feeder roots grow. Ploughs were initially powered by humans, but the use of farm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Threshing
Threshing, or thrashing, is the process of loosening the edible part of grain (or other crop) from the straw to which it is attached. It is the step in grain preparation after reaping. Threshing does not remove the bran from the grain. History of threshing Through much of the history of agriculture, threshing was time-consuming and usually laborious, with a bushel of wheat taking about an hour. In the late 18th century, before threshing was mechanized, about one-quarter of agricultural labor was devoted to it. It is likely that in the earliest days of agriculture the little grain that was raised was shelled by hand, but as the quantity increased the grain was probably beaten out with a stick, or the sheaf beaten upon the ground. An improvement on this, as the quantity further increased, was the practice of the ancient Egyptians of spreading out the loosened sheaves on a circular enclosure of hard ground, and driving oxen, sheep or other animals round and round over it so as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lime Plaster
Lime plaster is a type of plaster composed of sand, water, and lime, usually non-hydraulic hydrated lime (also known as slaked lime, high calcium lime or air lime). Ancient lime plaster often contained horse hair for reinforcement and pozzolan additives to reduce the working time. Traditional non-hydraulic hydrated lime only sets through carbonatation when the plaster is kept moist and access of CO2 from the air is possible. It will not set when submersed in water. When a very thick layer or several layers are applied, the lime can remain soft for weeks. The curing time of lime plaster can be shortened by using (natural) hydraulic lime or adding pozzolan additives, transforming it into artificially hydraulic lime. In ancient times, Roman lime plaster incorporated pozzolanic volcanic ash; in modern times, fly ash is preferred. Non-hydraulic lime plaster can also be made to set faster by adding gypsum. Lime production for use in plastering home-made cisterns (in making them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
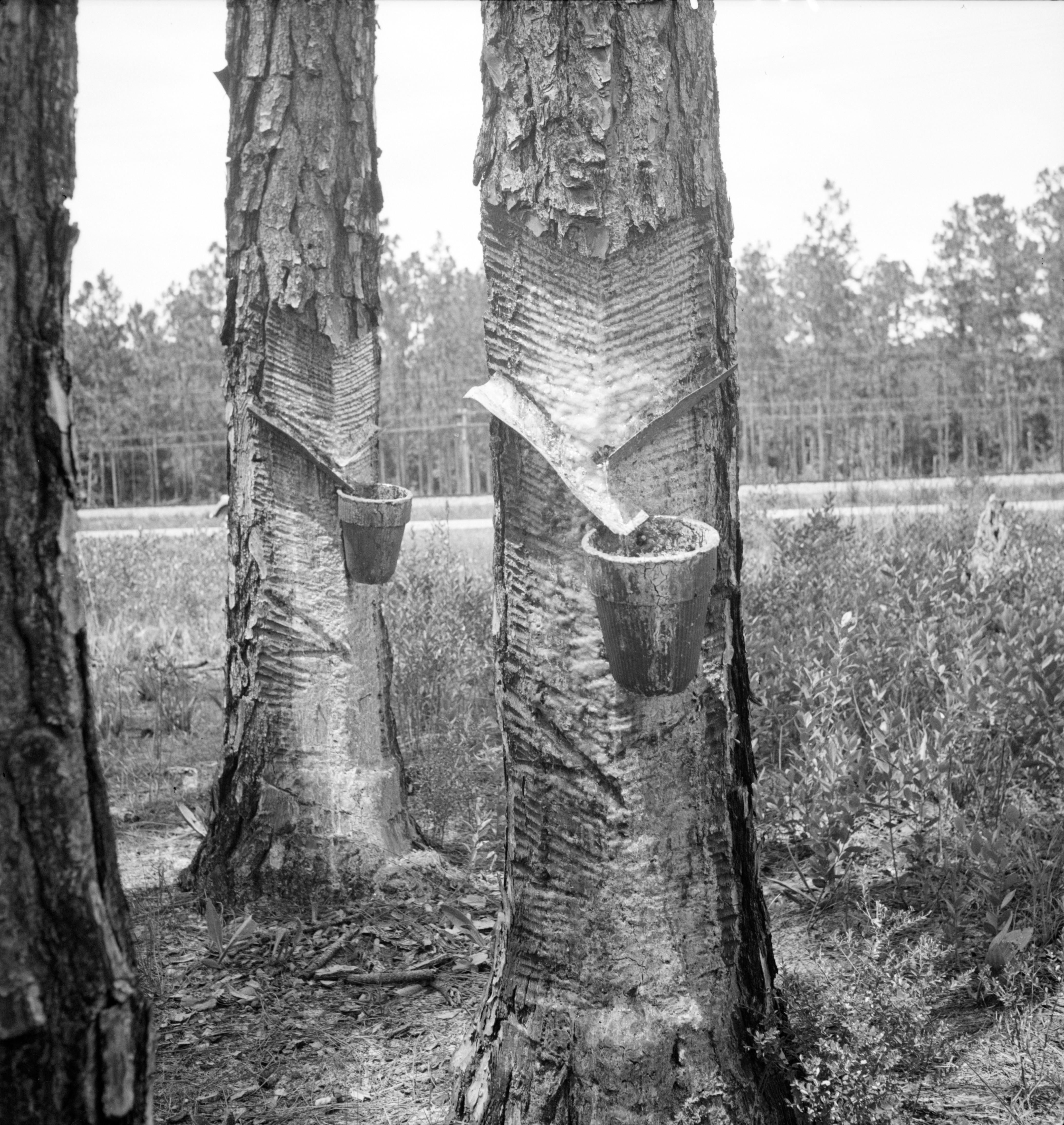
Turpentine
Turpentine (which is also called spirit of turpentine, oil of turpentine, terebenthene, terebinthine and (colloquially) turps) is a fluid obtained by the distillation of resin harvested from living trees, mainly pines. Mainly used as a specialized solvent, it is also a source of material for organic syntheses. Turpentine is composed of terpenes, primarily the monoterpenes alpha- and beta-pinene, with lesser amounts of carene, camphene, dipentene, and terpinolene.Kent, James A. ''Riegel's Handbook of Industrial Chemistry'' (Eighth Edition) Van Nostrand Reinhold Company (1983) p.569 Mineral turpentine or other petroleum distillates are used to replace turpentine – although the constituent chemicals are very different. Etymology The word ''turpentine'' derives (via French and Latin), from the Greek word τερεβινθίνη ''terebinthine'', in turn the feminine form (to conform to the feminine gender of the Greek word, which means "resin") of an adjective (τερεβί ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bed Bug (insect)
''Cimex'' is a genus of insects in the family Cimicidae. ''Cimex'' species are ectoparasites that typically feed on the blood of birds and mammals. Two species, ''Cimex lectularius'' and ''Cimex hemipterus'', are known as bed bugs and frequently feed on humans, although other species may parasitize humans opportunistically. Species that primarily parasitize bats are known as bat bugs. The insects are long and have flattened reddish-brown bodies with small nonfunctional wings. Description Adult ''Cimex'' are light brown to reddish-brown, flat and oval. The mouthparts are beak-like, and adapted for piercing and sucking. Following a blood meal the abdomen is plump and darker in colour. The front wings are vestigial and reduced to pad-like structures and there are no hind wings. ''Cimex'' have segmented abdomens with microscopic hairs that give them a banded appearance. Adults grow to long. The different species are very similar in morphology and can only be separated by micr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface flow under atmospheric pressure, and can be thought of as artificial rivers. In most cases, a canal has a series of dams and locks that create reservoirs of low speed current flow. These reservoirs are referred to as ''slack water levels'', often just called ''levels''. A canal can be called a ''navigation canal'' when it parallels a natural river and shares part of the latter's discharges and drainage basin, and leverages its resources by building dams and locks to increase and lengthen its stretches of slack water levels while staying in its valley. A canal can cut across a drainage divide atop a ridge, generally requiring an external water source above the highest elevation. The best-known example of such a canal is the Panama Canal. Many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |