|
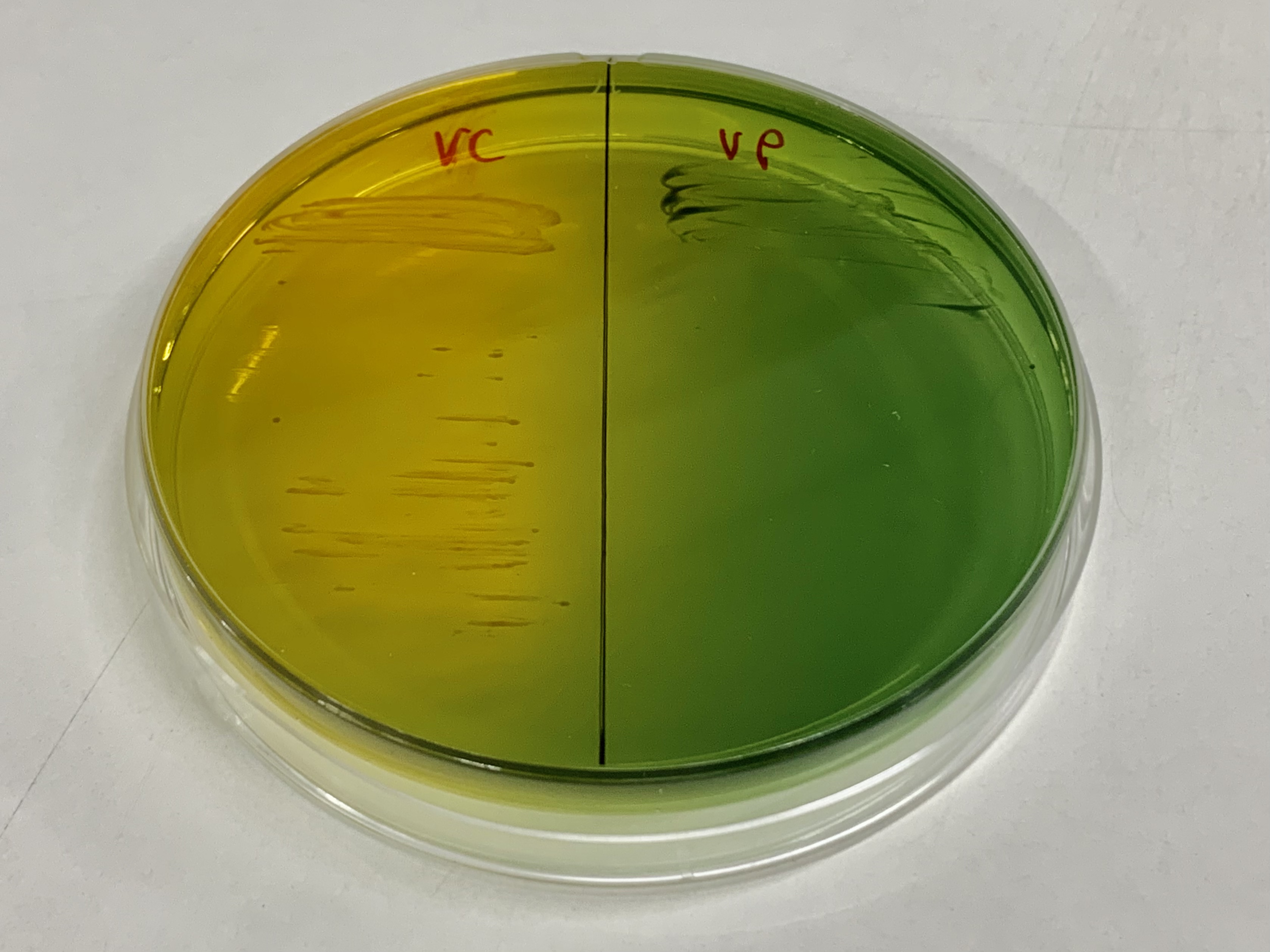
Vibrio Fluvialis
''Vibrio fluvialis'' is a water-borne bacterium first isolated from patients with severe diarrhoea in Bahrain in the 1970s by A. L. Furniss and his colleagues, and is considered to be an emerging pathogen with the potential to have a significant impact on public health. Upon discovery, this organism was considered to be similar to both ''Vibrio'' and ''Aeromonas'' species, but was ultimately determined to be more closely related to ''Vibrio''. ''V. fluvialis'' can be found in salt waters globally and also has the potential to infect both humans and a variety of crustacean Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group ...s. References Further reading * * * External linksType strain of ''Vibrio fluvialis'' at Bac''Dive'' - the Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase Vibrion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterium
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diarrhoea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin with loss of the normal stretchiness of the skin and irritable behaviour. This can progress to decreased urination, loss of skin color, a fast heart rate, and a decrease in responsiveness as it becomes more severe. Loose but non-watery stools in babies who are exclusively breastfed, however, are normal. The most common cause is an infection of the intestines due to either a virus, bacterium, or parasite—a condition also known as gastroenteritis. These infections are often acquired from food or water that has been contaminated by feces, or directly from another person who is infected. The three types of diarrhea are: short duration watery diarrhea, short duration bloody diarrhea, and persistent diarrhea (lasting more than two weeks, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahrain
Bahrain ( ; ; ar, البحرين, al-Bahrayn, locally ), officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, ' is an island country in Western Asia. It is situated on the Persian Gulf, and comprises a small archipelago made up of 50 natural islands and an additional 33 artificial islands, centered on Bahrain Island which makes up around 83 percent of the country's landmass. Bahrain is situated between Qatar and the northeastern coast of Saudi Arabia, to which it is connected by the King Fahd Causeway. According to the 2020 census, the country's population numbers 1,501,635, of which 712,362 are Bahraini nationals. Bahrain spans some , and is the third-smallest nation in Asia after the Maldives and Singapore. The capital and largest city is Manama. Bahrain is the site of the ancient Dilmun civilization.Oman: The Lost Land [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals". Analyzing the determinants of health of a population and the threats it faces is the basis for public health. The ''public'' can be as small as a handful of people or as large as a village or an entire city; in the case of a pandemic it may encompass several continents. The concept of ''health'' takes into account physical, psychological, and social well-being.What is the WHO definition of health? from the Preamble to the Constitution of WHO as adopted by the International Health Conference, New York, 19 June - 22 July 1946; signed on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibrio
''Vibrio'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria, possessing a curved-rod (comma) shape, several species of which can cause foodborne infection, usually associated with eating undercooked seafood. Being highly salt tolerant and unable to survive in fresh water, ''Vibrio'' spp. are commonly found in various salt water environments. ''Vibrio'' spp. are facultative anaerobes that test positive for oxidase and do not form spores. All members of the genus are motile. They are able to have polar or lateral flagellum with or without sheaths. ''Vibrio'' species typically possess two chromosomes, which is unusual for bacteria. Each chromosome has a distinct and independent origin of replication, and are conserved together over time in the genus. Recent phylogenies have been constructed based on a suite of genes (multilocus sequence analysis). O. F. Müller (1773, 1786) described eight species of the genus ''Vibrio'' (included in Infusoria), three of which were spirilliforms. Some of the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeromonas
''Aeromonas'' is a genus of Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria that morphologically resemble members of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Most of the 14 described species have been associated with human diseases. The most important pathogens are '' A. hydrophila'', '' A. caviae'', and '' A. veronii'' biovar ''sobria''. The organisms are ubiquitous in fresh and brackish water. They group with the gamma subclass of the Proteobacteria. Two major diseases associated with ''Aeromonas'' are gastroenteritis and wound infections, with or without bacteremia. Gastroenteritis typically occurs after the ingestion of contaminated water or food, whereas wound infections result from exposure to contaminated water. In its most severe form, ''Aeromonas'' spp. can cause necrotizing fasciitis, which is life-threatening, usually requiring treatment with antibiotics and even amputation. Although some potential virulence factors (e.g. endotoxins, hemolysins, enterotoxins, adheren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans (Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibrionales
The Vibrionaceae are a family of Pseudomonadota given their own order, Vibrionales. Inhabitants of fresh or salt water, several species are pathogenic, including the type species ''Vibrio cholerae'', which is the agent responsible for cholera. Most bioluminescent bacteria belong to this family, and are typically found as symbionts of deep-sea animals. Vibrionaceae are Gram-negative organisms and facultative anaerobes, capable of fermentation. They contain oxidase and have one or more flagella, which are generally polar. Originally, these characteristics defined the family, which was divided into four genera. Two of these, '' Vibrio'' and ''Photobacterium'', correspond to the modern group, although several new genera have been defined. Genetic studies have shown the other two original members—''Aeromonas'' and '' Plesiomonas''—belong to separate families. The family Vibrionaceae currently comprises eight validly published genera: ''Aliivibrio'', ''Catenococcus'', ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)