|
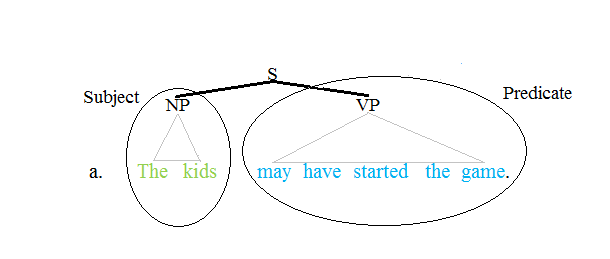
Verb Phrase
In linguistics, a verb phrase (VP) is a syntactic unit composed of a verb and its arguments except the subject of an independent clause or coordinate clause. Thus, in the sentence ''A fat man quickly put the money into the box'', the words ''quickly put the money into the box'' constitute a verb phrase; it consists of the verb ''put'' and its arguments, but not the subject ''a fat man''. A verb phrase is similar to what is considered a ''predicate'' in traditional grammars. Verb phrases generally are divided among two types: finite, of which the head of the phrase is a finite verb; and nonfinite, where the head is a nonfinite verb, such as an infinitive, participle or gerund. Phrase structure grammars acknowledge both types, but dependency grammars treat the subject as just another verbal dependent, and they do not recognize the finite verbal phrase constituent. Understanding verb phrase analysis depends on knowing which theory applies in context. In phrase structure grammars In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguistics is concerned with both the cognitive and social aspects of language. It is considered a scientific field as well as an academic discipline; it has been classified as a social science, natural science, cognitive science,Thagard, PaulCognitive Science, The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2008 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.). or part of the humanities. Traditional areas of linguistic analysis correspond to phenomena found in human linguistic systems, such as syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences); semantics (meaning); morphology (structure of words); phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages); phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language); and pragmatics (how social con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dependency Grammar
Dependency grammar (DG) is a class of modern grammatical theories that are all based on the dependency relation (as opposed to the ''constituency relation'' of phrase structure) and that can be traced back primarily to the work of Lucien Tesnière. Dependency is the notion that linguistic units, e.g. words, are connected to each other by directed links. The (finite) verb is taken to be the structural center of clause structure. All other syntactic units (words) are either directly or indirectly connected to the verb in terms of the directed links, which are called ''dependencies''. Dependency grammar differs from phrase structure grammar in that while it can identify phrases it tends to overlook phrasal nodes. A dependency structure is determined by the relation between a word (a head) and its dependents. Dependency structures are flatter than phrase structures in part because they lack a finite verb phrase constituent, and they are thus well suited for the analysis of languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principles And Parameters
Principles and parameters is a framework within generative linguistics in which the syntax of a natural language is described in accordance with general ''principles'' (i.e. abstract rules or grammars) and specific ''parameters'' (i.e. markers, switches) that for particular languages are either turned ''on'' or ''off''. For example, the position of heads in phrases is determined by a parameter. Whether a language is '' head-initial or head-final'' is regarded as a parameter which is either on or off for particular languages (i.e. English is ''head-initial'', whereas Japanese is ''head-final''). Principles and parameters was largely formulated by the linguists Noam Chomsky and Howard Lasnik. Many linguists have worked within this framework, and for a period of time it was considered the dominant form of mainstream generative linguistics. Principles and parameters as a grammar framework is also known as government and binding theory. That is, the two terms ''principles and paramete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predicate (grammar)
The term predicate is used in one of two ways in linguistics and its subfields. The first defines a predicate as everything in a standard declarative sentence except the subject, and the other views it as just the main content verb or associated predicative expression of a clause. Thus, by the first definition the predicate of the sentence ''Frank likes cake'' is ''likes cake''. By the second definition, the predicate of the same sentence is just the content verb ''likes'', whereby ''Frank'' and ''cake'' are the arguments of this predicate. Differences between these two definitions can lead to confusion. Syntax Traditional grammar The notion of a predicate in traditional grammar traces back to Aristotelian logic. A predicate is seen as a property that a subject has or is characterized by. A predicate is therefore an expression that can be ''true of'' something. Thus, the expression "is moving" is true of anything that is moving. This classical understanding of predicates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prepositional Phrase
An adpositional phrase, in linguistics, is a syntactic category that includes ''prepositional phrases'', ''postpositional phrases'', and ''circumpositional phrases''. Adpositional phrases contain an adposition (preposition, postposition, or circumposition) as head (linguistics), head and usually a Complement (linguistics), complement such as a noun phrase. Language syntax treats adpositional phrases as units that act as Argument (linguistics), arguments or Adjunct (grammar), adjuncts. Prepositional and postpositional phrases differ by the order of the words used. Languages that are primarily Head-directionality parameter, head-initial such as English language, English predominantly use prepositional phrases whereas head-final languages predominantly employ postpositional phrases. Many languages have both types, as well as circumpositional phrases. Types There are three types of adpositional phrases: prepositional phrases, postpositional phrases, and circumpositional phrases. Pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adverbial Phrase
In linguistics, an ''adverbial phrase'' ("AdvP") is a multi-word expression operating adverbially: its syntactic function is to modify other expressions, including verbs, adjectives, adverbs, adverbials, and sentences. Adverbial phrases can be divided into two types: complement adverbs and modifier adverbs. For example, in the sentence ''She sang very well'', the expression ''very well'' is an adverbial phrase, as it modifies the verb ''to sing''. More specifically, the adverbial phrase ''very well'' contains two adverbs, ''very'' and ''well'': while ''well'' modifies the verb to convey information about the manner of singing (for example, ''She sang well'' versus ''She sang badly''), ''very'' is a degree modifier that conveys information about the degree to which the action of singing well was accomplished (for example, ''Not only did she sing well, she sang very well''). Types The following examples illustrate some of the most common types of adverbial phrases. All adverbial phras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noun Phrase
In linguistics, a noun phrase, or nominal (phrase), is a phrase that has a noun or pronoun as its head or performs the same grammatical function as a noun. Noun phrases are very common cross-linguistically, and they may be the most frequently occurring phrase type. Noun phrases often function as verb subjects and objects, as predicative expressions and as the complements of prepositions. Noun phrases can be embedded inside each other; for instance, the noun phrase ''some of his constituents'' contains the shorter noun phrase ''his constituents''. In some more modern theories of grammar, noun phrases with determiners are analyzed as having the determiner as the head of the phrase, see for instance Chomsky (1995) and Hudson (1990). Identification Some examples of noun phrases are underlined in the sentences below. The head noun appears in bold. ::This election-year's politics are annoying for many people. ::Almost every sentence contains at least one noun phrase. ::Current ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adjunct (grammar)
In linguistics, an adjunct is an optional, or ''structurally dispensable'', part of a sentence, clause, or phrase that, if removed or discarded, will not structurally affect the remainder of the sentence. Example: In the sentence ''John helped Bill in Central Park'', the phrase ''in Central Park'' is an adjunct.See Lyons (1968). A more detailed definition of the adjunct emphasizes its attribute as a modifying form, word, or phrase that depends on another form, word, or phrase, being an element of clause structure with adverbial function. An adjunct is not an argument (nor is it a predicative expression), and an argument is not an adjunct. The argument–adjunct distinction is central in most theories of syntax and semantics. The terminology used to denote arguments and adjuncts can vary depending on the theory at hand. Some dependency grammars, for instance, employ the term ''circonstant'' (instead of ''adjunct''), following Tesnière (1959). The area of grammar that explores t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complement (linguistics)
In grammar, a complement is a word, phrase, or clause that is necessary to complete the meaning of a given expression. Complements are often also arguments (expressions that help complete the meaning of a predicate). Predicative, subject and object complements In many non-theoretical grammars, the terms '' subject complement'' and '' object complement'' are employed to denote the predicative expressions (such as predicative adjectives and nominals) that serve to assign a property to a subject or an object: ::Ryan is upset. – Predicative adjective as subject complement ::Rachelle is the boss. – Predicative nominal as subject complement ::That made Michael lazy. – Predicative adjective as object complement ::We call Rachelle the boss. – Predicative nominal as object complement This terminology is used in grammar books: However, this use of terminology is avoided by many modern theories of syntax, which typically view the expressions in bold as part of the clause pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specifier (linguistics)
In linguistics, X-bar theory is a model of phrase-structure grammar and a theory of syntactic category formation that was first proposed by Noam Chomsky in 1970Chomsky, Noam (1970). Remarks on Nominalization. In: R. Jacobs and P. Rosenbaum (eds.) ''Reading in English Transformational Grammar'', 184–221. Waltham: Ginn. and further developed by Ray Jackendoff (1974, 1977a, 1977bJackendoff, Ray (1977b) Constraints on Phrase Structure Rules, in P. W. Culicover, T. Wasow & A. Akmajian (eds.), ''Formal Syntax'', Academic Press, New York, pp. 249–83.), along the lines of the theory of generative grammar put forth in the 1950s by Chomsky. It attempts to capture the structure of phrasal categories with a single uniform structure called the X-bar schema, basing itself on the assumption that any phrase in natural language is an XP (X phrase) that is headed by a given syntactic category X. It played a significant role in resolving issues that phrase structure rules had, representative of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auxiliary Verb
An auxiliary verb (abbreviated ) is a verb that adds functional or grammatical meaning to the clause in which it occurs, so as to express tense, aspect, modality, voice, emphasis, etc. Auxiliary verbs usually accompany an infinitive verb or a participle, which respectively provide the main semantic content of the clause. An example is the verb ''have'' in the sentence ''I have finished my lunch.'' Here, the auxiliary ''have'' helps to express the perfect aspect along with the participle, ''finished''. Some sentences contain a chain of two or more auxiliary verbs. Auxiliary verbs are also called helping verbs, helper verbs, or (verbal) auxiliaries. Research has been conducted into split inflection in auxiliary verbs. Basic examples Below are some sentences that contain representative auxiliary verbs from English, Spanish, German and French, with the auxiliary verb marked in bold: ::a. Do you want tea? – ''do'' is an auxiliary accompanying the infinitive, ''want'', used here t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



.png)