|
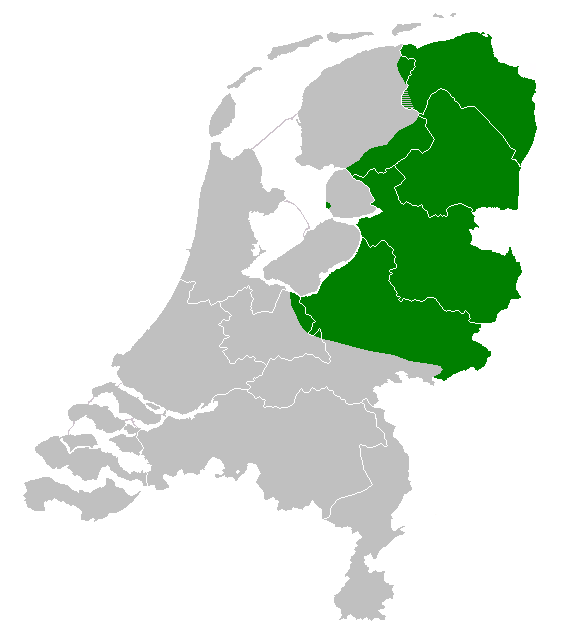
Veluws
Veluws is a Westphalian dialect which is spoken on the Veluwe, in the northwest of Gelderland, in central Netherlands. The language was recognized by the government of the Netherlands in 1996 (as part of Low Saxon). Dialects Veluws is usually divided into two main dialects, West-Veluws and Oost-Veluws (East Veluws), these two dialects are reasonably similar but differ in grammar. For example: in Oost-Veluws it is said ('you are working') and in West-Veluws ('you are working'). West-Veluws has more influenced from Dutch. Typically the closer one gets to the border with Oost-Veluws, the more the dialects differ from Standard Dutch. For example, in the central part where West-Veluws is spoken ('he is standing'); in the northwestern part the corresponding phrase sounds , compared to in Oost-Veluws. The latter has more Low Saxon influence. In Hattem Hattem () is a municipality and a town in the eastern Netherlands. The municipality had a population of in . The municipality ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West-Veluws Dialect
West-Veluws is a Low Saxon dialect of the Dutch province of Gelderland. It is spoken in several Veluwe municipalities and villages including: Nunspeet, Putten, Ermelo (''Armelo''), Harderwijk (''Harderwiek''), Uddel, Nijkerk (''Niekark''), Appel, Scherpenzeel (''Schaarpezeel''), the municipality of Barneveld (''Barreveld'') and some villages of the municipality of Ede. West-Veluws is also spoken in the Utrecht village of Bunschoten (''Bunsjoten'') and originally in Leusden and Amersfoort as well, but here the dialect has almost died out. The border between West-Veluwe in the northeast and Utrecht and South Gelderland in the southwest is very frayed: even the dialects of, for instance, Soest, Eemnes, Huizen and Laren still have Lowlands Saxon characteristics. In the articles Goois, Eemlands and Geldersevalleis these transitional dialects are discussed in more detail. Speakers West-Veluws is mainly spoken by older people, the Low Saxon dialect is not very popular among the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West-Veluws
West-Veluws is a Low Saxon dialect of the Dutch province of Gelderland. It is spoken in several Veluwe municipalities and villages including: Nunspeet, Putten, Ermelo (''Armelo''), Harderwijk (''Harderwiek''), Uddel, Nijkerk (''Niekark''), Appel, Scherpenzeel (''Schaarpezeel''), the municipality of Barneveld (''Barreveld'') and some villages of the municipality of Ede. West-Veluws is also spoken in the Utrecht village of Bunschoten (''Bunsjoten'') and originally in Leusden and Amersfoort as well, but here the dialect has almost died out. The border between West-Veluwe in the northeast and Utrecht and South Gelderland in the southwest is very frayed: even the dialects of, for instance, Soest, Eemnes, Huizen and Laren still have Lowlands Saxon characteristics. In the articles Goois, Eemlands and Geldersevalleis these transitional dialects are discussed in more detail. Speakers West-Veluws is mainly spoken by older people, the Low Saxon dialect is not very popular among th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oost-Veluws Dialect
Oost-Veluws (East Veluws) is one of the main dialects of Veluws and is therefore related to West-Veluws and Sallaans. It is spoken in the Dutch province Gelderland. The dialect is endangered as there are few native speakers left. Delimitation of Oost-Veluws Oost-Veluws is spoken in places such as the municipalities Elburg en Oldebroek, Epe, Vaassen, Apeldoorn en Dieren. The villages Elspeet, Uddel en Kootwijk in the middle of the Veluwe belong to West-Veluws. The delimitation to Sallaans is problematic to the point that some linguists prefer to make a division between Veluws (consisting of West-Veluws and some Oost-Veluws places as Elburg and Oldebroek) and Sallaans (consisting of Sallaans and the rest of the Oost-Veluws region).http://www.dbnl.org/tekst/weij005nede01/weij005nede01ill45.gif Differences to other dialect groups Differences to West-Veluws Most villages of the area called Veluwe lie on its borders, that is, not in the middle of this sandy woodland. The actual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Saxon Languages
: : : : : (70,000) (30,000) (8,000) , familycolor = Indo-European , fam2 = Germanic , fam3 = West Germanic , fam4 = North Sea Germanic , ancestor = Old Saxon , ancestor2 = Middle Low German , dia1 = West Low German , dia2 = East Low German , iso2 = nds , iso3 = nds , iso3comment = (Dutch varieties and Westphalian have separate codes) , lingua = 52-ACB , map = Nds Spraakrebeet na1945.svg , mapcaption = Present day Low German language area in Europe. , glotto = lowg1239 , glottoname = Low German , notice = IPA Low German or Low Saxon (in the language itself: , and other names; german: Plattdeutsch, ) is a West Germanic language variety spoken mainly in Northern Germany and the northeastern part of the Netherlands. The dialect of Plautdietsch is also spoken in the Russian Mennonite diaspora worldwid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of The Netherlands
The official language of the Netherlands is Dutch, spoken by almost all people in the Netherlands. Dutch is also spoken and official in Aruba, Bonaire, Belgium, Curaçao, Saba, Sint Eustatius, Sint Maarten and Suriname. It is a West Germanic, Low Franconian language that originated in the Early Middle Ages ( 470) and was standardised in the 16th century. There are also some recognised provincial languages and regional dialects. * West Frisian is a co-official language in the province of Friesland. West Frisian is spoken by 453,000 speakers. *English is an official language in the special municipalities of Saba and Sint Eustatius (BES Islands), as well as the autonomous states of Curaçao and Sint Maarten. It is widely spoken on Saba and Sint Eustatius. On Saba and St. Eustatius, the majority of the education is in English only, with some bilingual English-Dutch schools. 90-93% of the Dutch people can also speak English as a foreign language. (see also: English language in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Low German
Low Saxon, also known as West Low German ( nds, Nedersassisch, Nedersaksies; nl, Nedersaksisch) are a group of Low German dialects spoken in parts of the Netherlands, northwestern Germany and southern Denmark (in North Schleswig by parts of the German-speaking minority). It is one of two groups of mutually intelligible dialects, the other being East Low German dialects. A 2005 study found that there were approximately 1.8 million "daily speakers" of Low Saxon in the Netherlands. 53% spoke Low Saxon or Low Saxon and Dutch at home and 71% could speak it. loemhoff, H. (2005). Taaltelling Nedersaksisch. Een enquête naar het gebruik en de beheersing van het Nedersaksisch in Nederland. Groningen: Sasland./ref> According to another study the percentage of speakers among parents dropped from 34% in 1995 to 15% in 2011. The percentage of speakers among their children dropped from 8% to 2% in the same period. Extent The language area comprises the North German states of Lower Saxony, N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Language
Dutch ( ) is a West Germanic language spoken by about 25 million people as a first language and 5 million as a second language. It is the third most widely spoken Germanic language, after its close relatives German and English. ''Afrikaans'' is a separate but somewhat mutually intelligible daughter languageAfrikaans is a daughter language of Dutch; see , , , , , . Afrikaans was historically called Cape Dutch; see , , , , , . Afrikaans is rooted in 17th-century dialects of Dutch; see , , , . Afrikaans is variously described as a creole, a partially creolised language, or a deviant variety of Dutch; see . spoken, to some degree, by at least 16 million people, mainly in South Africa and Namibia, evolving from the Cape Dutch dialects of Southern Africa. The dialects used in Belgium (including Flemish) and in Suriname, meanwhile, are all guided by the Dutch Language Union. In Europe, most of the population of the Netherlands (where it is the only official language spoken country ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Low Saxon
Dutch Low Saxon ( or ''Nederlaands Nedersaksies''; nl, Nederlands Nedersaksisch) are the Low Saxon dialects of the Low German language that are spoken in the northeastern Netherlands and are written there with local, unstandardised orthographies based on Standard Dutch orthography. The UNESCO Atlas of endangered languages lists the language as vulnerable. The percentage of speakers among parents dropped from 34% in 1995 to 15% in 2011. The percentage of speakers among their children dropped from 8% to 2% in the same period. According to a 2005 study 53% speaks Low Saxon or Low Saxon and Dutch at home and 71% could speak it in the researched area. The Netherlands recognizes Dutch Low Saxon as an official regional language under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. Classification The classification of Dutch Low Saxon is not unanimous. From a diachronic point of view, the Dutch Low Saxon dialects are merely the West Low German (Northern Low Saxon and Friso-S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westphalian Language
Westphalian or Westfalish ( Standard High German: ', Standard Dutch: ') is one of the major dialect groups of West Low German. Its most salient feature is its diphthongization (rising diphthongs). For example, speakers say () instead of or for "to eat". (There is also a difference in the use of consonants ''within'' the Westphalian dialects: North of the Wiehengebirge, people tend to speak unvoiced consonants, south of the Wiehengebirge they voiced their consonants, e.g. > .) The Westphalian dialect region includes the north-eastern part of North Rhine-Westphalia, i.e. the former Prussian province of Westphalia, without Siegerland and Wittgenstein, but including the southern part of former government district Weser-Ems (e.g. the region around Osnabrück and the landscape of Emsland in modern Lower Saxony). Traditionally, all Dutch Low Saxon dialects are considered Westphalian, with the notable exception of Gronings, which is grouped with the Northern Low Saxon and Friso-Sax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westphalian Dialect
Westphalian or Westfalish ( Standard High German: ', Standard Dutch: ') is one of the major dialect groups of West Low German. Its most salient feature is its diphthongization (rising diphthongs). For example, speakers say () instead of or for "to eat". (There is also a difference in the use of consonants ''within'' the Westphalian dialects: North of the Wiehengebirge, people tend to speak unvoiced consonants, south of the Wiehengebirge they voiced their consonants, e.g. > .) The Westphalian dialect region includes the north-eastern part of North Rhine-Westphalia, i.e. the former Prussian province of Westphalia, without Siegerland and Wittgenstein, but including the southern part of former government district Weser-Ems (e.g. the region around Osnabrück and the landscape of Emsland in modern Lower Saxony). Traditionally, all Dutch Low Saxon dialects are considered Westphalian, with the notable exception of Gronings, which is grouped with the Northern Low Saxon and Friso-Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westphalian Dialects
Westphalian may refer to: * The culture or people of the Westphalia region of Germany * Westphalian language, one of the major dialect groups of West Low German * Westphalian sovereignty, a concept in international relations * Westphalian (stage), in geology * Westphalian ham (Westfälischer Schinken) produced from acorn-fed pigs raised in Westphalia. The resulting meat is dry cured and then smoked over a mixture of beechwood and juniper branches. Animals * Westphalian horse, a warmblood horse bred in the Westphalia region of western Germany * Westphalian chicken, old hardy landrace of chicken * Westphalian Dachsbracke The Westphalian Dachsbracke is a small, short-legged scenthound, a breed of dog originating in Westphalia, a region of Germany. The Westphalian Dachsbracke was used in Sweden to develop the Drever. Appearance The Westphalian Dachsbracke (''We ..., a small, short legged scenthound {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sallands
Sallaans ( nl, Sallands; Low Saxon: ''Sallaands'') is a collective term for the Westphalian dialects of the region Salland, in the province of Overijssel, as well as in minor parts of Gelderland and Drenthe in the Eastern Netherlands. In the Kop van Overijssel, the Stellingwarfs dialect is spoken. A common term used by native speakers for their dialect, which is also used by Low Saxon speakers from other regions for their respective dialects, is ''plat'' or simply ''dialect''. Yet another common usage is to refer to the language by the name of the local variety, where for instance ''Dal(f)sens'' would be the name for the Sallaans variety spoken in the village of Dalfsen. Sallands is more influenced by the Hollandic dialects than Twents or Achterhoeks Achterhooks (Dutch Low Saxon: ; nl, Achterhoeks ) is a Westphalian dialect spoken in Gelderland. Geographic distribution The Achterhooks language is spoken in the Netherlands in western Europe, Northeast, with speakers concen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |