|
Vaykunik
Kalbajar District ( az, Kəlbəcər rayonu) is one of the 66 districts of Azerbaijan. It is located in the west of the country and belongs to the East Zangezur Economic Region. The district borders the districts of Lachin, Khojaly, Agdam, Tartar, Goranboy, Goygol and Dashkasan districts of Azerbaijan, as well as the Gegharkunik and Vayots Dzor provinces of Armenia. Its capital and largest city is Kalbajar. As of 2020, the district had a nominal population of 94,100. History In Turkic ''Kalbajar'' means ''"Castle on the mouth of the river"''. The city of Kalbajar was renamed to ''Karvachar'' ( hy, Քարվաճառ) after its occupation in the First Nagorno-Karabakh war, which corresponds to the ancient district of Vaykunik, one of 12 cantons of Artsakh.Robert H. Hewsen, ''Armenia: A Historical Atlas''. The University of Chicago Press, 2001, pp. 40, 101–102, 264–265. It was also known as ''Upper-Khachen'' or ''Tsar'' ( after its chief town) and was ruled by one of the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artsakh (historic Province)
Artsakh ( hy, Արցախ, Artsʻakh, ) was the tenth province (''nahang'') of the Kingdom of Armenia from c. 189 BC until 387 AD, when it was made part of Caucasian Albania, a subject principality of the Sasanian Empire, following the Peace of Acilisene. From the 7th to 9th centuries, it fell under Arab control. In 821, it formed the Armenian principality of Khachen and around the year 1000 was proclaimed the Kingdom of Artsakh, one of the last medieval eastern Armenian kingdoms and principalities to maintain its autonomy following the Turkic invasions of the 11th to 14th centuries. Name Cuneiform inscriptions left by Urartian kings mention a land or lands called "Ardakh/Adakh", "Urdekhe/Urtekhini", and "Atakhuni", which some scholars identify with Artsakh. When speaking about Armenia in his ''Geography'', the classical historian Strabo refers to an Armenian region which he calls "Orchistene", which is also believed to be a rendering of the name Artsakh.Strabo. ''Geography'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khachen
The Principality of Khachen ( hy, Խաչենի իշխանություն, Khacheni ishkhanutyun) was a medieval Armenian principality on the territory of historical Artsakh (present-day Nagorno-Karabakh). The provinces of Artsakh and Utik were attached to the Kingdom of Armenia in antiquity. In the early medieval period, these provinces were under Sassanid or Arab suzerainty until the establishment of the Bagratid Kingdom of Armenia in the 9th century. From the 12th century the Armenian Principality of Khachen dominated the region. The Byzantine emperor Constantine VII addressed his letters to the prince of Khachen with the inscription "To Prince of Khachen, Armenia." According to Abū Dulaf, an Arab traveller of the time, Khachen was an Armenian principality immediately south of Barda'a (modern-day Barda, Azerbaijan).Abū-Dulaf Misʻar Ibn Muhalhil's Travels in Iran (circa A.D. 950) / Ed. and trans. by V. Minorsky. — Cairo University Press, 1955. — p. 74:"''Khajin (Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zar, Azerbaijan
Zar (; hy, Ծար, Tsar; , also ''Tzar'') is a village in the Kalbajar District of Azerbaijan. Etymology Armenian architectural historian Samvel Karapetyan writes that the settlement was first mentioned as "Tsar" in 1289. In the records of Dadivank Monastery in 1763, it is referred to as ''Mets Tsar'' ( hy, Մեծ Ծար, ), and in the 18th century, with an increased nomadic presence in the region, ''Zar'', a derivative of ''Tsar'', began to be used as a name for the village. An Azerbaijani legend suggests a different origin. A poor young man named Zaza once lived in this village. He was in love with a girl named Nazı, but her parents were against their relationship. Zaza then decided to seek assistance from Nadir Shah. He planted a watermelon in a narrow-necked jar. The surprised shah approved and ordered that Nazı be given to Zaza. However, as soon as Nadir Shah left town, Nazı's family went to Zaza's house and murdered him before throwing his body into a well. Zaza's mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
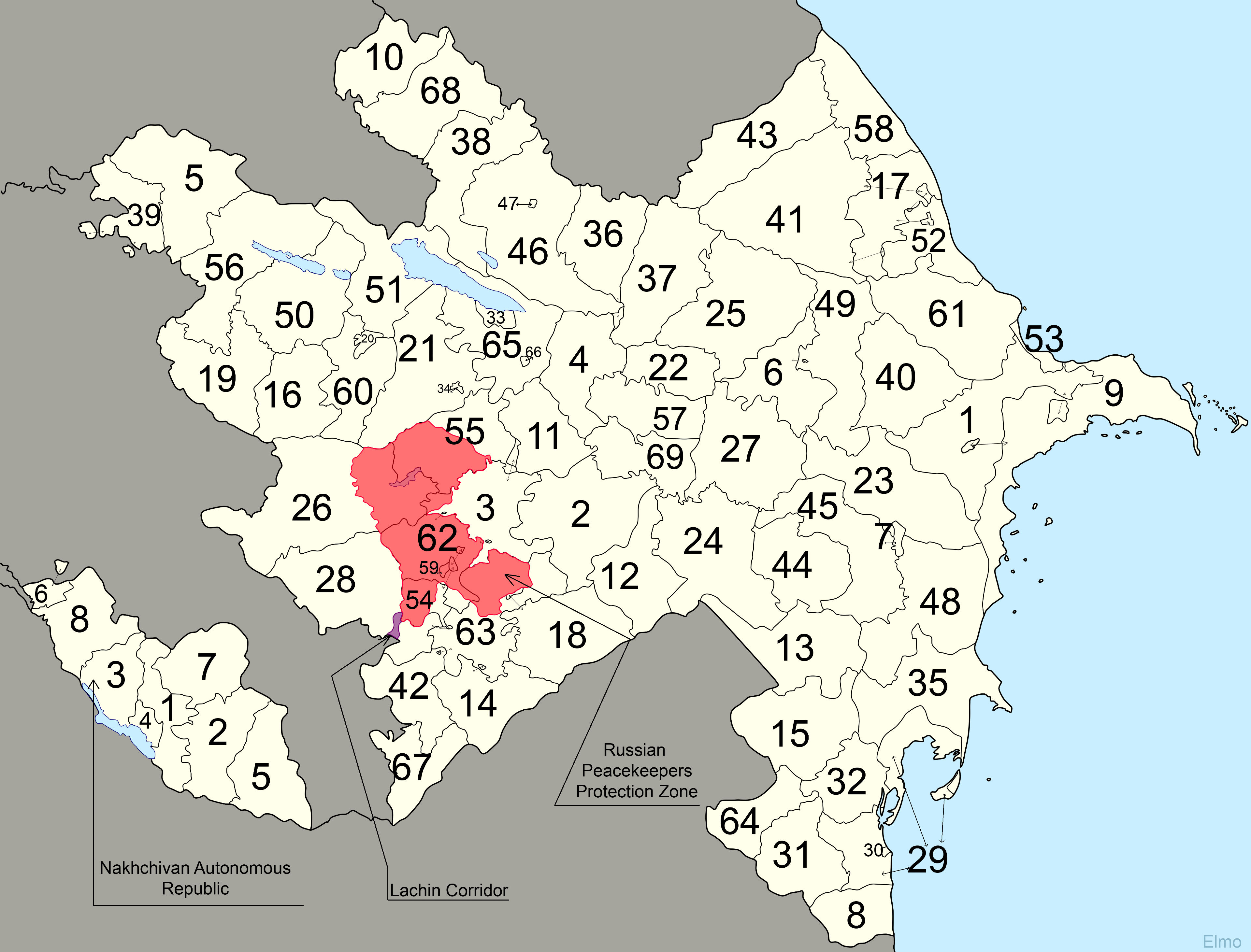
Administrative Divisions Of Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan is administratively divided into 66 districts () and 11 cities () that are subordinate to the Republic. Out of these, 7 districts and 1 city is located within the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic. The districts are further divided into municipalities (). Additionally, the districts of Azerbaijan are grouped into 14 Economic Regions (). On July 7, 2021, the President of Azerbaijan Ilham Aliyev signed Decree "On the new division of economic regions in the Republic of Azerbaijan". Administrative divisions Contiguous Azerbaijan The territory of former Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast presently consists of the districts of Khojavend, Shusha, Khojaly, the eastern portion of Kalbajar and the western portion of Tartar. The Autonomous Oblast was abolished on 26 November 1991, by the Supreme Soviet of the Azerbaijan SSR. Since then, the territory of the autonomous oblast has been administratively split between the aforementioned districts. As a result of the First N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dashkasan District
Dashkasan District ( az, Daşkəsən rayonu) is one of the 66 districts of Azerbaijan. It is located in the west of the country and belongs to the Ganja-Dashkasan Economic Region. The district borders the districts of Goygol, Kalbajar, Gadabay, Shamkir, and the Gegharkunik Province of Armenia. Its capital and largest city is Dashkasan. As of 2020, the district had a population of 35,400. History The district was established on 8 August 1930 and was known as ''Dastafur'' ( az, Dəstəfur) until 1956, when it was changed to Dashkasan. The capital was established as an urban facility on March 16, 1948, after the end of World War I, mainly to explore and mine iron ore and other natural resources. Administrative divisions The rayon itself was founded as an administrative center in 1930 and was named Dastafur until 1956 when it was renamed Dashkasan. In 1963, the rayon status was eliminated and Dashkasan province was merged with Khanlar District. However, in 1965, it was split ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mardakert District (NKAO)
Mardakert District ( az, Mardakert rayonu, Мардакерт рајону; hy, Մարդակերտի շրջան) was an administrative unit within the former Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast (NKAO) of the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic. History The district was formed on 8 August 1930, as the ''Jrabert district''. It was renamed to Mardakert district on 17 September 1939. The administrative centre of the district was Mardakert. 3 urban-type settlements existed in the region: Madagiz (gained urban status in 1943), Mardakert (since 1960), Leninavan (since 1966). The district was the largest one in NKAO in terms of area and population. The Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast was abolished on 26 November 1991 and the district was renamed Aghdara ( az, Ağdərə). On 13 October 1992, the Aghdara district was also abolished and split between the three neighbouring districts, with the western part being incorporated into Kalbajar District, the northeastern part into the Tar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karabakh
Karabakh ( az, Qarabağ ; hy, Ղարաբաղ, Ġarabaġ ) is a geographic region in present-day southwestern Azerbaijan and eastern Armenia, extending from the highlands of the Lesser Caucasus down to the lowlands between the rivers Kura (Caspian Sea), Kura and Aras River, Aras. It is conventionally divided into three regions: Highland Karabakh, Lowland Karabakh (the steppes between the Kura (Caspian Sea), Kura and Aras river, Aras rivers), and the eastern slopes of the Zangezur Mountains (roughly Syunik Province, Syunik and Kalbajar–Lachin Economic Region, Kalbajar–Lachin).Robert H. Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Meliks of Eastern Armenia: A Preliminary Study," ''Revue des Études Arméniennes'' 9 (1972), p. 289, note 17. Etymology The Russian language, Russian name , Romanization of Russian, transliterated , derives from the Azerbaijani language, Azerbaijani , which is generally believed to be a compound of the Turkic language, Turkic word ''kara'' (black) and the Irania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The University Of Chicago Press
The University of Chicago Press is the largest and one of the oldest university presses in the United States. It is operated by the University of Chicago and publishes a wide variety of academic titles, including ''The Chicago Manual of Style'', numerous academic journals, and advanced monographs in the academic fields. One of its quasi-independent projects is the BiblioVault, a digital repository for scholarly books. The Press building is located just south of the Midway Plaisance on the University of Chicago campus. History The University of Chicago Press was founded in 1890, making it one of the oldest continuously operating university presses in the United States. Its first published book was Robert F. Harper's ''Assyrian and Babylonian Letters Belonging to the Kouyunjik Collections of the British Museum''. The book sold five copies during its first two years, but by 1900 the University of Chicago Press had published 127 books and pamphlets and 11 scholarly journals, includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert H
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe it entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including English, German, Dutch, Norwegian, Swedish, Scots, Danish, and Icelandic. It can be use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Nagorno-Karabakh War
The First Nagorno-Karabakh War, referred to in Armenia as the Artsakh Liberation War ( hy, Արցախյան ազատամարտ, Artsakhyan azatamart) was an ethnic and territorial conflict that took place from February 1988 to May 1994, in the enclave of Nagorno-Karabakh in southwestern Azerbaijan, between the majority ethnic Armenians of Nagorno-Karabakh backed by Armenia, and the Republic of Azerbaijan. As the war progressed, Armenia and Azerbaijan, both former Soviet Republics, entangled themselves in protracted, undeclared mountain warfare in the mountainous heights of Karabakh as Azerbaijan attempted to curb the secessionist movement in Nagorno-Karabakh. The enclave's parliament had voted in favor of uniting with Armenia and a referendum, boycotted by the Azerbaijani population of Nagorno-Karabakh, was held, in which a majority voted in favor of independence. The demand to unify with Armenia began in a relatively peaceful manner in 1988; in the following months, as the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkic Languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of over 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and Western Asia. The Turkic languages originated in a region of East Asia spanning from Mongolia to Northwest China, where Proto-Turkic is thought to have been spoken, from where they expanded to Central Asia and farther west during the first millennium. They are characterized as a dialect continuum. Turkic languages are spoken by some 200 million people. The Turkic language with the greatest number of speakers is Turkish language, Turkish, spoken mainly in Anatolia and the Balkans; its native speakers account for about 38% of all Turkic speakers. Characteristic features such as vowel harmony, agglutination, subject-object-verb order, and lack of grammatical gender, are almost universal within the Turkic family. There is a high degree of mutual intelligibility, upon mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dadivank View
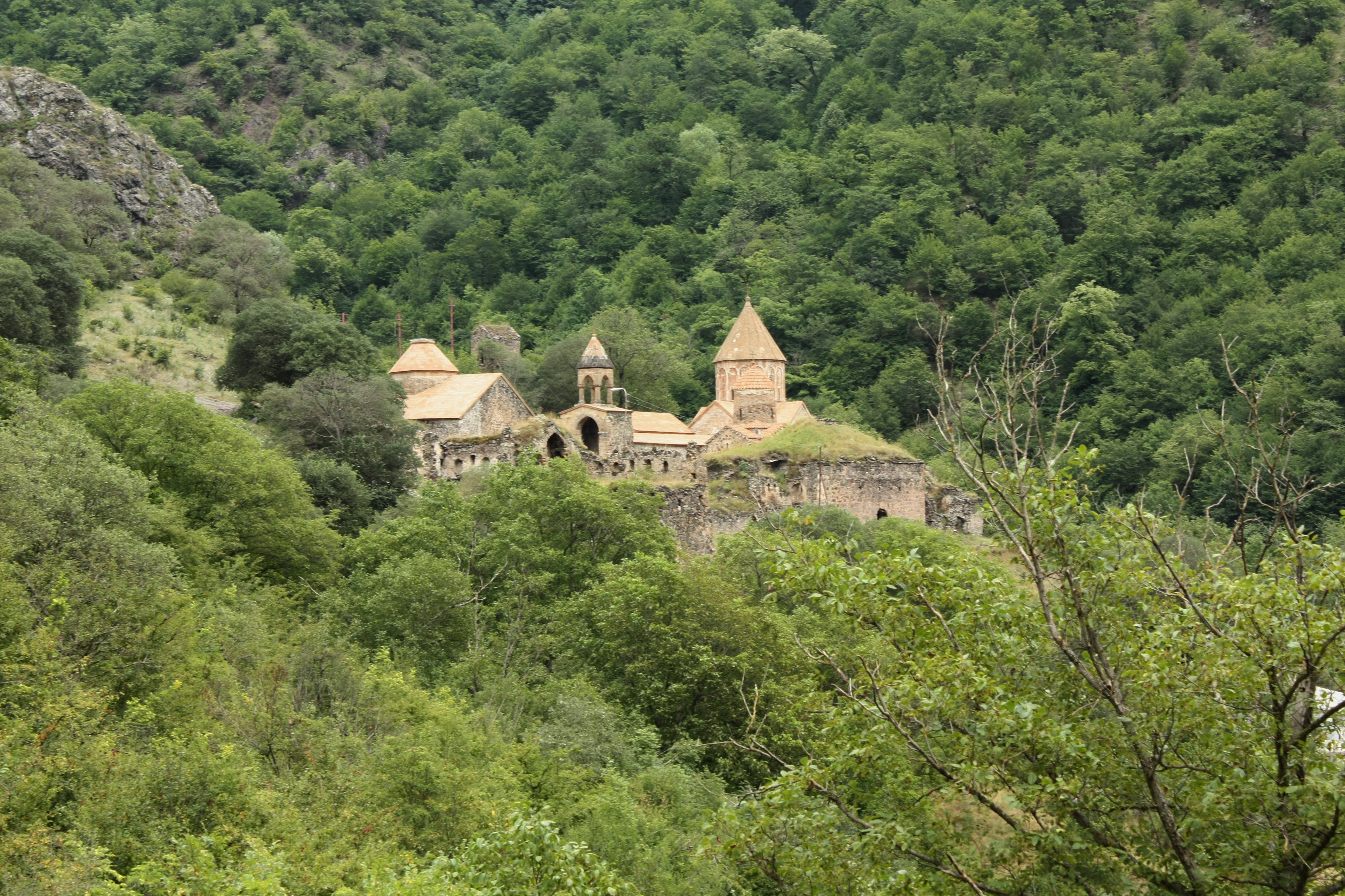
Dadivank ( hy, Դադիվանք) or Khutavank ( hy, Խութավանք, translation=monastery on the hillЖеан-Паул Лабурдетьте, Доминикуе Аузиас, Армения, Petit Futé, 2007 – p. 203) is an Armenian Apostolic monastery in the Kalbajar District of Azerbaijan bordering the Martakert Province of the self-proclaimed Republic of Artsakh. It was built between the 9th and 13th centuries and is one of the main monastic complexes of medieval Armenia. In Azerbaijan, the monastery is called Dadivəng or Xudavəng. The state denies the monastery's Armenian Apostolic heritage, instead referring to it as "Caucasian Albanian." History and architecture The monastery is said to have been founded by St. Dadi, a disciple of Thaddeus the Apostle who spread Christianity in Eastern Armenia during the first century AD. However, the monastery is only first mentioned in the 9th century. In July 2007, the grave said to belong to St. Dadi was discovered under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |