|
Vassago
Vassago (also ''Vasago'', ''Usagoo'') is a demon described in demonological grimoires such as the ''Lesser Key of Solomon'' and the '' Book of the Office of Spirits''. Lesser Key of Solomon He is the third demon in the ''Lesser Key'' (including Thomas Rudd's variant) as a prince "of a good nature" and of the "same nature as Agares". He rules twenty-six legions of spirits, and is summoned to tell magicians of past and future events, and locate lost objects. He is one of the few spirits found in the Lesser Key of Solomon but not in Johann Weyer's Pseudomonarchia Daemonum. According to Rudd, Vassago is opposed by the Shemhamphorasch angel Sitael. Other works Vassago is mentioned in the Book of the Office of Spirits as Usagoo, appearing as an angel, "just and true in all his doings," with the powers of inciting the love of women and revealing hidden treasures, in addition to ruling twenty spirits. Sloane MS 3824 mentions Vassago in invocations to summon spirits that guard tre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
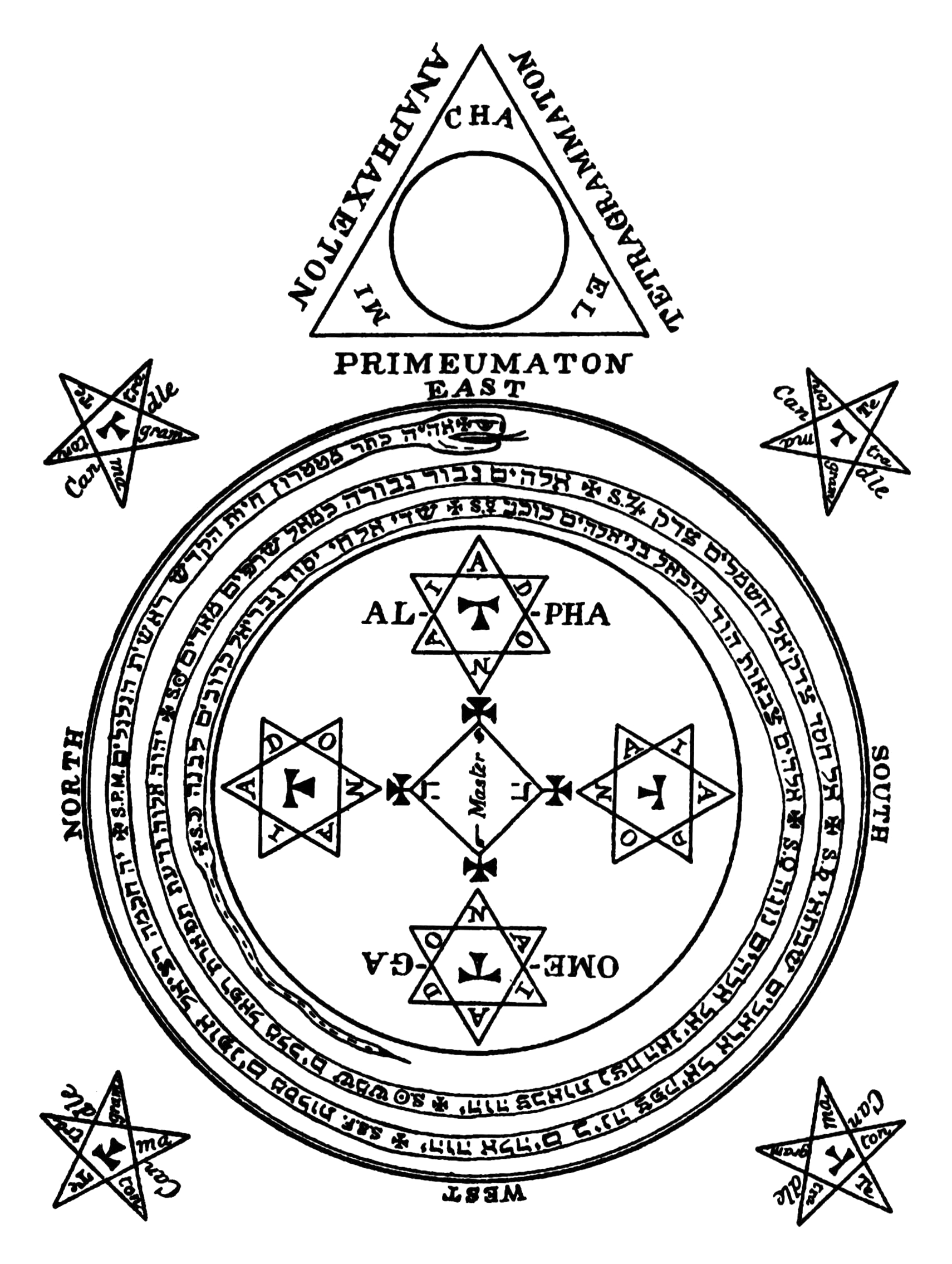
Lesser Key Of Solomon
''The Lesser Key of Solomon'', also known as ''Lemegeton Clavicula Salomonis'' or simply ''Lemegeton'', is an anonymous grimoire on demonology. It was compiled in the mid-17th century, mostly from materials a couple of centuries older.''Lemegeton Clavicula Salomonis: The Lesser Key of Solomon, Detailing the Ceremonial Art of Commanding Spirits Both Good and Evil''; ed. Joseph H. Peterson; Weiser Books Maine; 2001. pp. xi–xvii.''The Goetia of Dr Rudd''; Thomas Rudd, Eds. Stephen Skinner & David Rankine; 2007, Golden Hoard Press. p. 399. It is divided into five books—the ''Ars Goetia'', ''Ars Theurgia-Goetia'', ''Ars Paulina'', ''Ars Almadel'', and ''Ars Notoria''. ''Ars Goetia'' Etymology The text is more properly called "Lemegeton Clavicula Salomonis, or, The little Key of Solomon". The title most commonly used, "The Lesser Key of Solomon," does not in fact occur in the manuscripts. A.E. Waite, in his 1898 ''Book of Black Magic and of Pacts'' does use the ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudomonarchia Daemonum
''Pseudomonarchia Daemonum'', or ''False Monarchy of Demons'', first appears as an Appendix to ''De praestigiis daemonum'' (1577) by Johann Weyer.Pseudomonarchia Daemonum (Liber officiorum spirituum); Johann Weyer, ed. Joseph Peterson; 2000. Available online aEsoteric Archives/ref> An abridgment of a grimoire similar in nature to the ''Ars Goetia'' (first book of ''The Lesser Key of Solomon''), it contains a list of demons, and the appropriate hours and rituals to conjure them. The ''Pseudomonarchia'' predates, and differs somewhat from, ''Ars Goetia''. The ''Pseudomonarchia'' lists sixty-nine demons (in contrast to the later seventy-two), and their sequence varies, along with some of their characteristics. The demon Pruflas appears only in ''Pseudomonarchia'',''The Lesser Key of Solomon'' add the demons Vassago, Seere, Dantalion, and Andromalius. and ''Pseudomonarchia'' does not attribute any sigils to the demons. Weyer referred to his source manuscript as ''Liber officiorum s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liber Officiorum Spirituum
''Liber Officiorum Spirituum'' (English: ''The Book of the Office of Spirits'')A Book of the Office of Spirits; John Porter, Trans. Frederick Hockley, Ed. Colin D. Campbell; Teitan Press, 2011.''The Book of Oberon,'' eds. Daniel Harms and Joseph Peterson, Llewllyn Publications, 2015 was a demonological grimoire and a major source for Johann Weyer's ''Pseudomonarchia Daemonum'' and the ''Ars Goetia''. The original work (if it is a single work) has not been located, but some derived texts bearing the title have been found, some in the Sloane manuscripts, some in the Folger Shakespeare Library. Each version bears many similarities to each other and to the ''Pseudomonarchia Daemonum'' and the ''Ars Goetia'', though they are far from identical.Porter, Hockley, Campbell, p.vii-xvii''The Book of Oberon,'' eds. Daniel Harms and Joseph Peterson, Llewllyn Publications, 2015, p.1-30 History Johannes Trithemius mentions two separate works (''Liber'' quoque ''Officiorum'', and ''De Offi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shemhamphorasch
''Shem HaMephorash'' ( he, שֵׁם הַמְּפֹרָשׁ ''Šēm hamMəfōrāš'', also ''Shem ha-Mephorash''), meaning "the explicit name," is originally a Tannaitic term describing the Tetragrammaton. In Kabbalah, it may refer to a name of God composed of either 4, 12, 22, 42, or 72 letters (or triads of letters), the latter version being the most common. 12-, 22-, and 42-letter names Early sources, from the Mishnah to Maimonides, only use "Shem ha-Mephorash" to refer to the four letter Tetragrammaton. b. Qiddushin 72a describes a 12-letter name (apparently a mundane euphemism, YHWH-EHYH-ADNY or YHWH-YHWH-YHWH) and a 42-letter name (holy but unknown; Hayy Gaon says it is the acronym of the medieval piyyut Ana b'Koachתשובה אל יוסף בן ברכיה ותלמידי יעקב בן נסים בעניין שמות והשבעות, קונטרס "הדר עם הנכרי בחצר"). A 22-letter name appears in ''Sefer Raziel HaMalakh'', without interpretation, as ('). Its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demon
A demon is a malevolent supernatural entity. Historically, belief in demons, or stories about demons, occurs in religion, occultism, literature, fiction, mythology, and folklore; as well as in media such as comics, video games, movies, anime, and television series. Belief in demons probably goes back to the Paleolithic age, stemming from humanity's fear of the unknown, the strange and the horrific. ''A Dictionary of Comparative Religion'' edited by S.G.F. Brandon 1970 In ancient Near Eastern religions and in the Abrahamic religions, including early Judaism and ancient-medieval Christian demonology, a demon is considered a harmful spiritual entity which may cause demonic possession, calling for an exorcism. Large portions of Jewish demonology, a key influence on Christianity and Islam, originated from a later form of Zoroastrianism, and was transferred to Judaism during the Persian era. Demons may or may not also be considered to be devils: minions of the Devil. In ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cult
In modern English, ''cult'' is usually a pejorative term for a social group that is defined by its unusual religious, spiritual, or philosophical beliefs and rituals, or its common interest in a particular personality, object, or goal. This sense of the term is controversial and weakly defined—having divergent definitions both in popular culture and academia—and has also been an ongoing source of contention among scholars across several fields of study. Richardson, James T. 1993. "Definitions of Cult: From Sociological-Technical to Popular-Negative." ''Review of Religious Research'' 34(4):348–56. . . An older sense of the word involves a set of religious devotional practices that are conventional within their culture, related to a particular figure, and often associated with a particular place. References to the "cult" of a particular Catholic saint, or the imperial cult of ancient Rome, for example, use this sense of the word. While the literal and original sense of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vampire
A vampire is a mythical creature that subsists by feeding on the Vitalism, vital essence (generally in the form of blood) of the living. In European folklore, vampires are undead, undead creatures that often visited loved ones and caused mischief or deaths in the neighbourhoods they inhabited while they were alive. They wore shrouds and were often described as bloated and of ruddy or dark countenance, markedly different from today's gaunt, pale vampire which dates from the early 19th century. Vampiric entities have been Vampire folklore by region, recorded in cultures around the world; the term ''vampire'' was popularized in Western Europe after reports of an 18th-century mass hysteria of a pre-existing folk belief in the Balkans and Eastern Europe that in some cases resulted in corpses being staked and people being accused of vampirism. Local variants in Eastern Europe were also known by different names, such as ''shtriga'' in Albanian mythology, Albania, ''vrykolakas'' in G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murder
Murder is the unlawful killing of another human without justification (jurisprudence), justification or valid excuse (legal), excuse, especially the unlawful killing of another human with malice aforethought. ("The killing of another person without justification or excuse, especially the crime of killing a person with malice aforethought or with recklessness manifesting extreme indifference to the value of human life.") This state of mind may, depending upon the jurisdiction (area), jurisdiction, distinguish murder from other forms of unlawful homicide, such as manslaughter. Manslaughter is killing committed in the absence of Malice (law), ''malice'',This is "malice" in a technical legal sense, not the more usual English sense denoting an emotional state. See malice (law). brought about by reasonable Provocation (legal), provocation, or diminished capacity. Involuntary manslaughter, ''Involuntary'' manslaughter, where it is recognized, is a killing that lacks all but the most a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jefferson, North Carolina
Jefferson is a town in and the county seat of Ashe County, North Carolina, United States. The population was 1,611 at the 2010 census. History The North Carolina General Assembly created a special commission in 1799 to found a county seat for Ashe County. The commission purchased of land to form the town of Jeffersonton, later named Jefferson. It is one of the first towns in the nation to bear the name of Thomas Jefferson, who was the vice president of the United States in 1799. The Ashe County Courthouse and Poe Fish Weir are listed on the National Register of Historic Places. Geography Jefferson is located at in the Appalachian Mountains. According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of , of which , or 0.20%, is water. The New River, which is part of the Ohio River watershed and one of the oldest and most scenic rivers in the eastern United States, flows through the town. Climate Demographics 2020 census As of the 2020 United States census, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Weyer
Johann Weyer or Johannes Wier ( la, Ioannes Wierus or '; 1515 – 24 February 1588) was a Dutch physician, occultist and demonologist, disciple and follower of Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa. He was among the first to publish against the persecution of witches. His most influential work is ('On the Illusions of the Demons and on Spells and Poisons'; 1563). Biography Weyer was born in Grave, a small town in the Duchy of Brabant in the Habsburg Netherlands. He attended the Latin schools in 's-Hertogenbosch and Leuven and when he was about 14 years of age, he became a live-in student of Agrippa, in Antwerp. Agrippa had to leave Antwerp in 1532 and he and Weyer settled in Bonn, under the protection of prince-bishop Hermann von Wied. (Agrippa completed a work on demons in 1533 and perished two years later while on a trip to France). From 1534, Weyer studied medicine in Paris and later in Orléans, but it appears unlikely that he obtained the title of Doctor through these s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demonology
Demonology is the study of demons within religious belief and myth. Depending on context, it can refer to studies within theology, religious doctrine, or pseudoscience. In many faiths, it concerns the study of a hierarchy of demons. Demons may be nonhuman, separable souls, or discarnate spirits which have never inhabited a body. A sharp distinction is often drawn between these two classes, notably by the Melanesians, several African groups, and others. The Islamic jinn, for example, are not reducible to modified human souls. At the same time these classes are frequently conceived as producing identical results, e.g. diseases.van der Toorn, Becking, van der Horst (1999), ''Dictionary of Deities and Demons in The Bible'', Second Extensively Revised Edition, Entry: Demon, pp. 235-240, William B. Eerdmans Publishing Company, Prevalence of demons According to some societies, all the affairs of the universe are supposed to be under the control of spirits, each ruling a certain " e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)