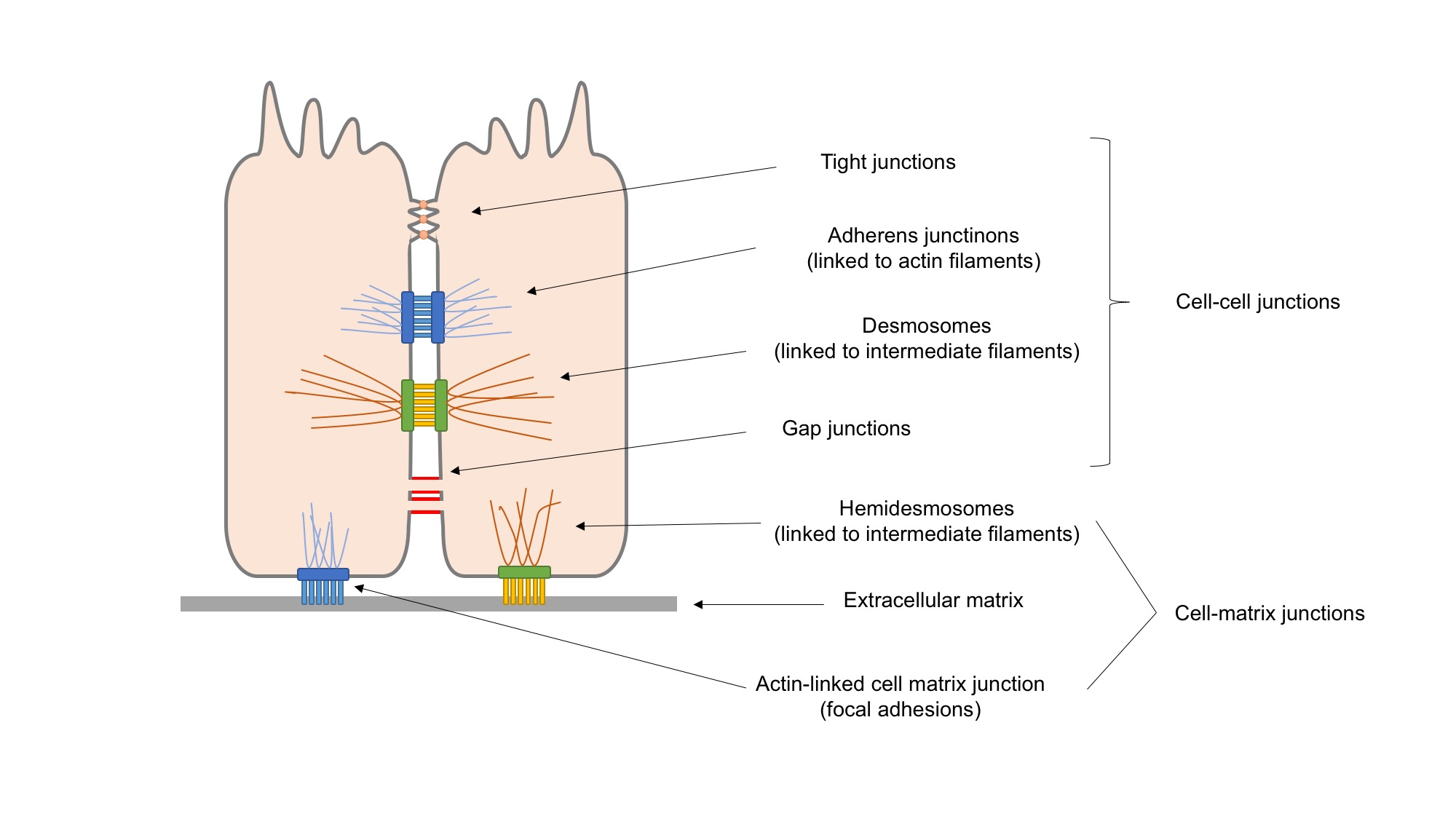
|
Vasodilator-stimulated Phosphoprotein
Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''VASP'' gene. Function Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) is a member of the Ena-VASP protein family. Ena-VASP family members contain an N-terminal EVH1 domain that binds proteins containing E/DFPPPPXD/E motifs and targets Ena-VASP proteins to focal adhesions cell membranes. In the mid-region of the protein, family members have a proline-rich region that binds SH3 and WW domain-containing proteins. Their C-terminal EVH2 domain mediates tetramerization and binds both G and F actin. VASP is associated with filamentous actin formation and likely plays a widespread role in cell adhesion and motility. VASP may also be involved in the intracellular signaling pathways that regulate integrin-extracellular matrix interactions. VASP is regulated by the cyclic nucleotide-dependent kinases PKA and PKG. Interactions Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein has been shown to interact with Zyxin, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Motility
Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy. Definitions Motility, the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy, can be contrasted with sessility, the state of organisms that do not possess a means of self-locomotion and are normally immobile. Motility differs from mobility, the ability of an object to be moved. The term vagility encompasses both motility and mobility; sessile organisms including plants and fungi often have vagile parts such as fruits, seeds, or spores which may be dispersed by other agents such as wind, water, or other organisms. Motility is genetically determined, but may be affected by environmental factors such as toxins. The nervous system and musculoskeletal system provide the majority of mammalian motility. In addition to animal locomotion, most animals are motile, though some are vagile, described as having passive locomotion. Many bacteria and other microorganisms, and multicellu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Profilin 1
Profilin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PFN1'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a ubiquitous actin monomer-binding protein belonging to the profilin family. It is thought to regulate actin polymerization in response to extracellular signals. Deletion of this gene is associated with Miller-Dieker syndrome. Mutations in this gene may be a rare cause of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, also called Lou Gehrig's disease. Interactions Profilin 1 has been shown to interact with: * FMNL1, * MLLT4 * Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein, * WASF1 Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome protein family member 1, also known as WASP-family verprolin homologous protein 1 (WAVE1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''WASF1'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene, a member of the Wisko ..., and * WASL. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{Cytoskeletal Proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zyxin
Zyxin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ZYX'' gene. Function Focal adhesions are actin-rich structures that enable cells to adhere to the extracellular matrix and at which protein complexes involved in signal transduction assemble. Zyxin is a zinc-binding phosphoprotein that concentrates at focal adhesions and along the actin cytoskeleton. Zyxin has an N-terminal proline-rich domain and three LIM domains in its C-terminal half. The proline-rich domain may interact with SH3 domains of proteins involved in signal transduction pathways while the LIM domains are likely involved in protein-protein binding. Zyxin may function as a messenger in the signal transduction pathway that mediates adhesion-stimulated changes in gene expression and may modulate the cytoskeletal organization of actin bundles. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants that encode the same isoform. Interactions Zyxin has been shown to interact with: * Actinin, alpha 1 * ENAH, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CGMP-dependent Protein Kinase
cGMP-dependent protein kinase or protein kinase G (PKG) is a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase that is activated by cGMP. It phosphorylates a number of biologically important targets and is implicated in the regulation of smooth muscle relaxation, platelet function, sperm metabolism, cell division, and nucleic acid synthesis. Genes and proteins PKG are serine/threonine kinases that are present in a variety of eukaryotes ranging from the unicellular organism ''Paramecium'' to humans. Two PKG genes, coding for PKG type I (PKG-I) and type II (PKG-II), have been identified in mammals. The N-terminus of PKG-I is encoded by two alternatively spliced exons that specify for the PKG-Iα and PKG-Iβ isoforms. PKG-Iβ is activated at ~10-fold higher cGMP concentrations than PKG-Iα. The PKG-I and PKG-II are homodimers of two identical subunits (~75 kDa and ~85 kDa, respectively) and share common structural features. Each subunit is composed of three functional domains: * ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Kinase A
In cell biology, protein kinase A (PKA) is a family of enzymes whose activity is dependent on cellular levels of cyclic AMP (cAMP). PKA is also known as cAMP-dependent protein kinase (). PKA has several functions in the cell, including regulation of glycogen, sugar, and lipid metabolism. It should not be confused with 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMP-activated protein kinase). History Protein kinase A, more precisely known as adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate (cyclic AMP)-dependent protein kinase, abbreviated to PKA, was discovered by chemists Edmond H. Fischer and Edwin G. Krebs in 1968. They won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1992 for their work on phosphorylation and dephosphorylation and how it relates to PKA activity. PKA is one of the most widely researched protein kinases, in part because of its uniqueness; out of 540 different protein kinase genes that make up the human kinome, only one other protein kinase, casein kinase 2, is known to exist in a physio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extracellular Matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM. The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the Interstitial fluid, interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrin
Integrins are transmembrane receptors that facilitate cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion. Upon ligand binding, integrins activate signal transduction pathways that mediate cellular signals such as regulation of the cell cycle, organization of the intracellular cytoskeleton, and movement of new receptors to the cell membrane. The presence of integrins allows rapid and flexible responses to events at the cell surface (''e.g''. signal platelets to initiate an interaction with coagulation factors). Several types of integrins exist, and one cell generally has multiple different types on its surface. Integrins are found in all animals while integrin-like receptors are found in plant cells. Integrins work alongside other proteins such as cadherins, the immunoglobulin superfamily cell adhesion molecules, selectins and syndecans, to mediate cell–cell and cell–matrix interaction. Ligands for integrins include fibronectin, vitronectin, collagen and laminin. Stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Adhesion
Cell adhesion is the process by which cells interact and attach to neighbouring cells through specialised molecules of the cell surface. This process can occur either through direct contact between cell surfaces such as cell junctions or indirect interaction, where cells attach to surrounding extracellular matrix, a gel-like structure containing molecules released by cells into spaces between them. Cells adhesion occurs from the interactions between cell-adhesion molecules (CAMs), transmembrane proteins located on the cell surface. Cell adhesion links cells in different ways and can be involved in signal transduction for cells to detect and respond to changes in the surroundings. Other cellular processes regulated by cell adhesion include cell migration and tissue development in multicellular organisms. Alterations in cell adhesion can disrupt important cellular processes and lead to a variety of diseases, including cancer and arthritis. Cell adhesion is also essential for in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of over 100 μM; its mass is roughly 42 kDa, with a diameter of 4 to 7 nm. An actin protein is the monomeric subunit of two types of filaments in cells: microfilaments, one of the three major components of the cytoskeleton, and thin filaments, part of the contractile apparatus in muscle cells. It can be present as either a free monomer called G-actin (globular) or as part of a linear polymer microfilament called F-actin (filamentous), both of which are essential for such important cellular functions as the mobility and contraction of cells during cell division. Actin participates in many important cellular processes, including muscle contraction, cell motility, cell division and cytokinesis, vesicle and organelle movement, cell sign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |