|
Vardarski Rid
View of forum Vardarski Rid is an archaeological site in Gevgelija, North Macedonia of a town dating from Early Antiquity. Archaeological excavations reveal the architectural layout of the monumental stoa, an acropolis, and other segments from the settlement. Vardarski Rid is also used today as a picnic spot. Geography Vardarski Rid is located in the central part of the Lower Vardar Valley. It is located at a dominant strategic position above the Gevgelija Plain, Gevgelija, and the Vardar River. The Vardar River surrounds the ancient town's northern and eastern border. The lowlands of the Gevgelija Plain stretch west and south of Vardarski Rid. The site consists of two hills, one hill is taller and steeper, and the other is shorter. Museum Parts of the excavations are exhibited in the municipal museum, Gevgelija. See also *Heraclea Lyncestis Heraclea Lyncestis, also transliterated Herakleia Lynkestis ( grc, ß╝®Žü╬¼╬║╬╗╬Ą╬╣╬▒ ╬øŽģ╬│╬║╬ĘŽāŽä╬»Žé; la, Heraclea Lyncestis; mk, ąźą ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forum 02484
Forum or The Forum (plural forums or fora) may refer to: Common uses *Forum (legal), designated space for public expression in the United States *Forum (Roman), open public space within a Roman city **Roman Forum, most famous example *Internet forum, discussion board on the Internet *Public forum debate, a type of high school debate Arts and entertainment * Forum & Forum Expanded, a section of the Berlin International Film Festival * ''Forum'' (album), a 2001 pop/soft rock album by Invertigo *The Forum (vocal group), organized by American musician Les Baxter *Forum theatre, a type of theatrical technique created by Brazilian theatre director Augusto Boal *Forum Theatre (Washington, D.C.), a former theatre group Buildings Shopping centres *Foorum, Tallinn, Estonia *Forum (shopping centre), Helsinki, Finland * The Forum (shopping mall), Bangalore, India *Forum Mall (Kolkata), Kolkata, India *Forum The Shopping Mall, Singapore *The Forum on Peachtree Parkway, Peachtree Corners, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Site
An archaeological site is a place (or group of physical sites) in which evidence of past activity is preserved (either prehistoric or historic or contemporary), and which has been, or may be, investigated using the discipline of archaeology and represents a part of the archaeological record. Sites may range from those with few or no remains visible above ground, to buildings and other structures still in use. Beyond this, the definition and geographical extent of a "site" can vary widely, depending on the period studied and the theoretical approach of the archaeologist. Geographical extent It is almost invariably difficult to delimit a site. It is sometimes taken to indicate a settlement of some sort although the archaeologist must also define the limits of human activity around the settlement. Any episode of deposition such as a hoard or burial can form a site as well. Development-led archaeology undertaken as cultural resources management has the disadvantage (or the ben ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gevgelija
Gevgelija ( mk, ąōąĄą▓ą│ąĄą╗ąĖčśą░; ) is a town with a population of 15,685 located in the very southeast of the North Macedonia along the banks of the Vardar River, situated at the country's main border with Greece (Bogorodica-Evzoni), the point which links the motorway from Skopje and three regional capitals, Belgrade, Zagreb, and Sofia with Thessaloniki in Greece. The town is the seat of Gevgelija municipality. Name In Macedonian the town is called ''Gevgelija'' (ąōąĄą▓ą│ąĄą╗ąĖčśą░). It is known as ''Gevgeli'' (ąōąĄą▓ą│ąĄą╗ąĖ) in Bulgarian, ''Gevgeli'' in Turkish, ''─Éev─æelija'' (ąéąĄą▓čÆąĄą╗ąĖčśą░, ) in Serbian and ''Yevyel├Ł'' (╬ō╬ĄŽģ╬│╬Ą╬╗╬«) in Greek. Furthermore, in Megleno-Romanian, the city is known as . Gevgelija is known as the "Balkan Las Vegas". History In the late 19th and early 20th century, Gevgelija was part of the Salonica Vilayet of the Ottoman Empire. According to the statistics of the French geographer Alexandre Synvet, the town had a total Christian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Macedonia
North Macedonia, ; sq, Maqedonia e Veriut, (Macedonia before February 2019), officially the Republic of North Macedonia,, is a country in Southeast Europe. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Yugoslavia. It is a landlocked country bordering Kosovo to the northwest, Serbia to the north, Bulgaria to the east, Greece to the south, and Albania to the west. It constitutes approximately the northern third of the larger geographical Macedonia (region), region of Macedonia. Skopje, the capital and largest city, is home to a quarter of the country's 1.83 million people. The majority of the residents are ethnic Macedonians (ethnic group), Macedonians, a South Slavs, South Slavic people. Albanians in North Macedonia, Albanians form a significant minority at around 25%, followed by Turks in North Macedonia, Turks, Romani people in North Macedonia, Romani, Serbs in North Macedonia, Serbs, Bosniaks in North Mac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome known as the Greco-Roman world. It is the period in which both Greek and Roman societies flourished and wielded huge influence throughout much of Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia. Conventionally, it is taken to begin with the earliest-recorded Epic Greek poetry of Homer (8thŌĆō7th-century BC), and continues through the emergence of Christianity (1st century AD) and the fall of the Western Roman Empire (5th-century AD). It ends with the decline of classical culture during late antiquity (250ŌĆō750), a period overlapping with the Early Middle Ages (600ŌĆō1000). Such a wide span of history and territory covers many disparate cultures and periods. ''Classical antiquity'' may also refer to an idealized v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acropolis
An acropolis was the settlement of an upper part of an ancient Greek city, especially a citadel, and frequently a hill with precipitous sides, mainly chosen for purposes of defense. The term is typically used to refer to the Acropolis of Athens, yet every Greek city had an acropolis of its own. Acropoloi were used as religious centers and places of worship, forts, and places in which the royal and high-status resided. Acropolises became the nuclei of large cities of classical ancient times, and served as important centers of a community. Some well-known acropoloi have become the centers of tourism in present-day, and, especially, the Acropolis of Athens has been a revolutionary center for the studies of ancient Greece since the Mycenaean period. Many of them have become a source of revenue for Greece, and represent some great technology during the period. Origin An acropolis is defined by the Greek definition of ß╝Ć╬║ŽüŽīŽĆ╬┐╬╗╬╣Žé, akropolis; from akros (╬¼╬║Žü╬┐Žé) or (╬¼╬║ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vardar
The Vardar (; mk, , , ) or Axios () is the longest river in North Macedonia and the second longest river in Greece, in which it reaches the Aegean Sea at Thessaloniki. It is long, out of which are in Greece, and drains an area of around . The maximum depth of the river is . Etymology The origin of the name ''Vardar'' derives from Thracian ''Vard├Īrios''. It comes from Proto-Indo-European (PIE) *''(s)wordo-wori-'' ("black water"). It can be considered a translation or similar meaning of ''Axios'', which itself is Thracian for 'not-shining' from PIE *''n.-sk(e)i'' (cf. Avestan ''ax┼Īa─ōna'' ("dark-coloured")). It is found in another name of the city at the mouth of the Danube, called ''Ax├Łopa'' ("dark water") in Thracian, which was later translated into Slavic as '' Cernavod─ā'' (ŌĆ£black waterŌĆØ).Kati─Źic', Radoslav. ''Ancient Languages of the Balkans''. Paris: Mouton, 1976: 149 The name ''Vard├Īrios'' (╬Æ╬▒Žü╬┤╬¼Žü╬╣╬┐Žé) was sometimes used by the Ancient Greeks in the 3rd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heraclea Lyncestis
Heraclea Lyncestis, also transliterated Herakleia Lynkestis ( grc, ß╝®Žü╬¼╬║╬╗╬Ą╬╣╬▒ ╬øŽģ╬│╬║╬ĘŽāŽä╬»Žé; la, Heraclea Lyncestis; mk, ąźąĄčĆą░ą║ą╗ąĄčśą░ ąøąĖąĮą║ąĄčüčéąĖčü), was an ancient Greek city in Macedon, ruled later by the Romans. Its ruins are situated south of the present-day town of Bitola, North Macedonia. In the early Christian period, Heraclea was an important Episcopal seat and a waypoint on the Via Egnatia that once linked Byzantium with Rome through the Adriatic seaport Dyrrachium. Some of its bishops are mentioned in synods in Serdica and other nearby towns. The city was gradually abandoned in the 6th century AD following an earthquake and Slavic invasions. Foundation by Philip II It was founded by Philip II of Macedon in the middle of the 4th century BC. The city was named in honor of the mythological hero Heracles. The name ''Lynkestis'' originates from the name of the ancient kingdom, conquered by Philip, where the city was built. Heraclea was a stra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
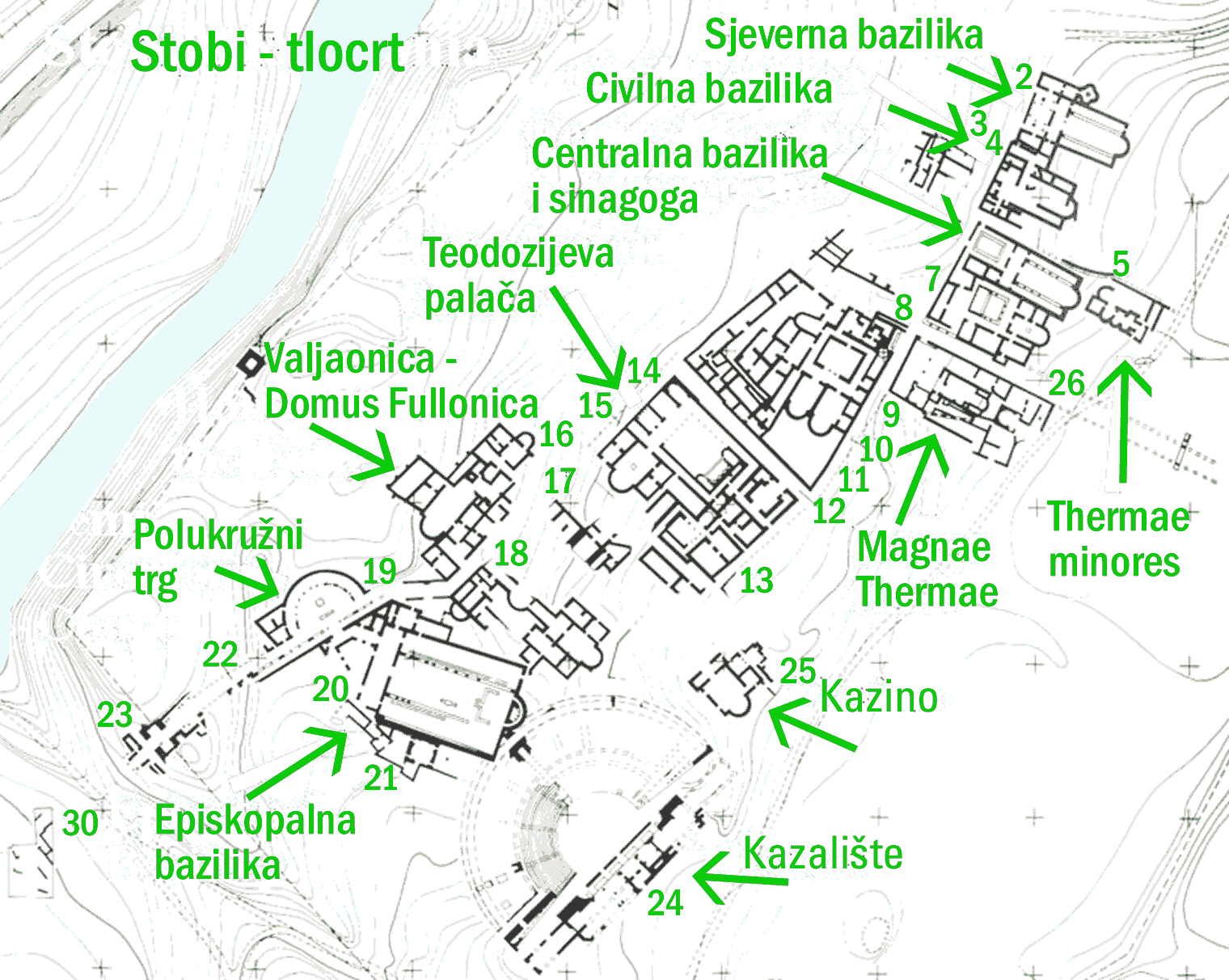
Stobi
Stobi or Stoboi ( grc, ╬ŻŽäŽī╬▓╬┐╬╣, St├│boi; la, Stobi; mk, ąĪč鹊ą▒ąĖ, Stobi), was an ancient town of Paeonia, later conquered by Macedon, and finally turned into the capital of the Roman province of Macedonia Salutaris. It is located near Gradsko, North Macedonia, on the main road that leads from the Danube to the Aegean Sea and is considered by many to be the most famous archaeological site in North Macedonia. Stobi was built where the Erigon (Crna River) joins the Axios (Vardar), making it strategically important as a center for both trade and warfare. The pre-Roman period Stobi developed from a Paeonian settlement established in the Archaic period. Located on the northern side of a terrace, the early town covered an area of about . Its proximity to the junction of the Erig├│n and Axi├│s Rivers as well as its position in the fertile central Vardar valley allowed it quickly to develop a flourishing economy and to establish trade. Nearby Mount Klepa was a lucrative s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In North Macedonia
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America ŌĆō the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Populated Places In The Balkans
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
