|
VNIR
The visible and near-infrared (VNIR) portion of the electromagnetic spectrum has wavelengths between approximately 400 and 1100 nanometers (nm). It combines the full visible spectrum with an adjacent portion of the infrared spectrum up to the water absorption band between 1400 and 1500 nm. Some definitions also include the short-wavelength infrared band from 1400 nm up to the water absorption band at 2500 nm. VNIR multi-spectral image cameras have wide applications in remote sensing and imaging spectroscopy. Hyperspectral Imaging Satellite carried two payloads, among which one was working on the spectral range of VNIR. See also * Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer * Airborne Real-time Cueing Hyperspectral Enhanced Reconnaissance * Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter * Near infrared spectroscopy Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is a spectroscopic method that uses the near-infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum (from 780 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission And Reflection Radiometer
The Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) is a Japanese remote sensing instrument onboard the Terra satellite launched by NASA in 1999. It has been collecting data since February 2000. ASTER provides high-resolution images of Earth in 14 different bands of the electromagnetic spectrum, ranging from visible to thermal infrared light. The resolution of images ranges between 15 and 90 meters. ASTER data is used to create detailed maps of surface temperature of land, emissivity, reflectance, and elevation. In April 2008, the SWIR detectors of ASTER began malfunctioning and were publicly declared non-operational by NASA in January 2009. All SWIR data collected after 1 April 2008 has been marked as unusable. The ASTER Global Digital Elevation Model (GDEM) is available at no charge to users worldwide via electronic download. As of 2 April 2016, the entire catalogue of ASTER image data became publicly available online at no cost. It can be download ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperspectral Imaging Satellite
HySIS (Hyperspectral Imaging Satellite) is an Earth observation satellite which will provide hyperspectral imaging services to India for a range of applications in agriculture, forestry and in the assessment of geography such as coastal zones and inland waterways The data will also be accessible to India's defence forces. Before HySIS, other Indian hyperspectral imaging payloads were HySI (Hyper Spectral Imager) on IMS-1 and Chandrayaan-1 and LiVHySI (Limb Viewing Hyper Spectral Imager) on YouthSat. Payloads HySIS carries two payloads, the first is the Visible Near Infrared (VNIR) with spectral range of 0.4 to 0.95 micrometres with 60 contiguous spectral bands and the second is the Shortwave Infrared Range (SWIR) with spectral range of 0.85 to 2.4 micrometres with a 10 nanometre bandwidth and 256 contiguous spectral bands. The satellite will have a spatial resolution of 30 metres and a swath of 30 km from its 630 km sun-synchronous orbit. Space Applications Cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remote Sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring information about Earth and other planets. Remote sensing is used in numerous fields, including geography, land surveying and most Earth science disciplines (e.g. hydrology, ecology, meteorology, oceanography, glaciology, geology); it also has military, intelligence, commercial, economic, planning, and humanitarian applications, among others. In current usage, the term ''remote sensing'' generally refers to the use of satellite- or aircraft-based sensor technologies to detect and classify objects on Earth. It includes the surface and the atmosphere and oceans, based on propagated signals (e.g. electromagnetic radiation). It may be split into "active" remote sensing (when a signal is emitted by a satellite or aircraft to the object and its reflection dete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' (MRO) is a spacecraft designed to study the geology and climate of Mars, provide reconnaissance of future landing sites, and relay data from surface missions back to Earth. It was launched on August 12, 2005, and reached Mars on March 10, 2006. In November 2006, after five months of aerobraking, it entered its final science orbit and began its primary science phase. The cost to develop and operate MRO through the end of its prime mission in 2010 was . The spacecraft continues to operate at Mars, far beyond its intended design life. Due to its critical role as a high-speed data-relay for ground missions, NASA intends to continue the mission as long as possible, at least through the late 2020s. Pre-launch After the twin failures of the ''Mars Climate Orbiter'' and the Mars Polar Lander missions in 1999, NASA reorganized and replanned its Mars Exploration Program. In October 2000, NASA announced its reformulated Mars plans, which reduced the nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landsat Art Ghadamis
The Landsat program is the longest-running enterprise for acquisition of satellite imagery of Earth. It is a joint NASA / USGS program. On 23 July 1972, the Earth Resources Technology Satellite was launched. This was eventually renamed to Landsat 1 in 1975. The most recent, Landsat 9, was launched on 27 September 2021. The instruments on the Landsat satellites have acquired millions of images. The images, archived in the United States and at Landsat receiving stations around the world, are a unique resource for global change research and applications in agriculture, cartography, geology, forestry, regional planning, surveillance and education, and can be viewed through the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) "EarthExplorer" website. Landsat 7 data has eight spectral bands with spatial resolutions ranging from ; the temporal resolution is 16 days. Landsat images are usually divided into scenes for easy downloading. Each Landsat scene is about 115 miles long and 115 miles wide ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
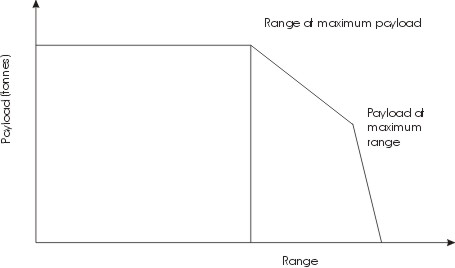
Payloads
Payload is the object or the entity which is being carried by an aircraft or launch vehicle. Sometimes payload also refers to the carrying capacity of an aircraft or launch vehicle, usually measured in terms of weight. Depending on the nature of the flight or mission, the payload of a vehicle may include cargo, passengers, flight crew, munitions, scientific instruments or experiments, or other equipment. Extra fuel, when optionally carried, is also considered part of the payload. In a commercial context (i.e., an airline or air freight carrier), payload may refer only to revenue-generating cargo or paying passengers. A payload of ordnance carried by a combat aircraft is sometimes alternatively referred to as the aircraft's warload. For a rocket, the payload can be a satellite, space probe, or spacecraft carrying humans, animals, or cargo. For a ballistic missile, the payload is one or more warheads and related systems; their total weight is referred to as the throw-weight. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imaging Spectroscopy
In imaging spectroscopy (also hyperspectral imaging or spectral imaging) each pixel of an image acquires many bands of light intensity data from the spectrum, instead of just the three bands of the RGB color model. More precisely, it is the simultaneous acquisition of spatially coregistered images in many spectrally contiguous bands. Some spectral images contain only a few image planes of a spectral data cube, while others are better thought of as full spectra at every location in the image. For example, solar physicists use the spectroheliograph to make images of the Sun built up by scanning the slit of a spectrograph, to study the behavior of surface features on the Sun; such a spectroheliogram may have a spectral resolution of over 100,000 (\lambda / \Delta \lambda) and be used to measure local motion (via the Doppler shift) and even the magnetic field (via the Zeeman splitting or Hanle effect) at each location in the image plane. The multispectral images collected by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-spectral Image
Multispectral imaging captures image data within specific wavelength ranges across the electromagnetic spectrum. The wavelengths may be separated by filters or detected with the use of instruments that are sensitive to particular wavelengths, including light from frequencies beyond the visible light range, i.e. infrared and ultra-violet. It can allow extraction of additional information the human eye fails to capture with its visible receptors for red, green and blue. It was originally developed for military target identification and reconnaissance. Early space-based imaging platforms incorporated multispectral imaging technology to map details of the Earth related to coastal boundaries, vegetation, and landforms. Multispectral imaging has also found use in document and painting analysis. Multispectral imaging measures light in a small number (typically 3 to 15) of spectral bands. Hyperspectral imaging is a special case of spectral imaging where often hundreds of contiguous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of frequencies (the spectrum) of electromagnetic radiation and their respective wavelengths and photon energies. The electromagnetic spectrum covers electromagnetic waves with frequencies ranging from below one hertz to above 1025 hertz, corresponding to wavelengths from thousands of kilometers down to a fraction of the size of an atomic nucleus. This frequency range is divided into separate bands, and the electromagnetic waves within each frequency band are called by different names; beginning at the low frequency (long wavelength) end of the spectrum these are: radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays at the high-frequency (short wavelength) end. The electromagnetic waves in each of these bands have different characteristics, such as how they are produced, how they interact with matter, and their practical applications. There is no known limit for long and short wavelengths. Extre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Absorption
The absorption of electromagnetic radiation by water depends on the state of the water. The absorption in the gas phase occurs in three regions of the spectrum. Rotational transitions are responsible for absorption in the microwave and far-infrared, vibrational transitions in the mid-infrared and near-infrared. Vibrational bands have rotational fine structure. Electronic transitions occur in the vacuum ultraviolet regions. Liquid water has no rotational spectrum but does absorb in the microwave region. Its weak absorption in the visible spectrum results in the pale blue color of water. Overview The water molecule, in the gaseous state, has three types of transition that can give rise to absorption of electromagnetic radiation: * Rotational transitions, in which the molecule gains a quantum of rotational energy. Atmospheric water vapour at ambient temperature and pressure gives rise to absorption in the far-infrared region of the spectrum, from about 200 cm−1 (50 � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrum
A spectrum (plural ''spectra'' or ''spectrums'') is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary, without gaps, across a continuum. The word was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light after passing through a prism. As scientific understanding of light advanced, it came to apply to the entire electromagnetic spectrum. It thereby became a mapping of a range of magnitudes (wavelengths) to a range of qualities, which are the perceived "colors of the rainbow" and other properties which correspond to wavelengths that lie outside of the visible light spectrum. Spectrum has since been applied by analogy to topics outside optics. Thus, one might talk about the " spectrum of political opinion", or the "spectrum of activity" of a drug, or the " autism spectrum". In these uses, values within a spectrum may not be associated with precisely quantifiable numbers or definitions. Such uses imply a broad range of cond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)