|
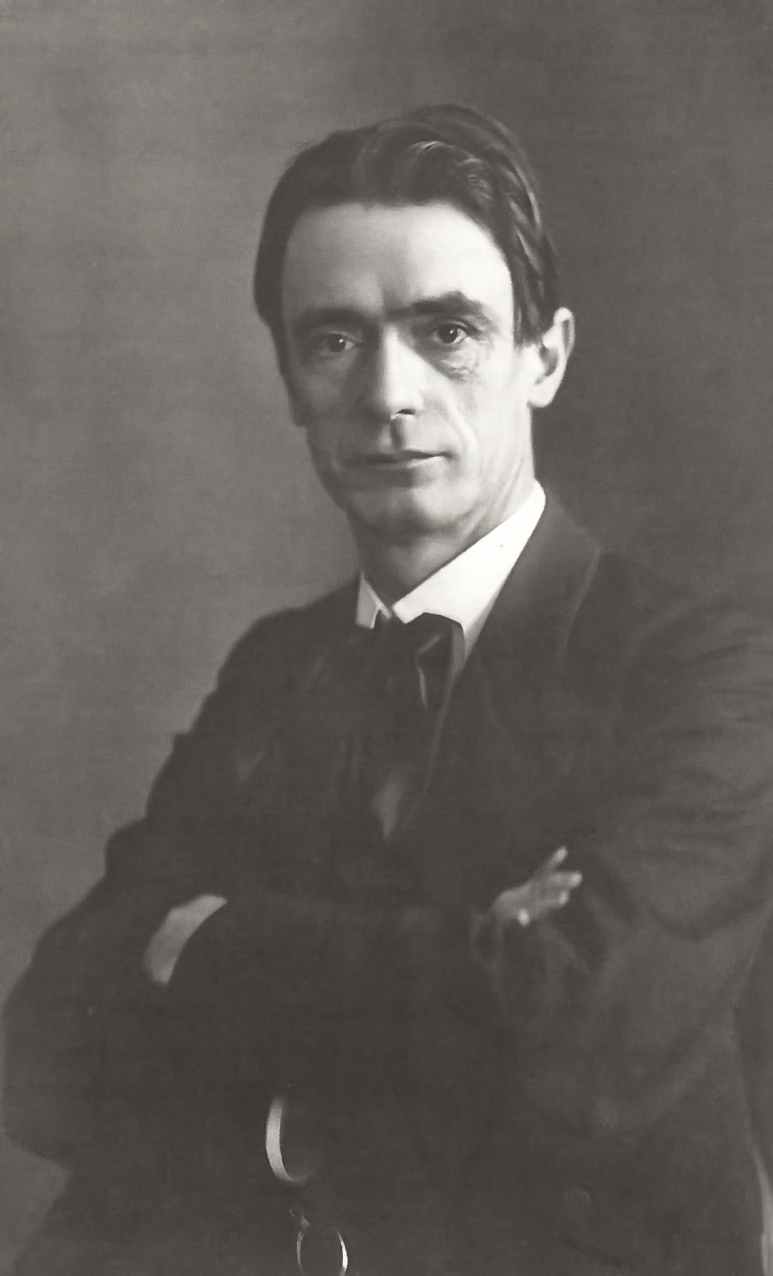
Vydūnas
Wilhelm Storost, artistic name Vilius Storostas-Vydūnas (22 March 1868 – 20 February 1953), mostly known as Vydūnas, was a Prussian-Lithuanian teacher, poet, humanist, philosopher and Lithuanian writer, a leader of the Prussian Lithuanian national movement in Lithuania Minor, and one of leaders of the theosophical movement in East Prussia. Biography The Storost family was a long-established family in East Prussia and Wilhelm was born in the village of Jonaten ( lt, Jonaičiai), near Heydekrug, in the Kingdom of Prussia. Wilhelm Storost was the name on his German passport, while Vilimas or Vilius Storostas was the literature Lithuanian form used by himself, his family, and other Lithuanians. "Vydūnas" was added to his surname as a pseudonym when he was about 40 years old. Storost was married to Klara Füllhase. Storost was educated as teacher at the Präparandenanstalt in Pillkallen (lit. Pilkalnis) (1883–85) and at teacher seminar in Ragnit (lit. Ragainė) (18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vydūnas Delivers A Speech
Wilhelm Storost, artistic name Vilius Storostas-Vydūnas (22 March 1868 – 20 February 1953), mostly known as Vydūnas, was a Prussian-Lithuanian teacher, poet, humanist, philosopher and Lithuanian writer, a leader of the Prussian Lithuanian national movement in Lithuania Minor, and one of leaders of the theosophical movement in East Prussia. Biography The Storost family was a long-established family in East Prussia and Wilhelm was born in the village of Jonaten ( lt, Jonaičiai), near Heydekrug, in the Kingdom of Prussia. Wilhelm Storost was the name on his German passport, while Vilimas or Vilius Storostas was the literature Lithuanian form used by himself, his family, and other Lithuanians. "Vydūnas" was added to his surname as a pseudonym when he was about 40 years old. Storost was married to Klara Füllhase. Storost was educated as teacher at the Präparandenanstalt in Pillkallen (lit. Pilkalnis) (1883–85) and at teacher seminar in Ragnit (lit. Ragainė) (1885 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vydūnas Plays A Harp
Wilhelm Storost, artistic name Vilius Storostas-Vydūnas (22 March 1868 – 20 February 1953), mostly known as Vydūnas, was a Prussian-Lithuanian teacher, poet, humanist, philosopher and Lithuanian writer, a leader of the Prussian Lithuanian national movement in Lithuania Minor, and one of leaders of the theosophical movement in East Prussia. Biography The Storost family was a long-established family in East Prussia and Wilhelm was born in the village of Jonaten ( lt, Jonaičiai), near Heydekrug, in the Kingdom of Prussia. Wilhelm Storost was the name on his German passport, while Vilimas or Vilius Storostas was the literature Lithuanian form used by himself, his family, and other Lithuanians. "Vydūnas" was added to his surname as a pseudonym when he was about 40 years old. Storost was married to Klara Füllhase. Storost was educated as teacher at the Präparandenanstalt in Pillkallen (lit. Pilkalnis) (1883–85) and at teacher seminar in Ragnit (lit. Ragainė) (1885 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romuva (religion)
Romuva is a neo-pagan movement derived from the traditional mythology of the Lithuanians, attempting to reconstruct the religious rituals of the Lithuanians before their forced Christianization in 1387. Practitioners of Romuva claim to continue Baltic pagan traditions which survived in folklore, customs and superstition. Romuva is a polytheistic pagan faith which asserts the sanctity of nature and ancestor worship. Practicing the Romuva faith is seen by many adherents as a form of cultural pride, along with celebrating traditional forms of art, retelling Baltic folklore, practising traditional holidays, playing traditional Baltic music, singing traditional (songs), as well as ecological activism and stewarding sacred places. Romuva primarily exists in Lithuania but there are also congregations of adherents in Australia, Canada, Russia, the United States, and England. There are believers of Baltic pagan faiths in other nations, including Dievturība in Latvia.Dundzila (200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthroposophic
Anthroposophy is a spiritualist movement founded in the early 20th century by the esotericist Rudolf Steiner that postulates the existence of an objective, intellectually comprehensible spiritual world, accessible to human experience. Followers of anthroposophy aim to engage in spiritual discovery through a mode of thought independent of sensory experience. While much of anthroposophy is pseudoscientific, proponents claim to present their ideas in a manner that is verifiable by rational discourse and say that they seek precision and clarity comparable to that obtained by scientists investigating the physical world. Anthroposophy has its roots in German idealism, mystical philosophies, and pseudoscience including racist pseudoscience. Steiner chose the term ''anthroposophy'' (from Greek , 'human', and '' sophia'', 'wisdom') to emphasize his philosophy's humanistic orientation. He defined it as "a scientific exploration of the spiritual world", Others have variously called it a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bitėnai
Bitėnai (german: Bittehnen) is a small village in the Pagėgiai Municipality, in western Lithuania. According to the 2011 census, it had population of 76, a decline from 119 in 2001. It is situated along the Neman River near the Rambynas hill and is known as the location of the Martynas Jankus printing press. Jankus Museum and the visitors' center of the Rambynas Regional Park are located in the village. History Bitėnai was a village of peasants and fishermen. In 1454, King Casimir IV Jagiellon incorporated the region to the Kingdom of Poland upon the request of the anti-Teutonic Prussian Confederation. After the subsequent Thirteen Years' War (1454–1466) the village was a part of Poland as a fief held by the Teutonic Knights,Górski, pp. 96–97, 214–215 and thus was located within the Polish–Lithuanian union, later elevated to the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. From the 18th century, it was part of the Kingdom of Prussia, and from 1871 it was also part of Germany, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kintai
Kintai is a small town in Klaipėda County, in Lithuania. It is the center of the Eldership (Seniūnija) Kintai and is part of the Šilutė District Municipality. According to the 2011 census, the town has a population of 616 people. Geography Kintai is located in western Lithuania, in the historic region of Lithuania Minor, at the Curonian Lagoon. There are three roads to Kintai, coming from Šilutė, Vent�and Priekulė, Lithuania, Priekulė. To the north of Kintai is the 800 ha wide forest of Kinta To the southeast is the Nemunas Delta Regional Park. Europes second highest Giant Cedar, with a height of 18m, is located in Kintai. History The towns name originates from the words ''Kintas, Kìnta''. Kintai began to appear in the 16th century, when it was located within the Polish–Lithuanian union, soon elevated to the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, as a fief of Poland held by Ducal Prussia. The settlement really started to grow in the beginning of the 18th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Šilutė District Municipality
Šilutė (, previously ''Šilokarčiama'', german: link=no, Heydekrug), is a city in the south of the Klaipėda County, Lithuania. The city was part of the Klaipėda Region and ethnographic Lithuania Minor. Šilutė was the interwar period, interwar capital of Šilutė County and is currently the capital of Šilutė District Municipality. Name Šilutė's origin dates to an Public house#Inns, inn (Krug, locally ''karčema'') catering to travelers and their horses which was located halfway between Klaipėda, Memel (Klaipėda) and Sovetsk, Kaliningrad Oblast, Tilsit (Tilžė). The German name of ''Heydekrug'' referred to a ''Krug'' (an archaic word for inn) in the ''Heide'' (heathland). The inn was known for being in the region where most people spoke the Memelland-Samogitian dialect ''Šilokarčema''. History A famous fish market was opened in Šilutė almost 500 years ago, when Georg Tallat purchased the inn together with the land and fishing rights in 1511. The town was a gather ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Šilutė
Šilutė (, previously ''Šilokarčiama'', german: link=no, Heydekrug), is a city in the south of the Klaipėda County, Lithuania. The city was part of the Klaipėda Region and ethnographic Lithuania Minor. Šilutė was the interwar capital of Šilutė County and is currently the capital of Šilutė District Municipality. Name Šilutė's origin dates to an inn (Krug, locally ''karčema'') catering to travelers and their horses which was located halfway between Memel (Klaipėda) and Tilsit (Tilžė). The German name of ''Heydekrug'' referred to a ''Krug'' (an archaic word for inn) in the ''Heide'' (heathland). The inn was known for being in the region where most people spoke the Memelland-Samogitian dialect ''Šilokarčema''. History A famous fish market was opened in Šilutė almost 500 years ago, when Georg Tallat purchased the inn together with the land and fishing rights in 1511. The town was a gathering place for peasants from nearby Samogitia and Curonian and Prussian fis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
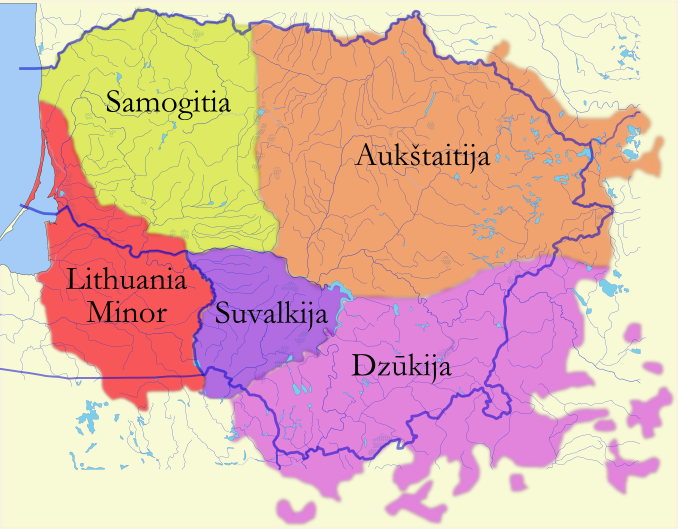
Lithuania Minor
Lithuania Minor ( lt, Mažoji Lietuva; german: Kleinlitauen; pl, Litwa Mniejsza; russian: Ма́лая Литва́), or Prussian Lithuania ( lt, Prūsų Lietuva; german: Preußisch-Litauen, pl, Litwa Pruska), is a historical ethnographic region of Prussia, where Prussian Lithuanians (or Lietuvininkai) lived, now located in Lithuania and the Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia. Lithuania Minor encompassed the northeastern part of the region and got its name from the territory's substantial Lithuanian-speaking population. Prior to the invasion of the Teutonic Knights in the 13th century, the main part of the territory later known as Lithuania Minor was inhabited by the tribes of Skalvians and Nadruvians. The land depopulated during the incessant war between Lithuania and the Teutonic Order. The war ended with the Treaty of Melno and the land was repopulated by Lithuanian newcomers, returning refugees, and the remaining indigenous Baltic peoples; the term Lithuania Minor appeared for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It was the driving force behind the unification of Germany in 1871 and was the leading state of the German Empire until its dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin. The kings of Prussia were from the House of Hohenzollern. Brandenburg-Prussia, predecessor of the kingdom, became a military power under Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg, known as "The Great Elector". As a kingdom, Prussia continued its rise to power, especially during the reign of Frederick II, more commonly known as Frederick the Great, who was the third son of Frederick William I.Horn, D. B. "The Youth of Frederick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
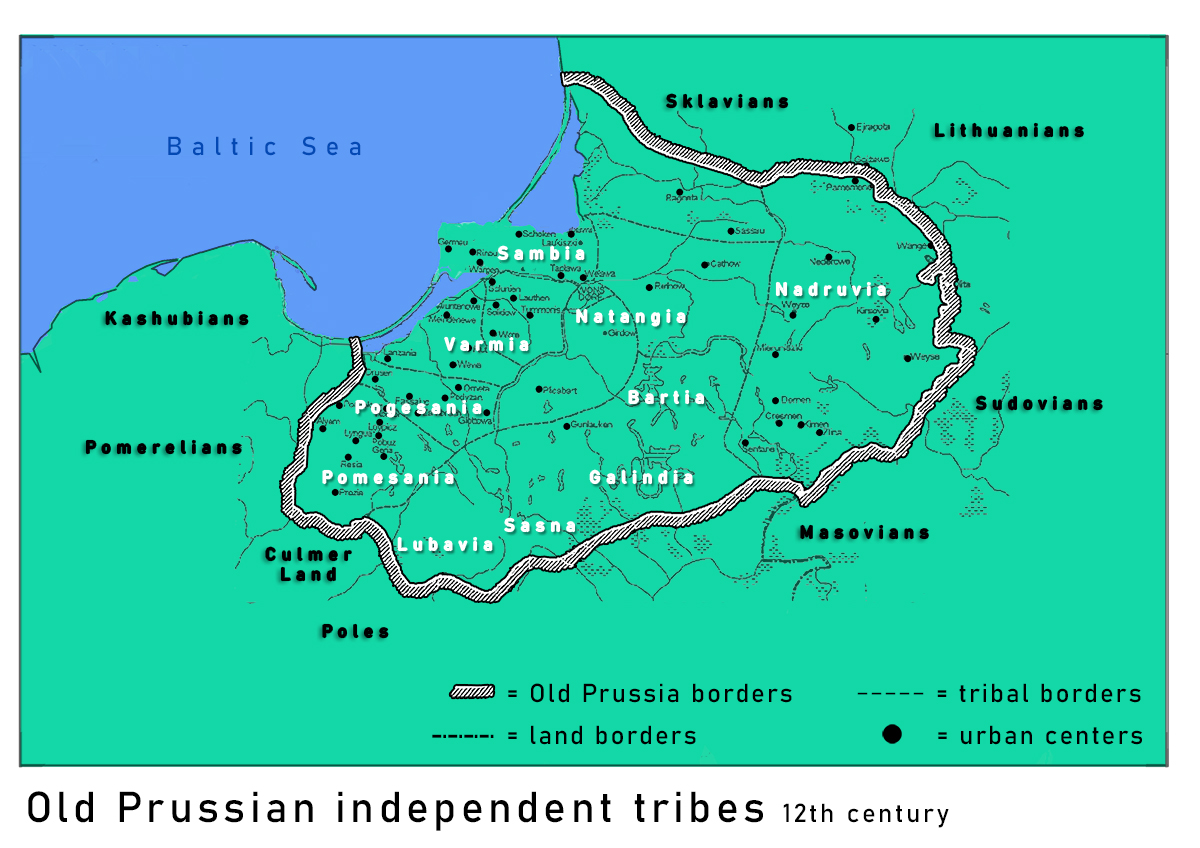
Old Prussians
Old Prussians, Baltic Prussians or simply Prussians (Old Prussian: ''prūsai''; german: Pruzzen or ''Prußen''; la, Pruteni; lv, prūši; lt, prūsai; pl, Prusowie; csb, Prësowié) were an indigenous tribe among the Baltic peoples that inhabited the region of Prussia, at the south-eastern shore of the Baltic Sea between the Vistula Lagoon to the west and the Curonian Lagoon to the east. The Old Prussians, who spoke an Indo-European language now known as Old Prussian and worshipped pre-Christian deities, lent their name, despite very few commonalities, to the later, predominantly Low German-speaking inhabitants of the region. The duchy of the Polans under Mieszko I, which was the predecessor of the Kingdom of Poland, first attempted to conquer and baptize the Baltic tribes during the 10th century, but repeatedly encountered strong resistance. Not until the 13th century were the Old Prussians subjugated and their lands conquered by the Teutonic Order. The remaining Old Prus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klaipėda
Klaipėda (; ; german: Memel; pl, Kłajpeda; russian: Клайпеда; sgs, Klaipieda) is a city in Lithuania on the Baltic Sea coast. The capital of the eponymous county, it is the third largest city and the only major seaport in Lithuania. The city has a complex recorded history, partially due to the combined regional importance of the usually ice-free Port of Klaipėda at the mouth of the river . Located in the region of Lithuania Minor, at various times, it was a part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Prussia and Germany until the 1919 Treaty of Versailles. As a result of the 1923 Klaipėda Revolt it was annexed by Lithuania and has remained with Lithuania to this day, except between 1939 and 1945 when it was occupied by Germany following the 1939 German ultimatum to Lithuania. The population has migrated from the city to its suburbs and hinterland. The number of inhabitants of Klaipėda city shrank from 202,929 in 1989 to 162,360 in 2011, but the urban zone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |