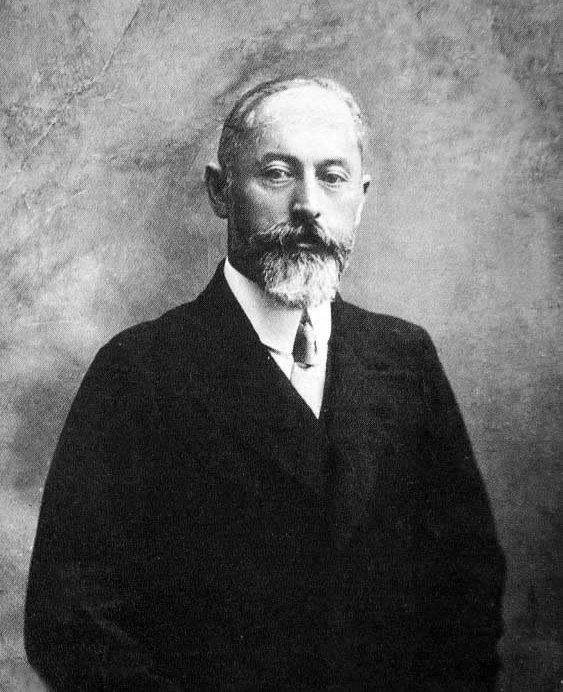|
Vsevolod Balytsky
Vsevolod Apollonovych Balytsky ( uk, Всеволод Аполлонович Балицький; russian: Всеволод Аполлонович Балицкий; 27 November 1892 – 27 November 1937) was a Soviet official, Commissar of State Security 1st Class (equivalent to Four-star General) of the NKVD and a member of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union. Balytsky was born in Verkhnodniprovsk, Yekaterinoslav Governorate in to the family of a Ukrainian clerk. Initially a Menshevik, he joined the Bolshevik Party in 1915. He directed the NKVD of Ukraine during the Great Famine. He blamed the famine on sabotage by the Polish Military Organization and its Ukrainian collaborators; in reality, the Polish Military Organization had been dissolved in 1921 after the Polish–Soviet War, and the remaining Polish spies in Soviet Ukraine were uninvolved in the famine. This story was used as a pretext for the NKVD's deportation of many ethnic Poles from ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Izrail Leplevsky
Izrail Moiseyevich Leplevsky (Russian: Израиль Моисеевич Леплевский; 1894 – July 28, 1938) was a Soviet security officer. He was part of the Intelligence Service and Secret police apparatus in the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, then People's Commissar of Internal Affairs of the Ukrainian SSR from June 14, 1937 to January 25, 1938. His brother Gregory Leplevsky also worked in senior positions in the Soviet Union, including as Prosecutor of the USSR. Early years Born into a Jewish family in Brest-Litovsk, Grodno Governorate, Leplevsky received a home education and worked afterwards in a hat shop, and in a pharmacy warehouse. In 1914 he was enrolled as a conscript in the Russian army and served on the Turkish front from October 1914 till June 1917. Political career In March 1917, Leplevsky became active in the Bolshevik party in Tbilisi. From June 1917 he was a member of the military organization of the RSDLP (Bolshevik) in Yekaterinoslav. Afterward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mensheviks
The Mensheviks (russian: меньшевики́, from меньшинство 'minority') were one of the three dominant factions in the Russian socialist movement, the others being the Bolsheviks and Socialist Revolutionaries. The factions emerged in 1903 following a dispute within the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) between Julius Martov and Vladimir Lenin. The dispute originated at the 2nd Congress of the RSDLP, ostensibly over minor issues of party organization. Martov's supporters, who were in the minority in a crucial vote on the question of party membership, came to be called ''Mensheviks'', derived from the Russian ('minority'), while Lenin's adherents were known as ''Bolsheviks'', from ('majority'). Despite the naming, neither side held a consistent majority over the course of the entire 2nd Congress, and indeed the numerical advantage fluctuated between both sides throughout the rest of the RSDLP's existence until the Russian Revolution. The split ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirror Weekly
''Dzerkalo Tyzhnia'' ( ua, Дзеркало тижня), usually referred to in English as the ''Mirror Weekly'', was one of Ukraine's most influential analytical weekly-publisher newspapers, founded in 1994.The press in Ukraine , ''BBC News'', 31 October 2006 On 27 December 2019 it published its last printed issue, it continued its life as a Ukrainian news website.Zee County: The Mirror of the Week ran its last issue Ukrayinska Pravda (27 December 2019) , its print circulation was 57,000. ''Dz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butovo Firing Range
The Butovo Firing Range or Butovo Shooting Range (russian: Бутовский полигон) was an execution site of the Soviet secret police located near Drozhzhino in Leninsky District, Moscow Oblast from 1938 to 1953. Its use for mass execution has been documented; it was prepared as a site for mass burial. As the late Arseny Roginsky explained: "firing range" was a popular euphemism adopted to describe the mysterious and closely-guarded plots of land that the NKVD began to set aside for mass burials on the eve of the Great Terror. Butovo was used for mass executions and mass graves during Joseph Stalin's Great Purge, with 20,761 prisoners of various nationalities documented as being transported to the site and executed by the NKVD and its successor agencies. The exact number of victims executed at Butovo remains unknown as only fragmentary data has been declassified. Notable victims at Butovo include Gustav Klutsis and Seraphim Chichagov; in addition, more than 1000 memb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Purge
The Great Purge or the Great Terror (russian: Большой террор), also known as the Year of '37 (russian: 37-й год, translit=Tridtsat sedmoi god, label=none) and the Yezhovshchina ('period of Nikolay Yezhov, Yezhov'), was General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, Soviet General Secretary Joseph Stalin's campaign to solidify his power over the party and the state; the Purge, purges were also designed to remove the remaining influence of Leon Trotsky as well as other prominent political rivals within the party. It occurred from August 1936 to March 1938. Following the Death and state funeral of Vladimir Lenin, death of Vladimir Lenin in 1924 a power vacuum opened in the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, Communist Party. Various established figures in Lenin's government attempted to succeed him. Joseph Stalin, the party's General Secretary, outmaneuvered political opponents and ultimately gained control of the Communist Party by 1928. Initially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe Between Hitler And Stalin
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. Comprising the westernmost peninsulas of Eurasia, it shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south and Asia to the east. Europe is commonly considered to be separated from Asia by the watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea and the waterways of the Turkish Straits. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and Europe ... is formed by the Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountains, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |