|
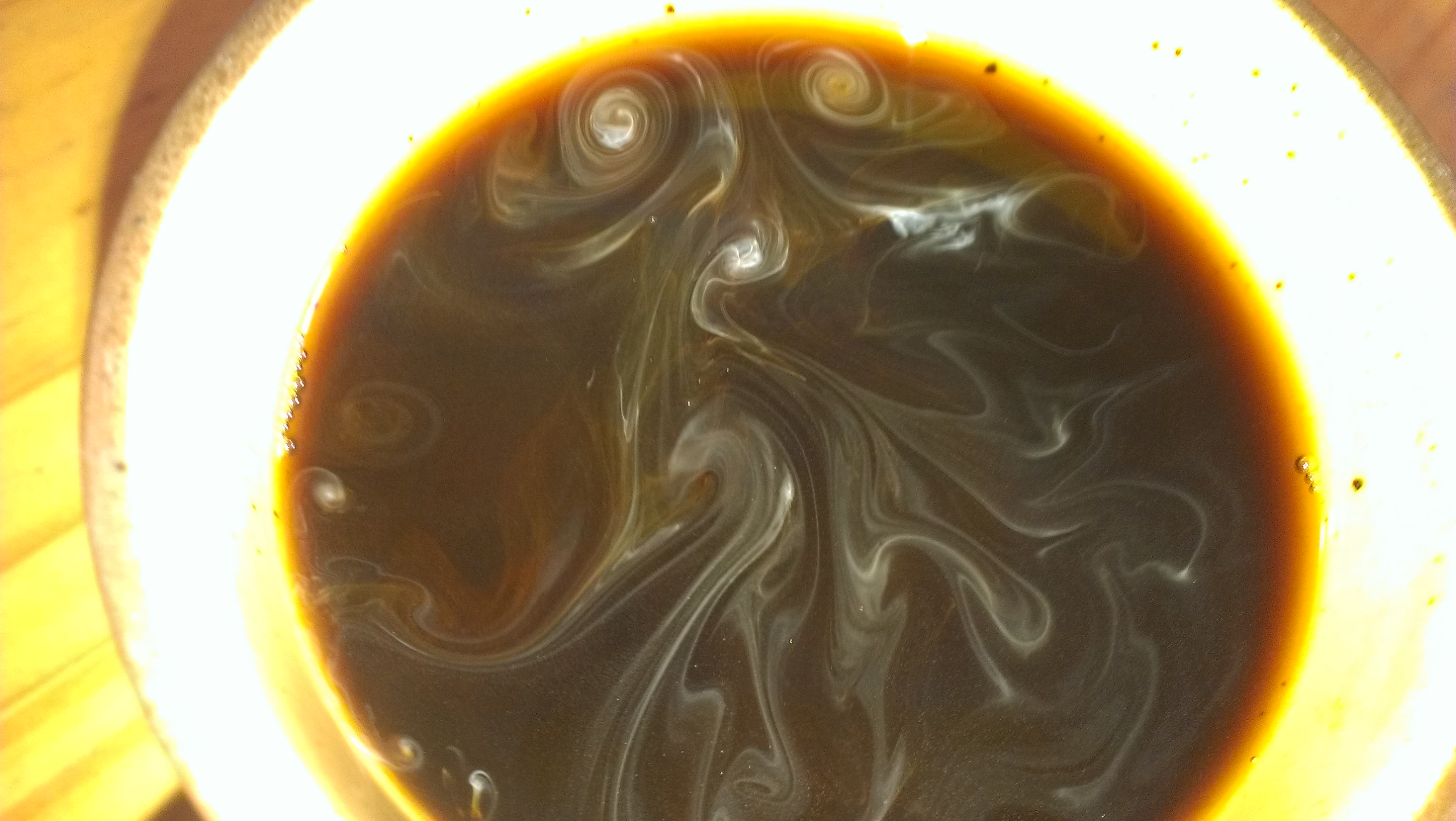
Vortex Ring
A vortex ring, also called a toroidal vortex, is a torus-shaped vortex in a fluid; that is, a region where the fluid mostly spins around an imaginary axis line that forms a closed loop. The dominant flow in a vortex ring is said to be toroidal, more precisely poloidal. Vortex rings are plentiful in turbulent flows of liquids and gases, but are rarely noticed unless the motion of the fluid is revealed by suspended particles—as in the smoke rings which are often produced intentionally or accidentally by smokers. Fiery vortex rings are also a commonly produced trick by fire eaters. Visible vortex rings can also be formed by the firing of certain artillery, in mushroom clouds, and in microbursts. A vortex ring usually tends to move in a direction that is perpendicular to the plane of the ring and such that the inner edge of the ring moves faster forward than the outer edge. Within a stationary body of fluid, a vortex ring can travel for relatively long distance, carrying the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
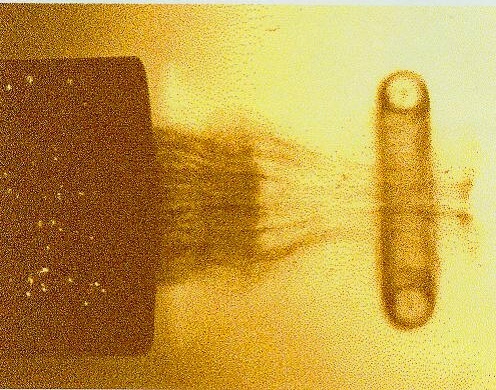
Vortex Ring Gun Schlierin
In fluid dynamics, a vortex ( : vortices or vortexes) is a region in a fluid in which the flow revolves around an axis line, which may be straight or curved. Vortices form in stirred fluids, and may be observed in smoke rings, whirlpools in the wake of a boat, and the winds surrounding a tropical cyclone, tornado or dust devil. Vortices are a major component of turbulent flow. The distribution of velocity, vorticity (the curl of the flow velocity), as well as the concept of circulation are used to characterise vortices. In most vortices, the fluid flow velocity is greatest next to its axis and decreases in inverse proportion to the distance from the axis. In the absence of external forces, viscous friction within the fluid tends to organise the flow into a collection of irrotational vortices, possibly superimposed to larger-scale flows, including larger-scale vortices. Once formed, vortices can move, stretch, twist, and interact in complex ways. A moving vortex carries som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vortex Ring Gun
The vortex ring gun is an experimental non-lethal weapon for crowd control that uses high-energy vortex rings of gas to knock down people or spray them with marking ink or other chemicals. The concept was explored by the US Army starting in 1998, and by some commercial firms. Knockdown of distant individuals currently seems unlikely even if the rings are launched at theoretical maximum speed. As for the delivery of chemicals, leakage during flight is still a problem. Weapons based on similar principles but different designs and purposes have been described before, typically using acetylene-air or hydrogen–oxygen explosions to create and propel the vortices. Operation In a typical concept, a blank cartridge is fired into a gun barrel that has a diverging nozzle screwed onto the muzzle. In the nozzle, the short pulse of high pressure gas briefly accelerates to a supersonic exit velocity, whereupon a portion of the exhaust transforms from axial flow into a subsonic, high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
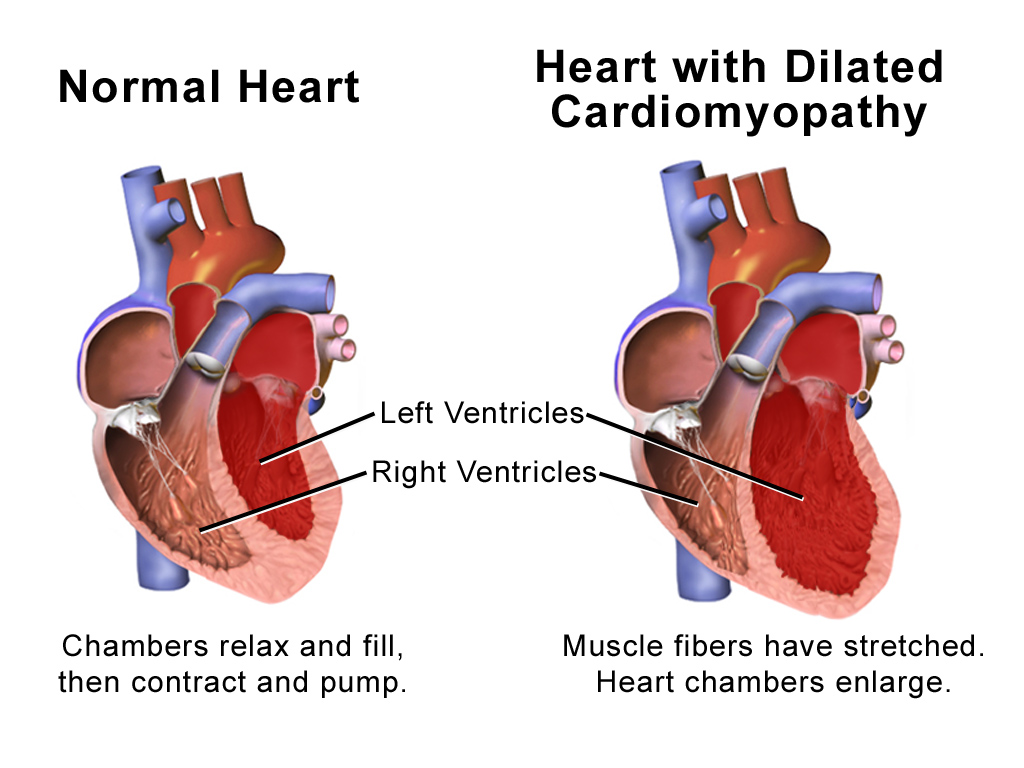
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a condition in which the heart becomes enlarged and cannot pump blood effectively. Symptoms vary from none to feeling tired, leg swelling, and shortness of breath. It may also result in chest pain or fainting. Complications can include heart failure, heart valve disease, or an irregular heartbeat. Causes include genetics, alcohol, cocaine, certain toxins, complications of pregnancy, and certain infections. Coronary artery disease and high blood pressure may play a role, but are not the primary cause. In many cases the cause remains unclear. It is a type of cardiomyopathy, a group of diseases that primarily affects the heart muscle. The diagnosis may be supported by an electrocardiogram, chest X-ray, or echocardiogram. In those with heart failure, treatment may include medications in the ACE inhibitor, beta blocker, and diuretic families. A low salt diet may also be helpful. In those with certain types of irregular heartbeat, blood thinners or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lolliguncula Brevis
''Lolliguncula brevis'', or the Atlantic brief squid, is a small species of squid in the Loliginidae family. It is found in shallow parts of the western Atlantic Ocean. Distribution The Atlantic brief squid occurs most frequently in shallow waters along the eastern seaboard of the United States as far north as Delaware. It has also been found in Argentina, Brazil, the British Virgin Islands, Colombia, Mexico, Panama, Puerto Rico, Suriname, Trinidad and Tobago and Venezuela. Description image:Lolliguncula brevis1.jpg, left, ''Lolliguncula brevis'' The female Atlantic brief squid is about 11 cm long and the male 9 cm. The basic colour is dark reddish-brown to yellow-brown and there are many chromatophores on the upper surface which enable the squid to change colour. The Mantle (mollusc), mantle is widest in the middle and tapers to a rounded point at the back. The fins are wider than they are long, rounded and about half the length of the mantle. The mantle has thick musc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Kelvin
William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, (26 June 182417 December 1907) was a British mathematician, mathematical physicist and engineer born in Belfast. Professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Glasgow for 53 years, he did important work in the mathematical analysis of electricity and formulation of the first and second laws of thermodynamics, and did much to unify the emerging discipline of physics in its contemporary form. He received the Royal Society's Copley Medal in 1883, was its president 1890–1895, and in 1892 was the first British scientist to be elevated to the House of Lords. Absolute temperatures are stated in units of kelvin in his honour. While the existence of a coldest possible temperature (absolute zero) was known prior to his work, Kelvin is known for determining its correct value as approximately −273.15 degrees Celsius or −459.67 degrees Fahrenheit. The Joule–Thomson effect is also named in his honour. He worked closely with mathematics pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Jet
In fluid dynamics, a synthetic jet flow — is a type of jet flow, which is made up of the surrounding fluid. Synthetic jets are generally formed by flow moving back and forth through a small opening. Synthetic jets are produced by periodic ejection and suction of fluid from an orifice induced by movement of a diaphragm inside a cavity among other ways. (http://www.crcpress.com/product/isbn/9781439868102 ) A ''jet flow'' is a fluid flow in which a stream of one fluid mixes with a surrounding medium. An example is a water jet that forms when you put your thumb over the end of a hose. The water mixes with air to form a jet. If you increase the flow of water or move your thumb to change the diameter of the exit, the jet will change dramatically. Jet flows vary depending on velocity and diameter of the flow and the density and viscosity of the fluid (Reynolds number and Mach number). When the velocities in the jet are greater than the speed of sound, important qualitative changes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poiseuille Flow
The poiseuille (symbol Pl) has been proposed as a derived SI unit of dynamic viscosity, named after the French physicist Jean Léonard Marie Poiseuille (1797–1869). In practice the unit has never been widely accepted and most international standards bodies do not include the poiseuille in their list of units. The third edition of the IUPAC Green Book, for example, lists Pa⋅s ( pascal-second The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ...) as the SI-unit for dynamic viscosity, and does not mention the poiseuille. The equivalent CGS unit, the poise, symbol P, is most widely used when reporting viscosity measurements. :1\ \text = 1\ \text\text = 1 \text/\text\text = 1 \text\text/\text^ = 10\ \text\text/\text^ = 10\ \text Liquid water has a viscosity of at at a pressur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kutta Condition
The Kutta condition is a principle in steady-flow fluid dynamics, especially aerodynamics, that is applicable to solid bodies with sharp corners, such as the trailing edges of airfoils. It is named for German mathematician and aerodynamicist Martin Kutta. Kuethe and Schetzer state the Kutta condition as follows:A body with a sharp trailing edge which is moving through a fluid will create about itself a circulation of sufficient strength to hold the rear stagnation point at the trailing edge. In fluid flow around a body with a sharp corner, the Kutta condition refers to the flow pattern in which fluid approaches the corner from above and below, meets at the corner, and then flows away from the body. None of the fluid flows around the sharp corner. The Kutta condition is significant when using the Kutta–Joukowski theorem to calculate the lift created by an airfoil with a sharp trailing edge. The value of circulation of the flow around the airfoil must be that value which woul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shear (fluid)
Shear stress, often denoted by (Greek: tau), is the component of stress coplanar with a material cross section. It arises from the shear force, the component of force vector parallel to the material cross section. ''Normal stress'', on the other hand, arises from the force vector component perpendicular to the material cross section on which it acts. General shear stress The formula to calculate average shear stress is force per unit area.: : \tau = , where: : = the shear stress; : = the force applied; : = the cross-sectional area of material with area parallel to the applied force vector. Other forms Wall shear stress Wall shear stress expresses the retarding force (per unit area) from a wall in the layers of a fluid flowing next to the wall. It is defined as: \tau_w:=\mu\left(\frac\right)_ Where \mu is the dynamic viscosity, u the flow velocity and y the distance from the wall. It is used, for example, in the description of arterial blood flow in which case which there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orifice Plate
An orifice plate is a device used for measuring flow rate, for reducing pressure or for restricting flow (in the latter two cases it is often called a '). Description An orifice plate is a thin plate with a hole in it, which is usually placed in a pipe. When a fluid (whether liquid or gaseous) passes through the orifice, its pressure builds up slightly upstream of the orifice but as the fluid is forced to converge to pass through the hole, the velocity increases and the fluid pressure decreases. A little downstream of the orifice the flow reaches its point of maximum convergence, the ''vena contracta'' (see drawing to the right) where the velocity reaches its maximum and the pressure reaches its minimum. Beyond that, the flow expands, the velocity falls and the pressure increases. By measuring the difference in fluid pressure across tappings upstream and downstream of the plate, the flow rate can be obtained from Bernoulli's equation using coefficients established from extensive r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Tension
Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces at rest to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension is what allows objects with a higher density than water such as razor blades and insects (e.g. water striders) to float on a water surface without becoming even partly submerged. At liquid–air interfaces, surface tension results from the greater attraction of liquid molecules to each other (due to cohesion) than to the molecules in the air (due to adhesion). There are two primary mechanisms in play. One is an inward force on the surface molecules causing the liquid to contract. Second is a tangential force parallel to the surface of the liquid. This ''tangential'' force is generally referred to as the surface tension. The net effect is the liquid behaves as if its surface were covered with a stretched elastic membrane. But this analogy must not be taken too far as the tension in an elastic membrane is dependent on the amount of deformation of the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |