|
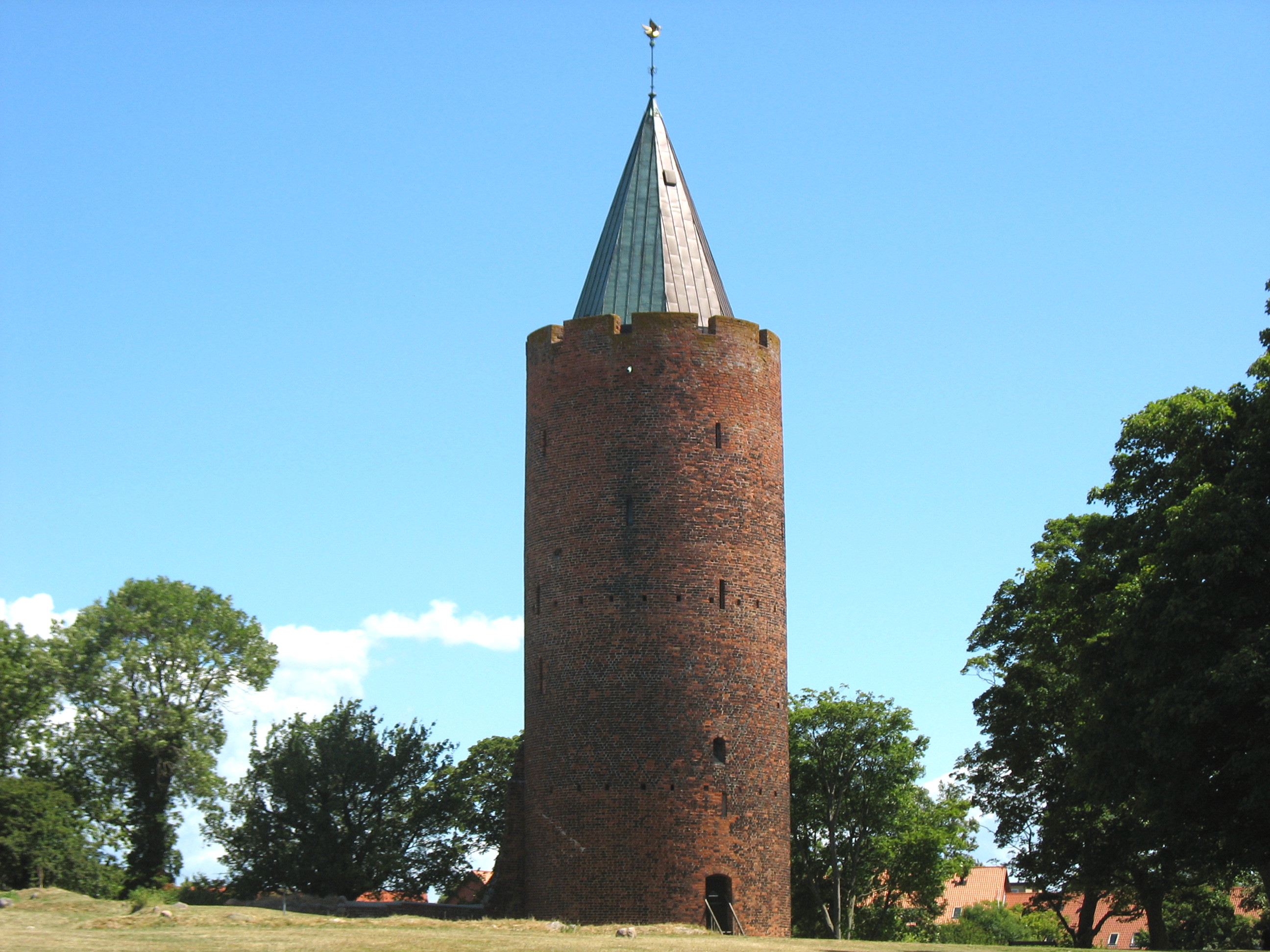
Vordingborg Castle
The Vordingborg Castle ruins (''Vordingborg Slotsruin'') are located in the town of Vordingborg, Denmark and are the town's most famous attraction. History The castle was built in 1175 by King Valdemar I of Denmark as a defensive fortress, and as a base from which to launch raids against the Germany, German coast. His half-brother built another castle in a remote location, which is now Copenhagen. Valdemar II of Denmark, King Valdemar II similarly used the castle for expansion into the Baltic, and in 1241, it was where he created the reformed legal system, the ''Codex Holmiensis, Code of Jutland''. By the time of Valdemar IV of Denmark, King Valdemar IV, the castle had nine towers and a defensive wall, 800 metres long. Large parts of the castle were demolished after the Swedish wars had ended, in order to construct a palace for Prince George of Denmark, Prince George, son of Frederick III of Denmark, King Frederick III. The prince never took up residence, and the palace too was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vordingborg - Gåsetårnet2
Vordingborg () is an old ferry town in Vordingborg Municipality in Denmark with around 18,000 inhabitants. Because of three large estates surrounding the town, a coherent urban development has not been possible, which is the reason why three satellite towns (former villages) have emerged around the town. Within the ring of estates, the town has 12,000 inhabitants, and 17,868 inhabitants when including the three satellite towns of Ørslev, Nyråd, and Stensved, situated 1, 3 and 5 kilometres, respectively, from the town of Vordingborg. Vordingborg Municipality (Kommune) has a population of 45,352. Long term head coach of the Danish national football team, Morten Olsen, was born in Vordingborg. History On 1 January 2007 the old Vordingborg municipality was, as the result of Municipalities of Denmark#Municipal Reform 2007, ''Kommunalreformen'' ("The Municipal Reform" of 2007), merged with Langebæk, Møn, and Præstø municipalities to form an enlarged Vordingborg municipality. G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Castles And Palaces In Denmark
This is a consolidated list of castles and palaces in Denmark. The Danish word ''slot '', like the word ''schloss'' in the related Germanic language— modern German— can mean either castle, a Country house or palace, in accordance with common English usage. Whenever possible traditional English translations provided by the Danish Palaces and Properties Agency, a national agency maintaining and utilising the states palaces, castles and gardens, have been used to determine whether a property should be called a castle or a palace. When not possible the following guidelines, which are in general keeping with the above translations, and with Wikipedia articles have been used: * Castle: Generally older building, generally a fortified building * Palace: Generally newer building, generally a non-fortified building used primarily as a residence Other related words The Danish word ''borg'', which appears at the end of many castle and palace names literally means "fortified castle", b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castles In Region Zealand
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified residence of a lord or noble. This is distinct from a palace, which is not fortified; from a fortress, which was not always a residence for royalty or nobility; from a ''pleasance'' which was a walled-in residence for nobility, but not adequately fortified; and from a fortified settlement, which was a public defence – though there are many similarities among these types of construction. Use of the term has varied over time and has also been applied to structures such as hill forts and 19th-20th century homes built to resemble castles. Over the approximately 900 years when genuine castles were built, they took on a great many forms with many different features, although some, such as curtain walls, arrowslits, and portcullises, were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Castles In Denmark
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruins In Denmark
Ruins () are the remains of a civilization's architecture. The term refers to formerly intact structures that have fallen into a state of partial or total disrepair over time due to a variety of factors, such as lack of maintenance, deliberate destruction by humans, or uncontrollable destruction by natural phenomena. The most common root causes that yield ruins in their wake are natural disasters, armed conflict, and population decline, with many structures becoming progressively derelict over time due to long-term weathering and scavenging. There are famous ruins all over the world, with notable sites originating from ancient China, the Indus Valley and other regions of ancient India, ancient Iran, ancient Israel and Judea, ancient Iraq, ancient Greece, ancient Egypt, Roman sites throughout the Mediterranean Basin, and Incan and Mayan sites in the Americas. Ruins are of great importance to historians, archaeologists and anthropologists, whether they were once individual fort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Towers In Denmark
A tower is a tall structure, taller than it is wide, often by a significant factor. Towers are distinguished from masts by their lack of guy-wires and are therefore, along with tall buildings, self-supporting structures. Towers are specifically distinguished from buildings in that they are built not to be habitable but to serve other functions using the height of the tower. For example, the height of a clock tower improves the visibility of the clock, and the height of a tower in a fortified building such as a castle increases the visibility of the surroundings for defensive purposes. Towers may also be built for observation, leisure, or telecommunication purposes. A tower can stand alone or be supported by adjacent buildings, or it may be a feature on top of a larger structure or building. Etymology Old English ''torr'' is from Latin ''turris'' via Old French ''tor''. The Latin term together with Greek τύρσις was loaned from a pre-Indo-European Mediterranean langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Vordingborg Municipality
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castles In Denmark
This is a consolidated list of castles and palaces in Denmark. The Danish word ''slot '', like the word ''schloss'' in the related Germanic language— modern German— can mean either castle, a Country house or palace, in accordance with common English usage. Whenever possible traditional English translations provided by the Danish Palaces and Properties Agency, a national agency maintaining and utilising the states palaces, castles and gardens, have been used to determine whether a property should be called a castle or a palace. When not possible the following guidelines, which are in general keeping with the above translations, and with Wikipedia articles have been used: * Castle: Generally older building, generally a fortified building * Palace: Generally newer building, generally a non-fortified building used primarily as a residence Other related words The Danish word ''borg'', which appears at the end of many castle and palace names literally means "fortified castle", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th-century Disestablishments In Denmark
The 18th century lasted from January 1, 1701 ( MDCCI) to December 31, 1800 ( MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the American, French, and Haitian Revolutions. During the century, slave trading and human trafficking expanded across the shores of the Atlantic, while declining in Russia, China, and Korea. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures, including the structures and beliefs that supported slavery. The Industrial Revolution began during mid-century, leading to radical changes in human society and the environment. Western historians have occasionally defined the 18th century otherwise for the purposes of their work. For example, the "short" 18th century may be defined as 1715–1789, denoting the period of time between the death of Louis XIV of France and the start of the French Revolution, with an emphasis on directly interconnected events. To historians who expand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12th-century Establishments In Denmark
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures Demolished In The 18th Century
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12th-century Fortifications
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |