|
Volga (rocket Stage)
Volga, GRAU index 14S46, also designated 141KS, is a rocket upper stage designed in Russia. It is used with the Soyuz-2.1a and Soyuz-2-1v rockets to insert payloads into sun-synchronous orbit. It is derived from the propulsion module of the Yantar spy satellite A reconnaissance satellite or intelligence satellite (commonly, although unofficially, referred to as a spy satellite) is an Earth observation satellite or communications satellite deployed for military or intelligence applications. The ...s. It is closely related to the retired Ikar upper stage. References Expendable space launch systems Rocket stages Space launch vehicles of Russia {{Rocket-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TsSKB-Progress
The Progress Rocket Space Centre (russian: Ракетно-космический центр «Прогресс»), formerly known as TsSKB-Progress (russian: ЦСКБ-Прогресс), is a Russian joint-stock company under the jurisdiction of Roscosmos State Corporation responsible for space science and aerospace research. It was the developer of the famous Soyuz-FG rocket that was used for crewed space flight, as well as the Soyuz-U that was used for launching uncrewed probes. Overview Progress Centre was the developer and manufacturer of the Soyuz FG series of launch vehicles that were used for human spaceflight launches, and the Soyuz-U series that were used for robotic spacecraft launches. Commercial marketing of these launch vehicles was handled by the company Starsem. TsSKB-Progress' satellite products include the Foton and Foton-M science satellite series, the Yantar military satellites and the Resurs DK Earth resource satellite. The company's main production ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinitrogen Tetraoxide
Dinitrogen tetroxide, commonly referred to as nitrogen tetroxide (NTO), and occasionally (usually among ex-USSR/Russia rocket engineers) as amyl, is the chemical compound N2O4. It is a useful reagent in chemical synthesis. It forms an equilibrium mixture with nitrogen dioxide. Its molar mass is 92.011 g/mol. Dinitrogen tetroxide is a powerful oxidizer that is hypergolic (spontaneously reacts) upon contact with various forms of hydrazine, which has made the pair a common bipropellant for rockets. Structure and properties Dinitrogen tetroxide could be regarded as two nitro groups (-NO2) bonded together. It forms an equilibrium mixture with nitrogen dioxide. The molecule is planar with an N-N bond distance of 1.78Å and N-O distances of 1.19Å. The N-N distance corresponds to a weak bond, since it is significantly longer than the average N-N single bond length of 1.45Å. This exceptionally weak σ bond (amounting to overlapping of the ''sp''2 hybrid orbitals of the two NO2 units) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UDMH
Unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine (UDMH; 1,1-dimethylhydrazine, НДМГ or codenamed Geptil) is a chemical compound with the formula H2NN(CH3)2 that is used as a rocket propellant. It is a colorless liquid, with a sharp, fishy, ammonia-like smell typical for organic amines. Samples turn yellowish on exposure to air and absorb oxygen and carbon dioxide. It is miscible with water, ethanol, and kerosene. In concentration between 2.5% and 95% in air, its vapors are flammable. It is not sensitive to shock. Symmetrical dimethylhydrazine, 1,2-dimethylhydrazine is also known but is not as useful. Production UDMH is produced industrially by two routes. Based on the Olin Raschig process, one method involves reaction of monochloramine with dimethylamine giving 1,1-dimethylhydrazinium chloride: :(CH3)2NH + NH2Cl → (CH3)2NNH2 ⋅ HCl In the presence of suitable catalysts, acetylhydrazine can be N-dimethylated using formaldehyde and hydrogen to give the N,N-dimethyl-N'-acetylhydrazine, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GRAU Index
The Main Missile and Artillery Directorate of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation (), commonly referred to by its transliterated Russian acronym GRAU (), is a department of the Russian Ministry of Defense. It is subordinate to the Chief of Armament and Munition of the Russian Armed Forces, a vice-minister of defense. The organization dates back to 1862 when it was established under the name Главное артиллерийское управление (ГАУ – GAU). The "R" from "rockets" was added to the title in 1960. In particular, the GRAU is responsible for assigning GRAU indices to Russian army munitions and equipment. Arsenals of the GRAU, according to Kommersant-Vlast in 2005, include the 60th at Kaluga, the 55th at Rzhev, the 75th at Serpukhov south of Moscow, (all three in the Moscow Military District) and the 80th at Gagarskiy, the 116th at Krasno-Oktyabrskiy and the 5th, all in the Volga–Urals Military District.Kommersant-Vlast, Vys Rossi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Stage
A multistage rocket or step rocket is a launch vehicle that uses two or more rocket ''stages'', each of which contains its own engines and propellant. A ''tandem'' or ''serial'' stage is mounted on top of another stage; a ''parallel'' stage is attached alongside another stage. The result is effectively two or more rockets stacked on top of or attached next to each other. Two-stage rockets are quite common, but rockets with as many as five separate stages have been successfully launched. By jettisoning stages when they run out of propellant, the mass of the remaining rocket is decreased. Each successive stage can also be optimized for its specific operating conditions, such as decreased atmospheric pressure at higher altitudes. This ''staging'' allows the thrust of the remaining stages to more easily accelerate the rocket to its final speed and height. In serial or tandem staging schemes, the first stage is at the bottom and is usually the largest, the second stage and subsequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz-2 (rocket)
Soyuz-2 (GRAU index 14A14) is a modernized version of the Soviet Soyuz rocket. In its basic form, it is a three-stage launch vehicle for placing payloads into low Earth orbit. Compared to the previous versions of the Soyuz, the first-stage boosters and two core stages feature uprated engines with improved injection systems. Digital flight control and telemetry systems allow the rocket to be launched from a fixed launch platform, whereas the launch platforms for earlier Soyuz rockets had to be rotated as the rocket could not perform a roll to change its heading in flight. Soyuz-2 is often flown with an upper stage, which allows it to lift payloads into higher orbits, such as Molniya and geosynchronous orbits. The upper stage is equipped with independent flight control and telemetry systems from those used in the rest of the rocket. The NPO Lavochkin manufactured Fregat is the most commonly used upper stage. Soyuz-2 rockets were first launched from Site 31 at the Baikonur Cosm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz-2-1v
The Soyuz-2.1v (russian: Союз 2.1в, ''Union 2.1v''), GRAU index 14A15, known earlier in development as the Soyuz-1 (russian: Союз 1, ''Union 1''), is a Russian expendable launch vehicle. It was derived from the Soyuz-2.1b, and is a member of the R-7 family of rockets. It is built by TsSKB Progress, at Samara in Russia. Launches are conducted from existing facilities at the Plesetsk Cosmodrome in Northwest Russia, with pads also available at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, and new facilities at the Vostochny Cosmodrome in Eastern Russia. Vehicle The Soyuz-2.1v represents a major departure from earlier Soyuz rockets. Unlike the Soyuz-2.1b upon which it is based, it does away with the four boosters used on all other R-7 vehicles. The first stage of the Soyuz-2.1v is a heavily modified derivative of the Soyuz-2 second stage, with a single-chamber NK-33 engine replacing the four-chamber RD-107 used on previous rockets along with structural modifications to the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun-synchronous Orbit
A Sun-synchronous orbit (SSO), also called a heliosynchronous orbit, is a nearly polar orbit around a planet, in which the satellite passes over any given point of the planet's surface at the same local mean solar time. More technically, it is an orbit arranged so that it precesses through one complete revolution each year, so it always maintains the same relationship with the Sun. Applications A Sun-synchronous orbit is useful for imaging, reconnaissance, and weather satellites, because every time that the satellite is overhead, the surface illumination angle on the planet underneath it is nearly the same. This consistent lighting is a useful characteristic for satellites that image the Earth's surface in visible or infrared wavelengths, such as weather and spy satellites, and for other remote-sensing satellites, such as those carrying ocean and atmospheric remote-sensing instruments that require sunlight. For example, a satellite in Sun-synchronous orbit might ascend acros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yantar (satellite)
Yantar ( rus, Янтарь meaning amber) is a series of Russian (previously Soviet) reconnaissance satellites, which supplemented and eventually replaced the Zenit spacecraft. Kosmos 2175, a Yantar-4K2 or ''Kobalt'' spacecraft, was the first satellite to be launched by the Russian Federation following the dissolution of the Soviet Union. Yantar-Terilen was the first real-time digital system. Yantar satellites also formed the basis for the later Orlets, Resurs and Persona satellites. 179 have been launched, nine of which were lost in launch failures. All Yantar satellites were launched using the Soyuz-U carrier rocket until Kosmos 2480 in 2012 which was announced as the last launch of that rocket from Plesetsk. Subsequent launches used the modernized Soyuz-2.1a rocket. The last Yantar mission was Kosmos 2505, a Yantar-4K2M or ''Kobalt-M'', launched on 5 June 2015. Reconnaissance missions have been taken over by the Persona class of satellites. History In 1964, Soviet design bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
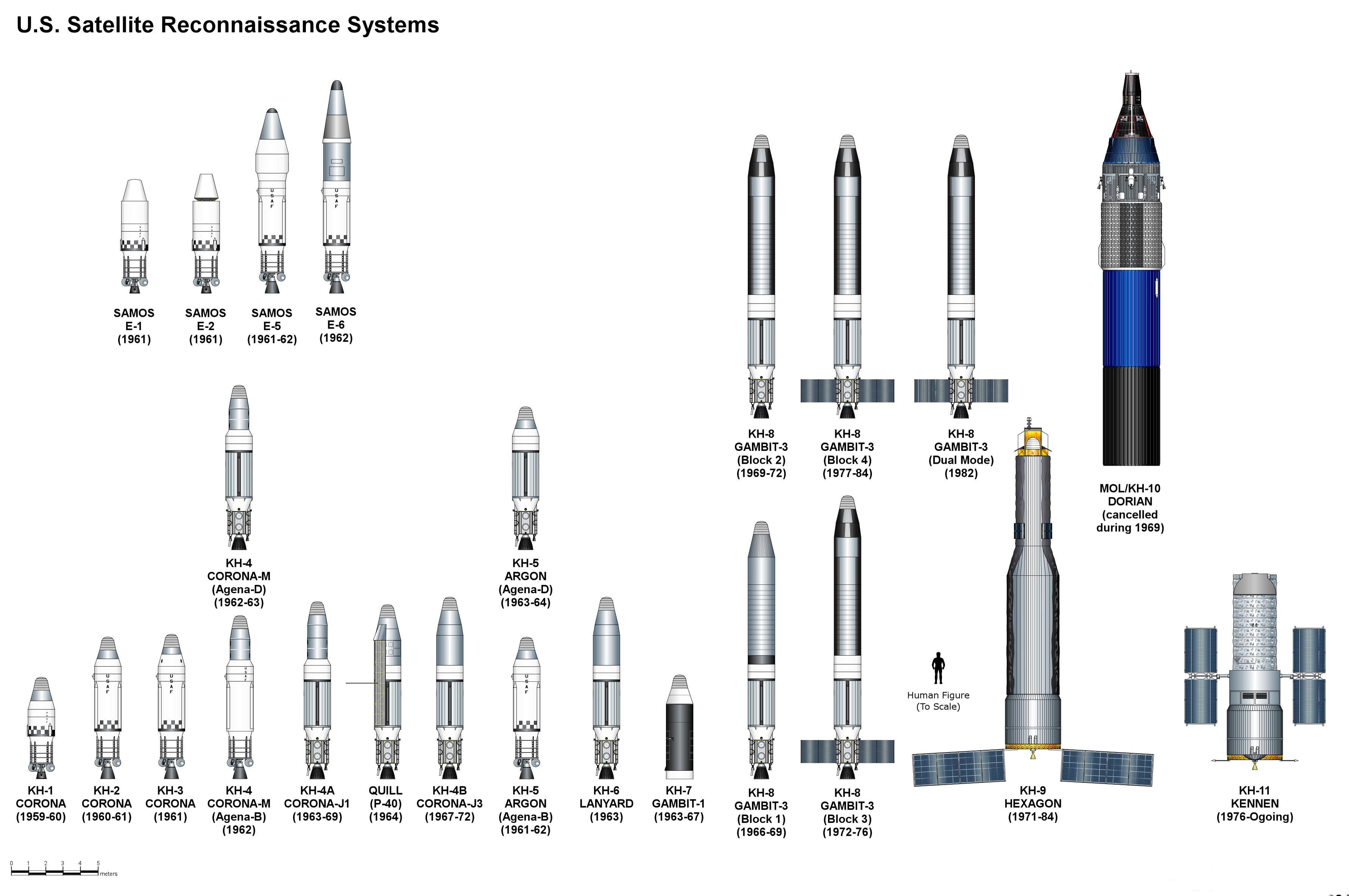
Spy Satellite
A reconnaissance satellite or intelligence satellite (commonly, although unofficially, referred to as a spy satellite) is an Earth observation satellite or communications satellite deployed for military or intelligence applications. The first generation type (i.e., Corona and Zenit) took photographs, then ejected canisters of photographic film which would descend back down into Earth's atmosphere. Corona capsules were retrieved in mid-air as they floated down on parachutes. Later, spacecraft had digital imaging systems and downloaded the images via encrypted radio links. In the United States, most information available about reconnaissance satellites is on programs that existed up to 1972, as this information has been declassified due to its age. Some information about programs before that time is still classified information, and a small amount of information is available on subsequent missions. A few up-to-date reconnaissance satellite images have been declassified o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ikar (rocket Stage)
The Ikar was a rocket upper stage designed in Russia in 1999 to be used with the Soyuz 11A511U rocket as Soyuz-Ikar. It was derived from the propulsion module of the Yantar spy satellite A reconnaissance satellite or intelligence satellite (commonly, although unofficially, referred to as a spy satellite) is an Earth observation satellite or communications satellite deployed for military or intelligence applications. The ...s. References Expendable space launch systems Rocket stages Space launch vehicles of Russia {{Rocket-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |