|
Voice-grade Copper
Category 3 cable, commonly known as or station wire, and less commonly known as VG or voice-grade (as, for example, in 100BaseVG), is an unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable used in telephone wiring. It is part of a family of standards defined jointly by the Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) and the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) and published in TIA/EIA-568-B. Although designed to reliably carry data up to 10 Mbit/s, modern data networks run at much higher speeds, and or better cable is generally used for new installations. Networking was widely used in computer networking in the early 1990s for 10BASE-T Ethernet and, to a much lesser extent, for 100BaseVG Ethernet, Token Ring and 100BASE-T4. The original Power over Ethernet 802.3af specification supports the use of cable, but the later 802.3at Type 2 high-power variation does not.IEEE 802.3at-2009, clause 33.1.1c In some use cases and for short distances, Cat 3 may be capable of carrying 100BAS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
100BaseVG
100BaseVG is a 100 Mbit/s Ethernet standard specified to run over four pairs of category 3 cable (cable also known as voice grade, hence the "VG"). It is also called 100VG-AnyLAN because it was defined to carry both Ethernet and Token Ring frame types. 100BaseVG was originally proposed by Hewlett-Packard, ratified by the IEEE in 1995 and was practically extinct by 1998. In 2001 IEEE recorded the status of its 100BaseVG standard as being a "Withdrawn Standard" (defined as "A standard which is no longer maintained and which may contain significant obsolete or erroneous information.") Standardization 100BaseVG started in the IEEE 802.3 committee as Fast Ethernet. One faction wanted to keep carrier-sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) in order to keep it pure Ethernet, even though the collision domain problem limited the distances to one tenth that of 10BASE-T. Another faction wanted to change to a polling architecture from the hub (they called it " De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
100BASE-T4
In computer networking, Fast Ethernet physical layers carry traffic at the nominal rate of 100 Mbit/s. The prior Ethernet speed was 10 Mbit/s. Of the Fast Ethernet physical layers, 100BASE-TX is by far the most common. Fast Ethernet was introduced in 1995 as the IEEE 802.3u standard and remained the fastest version of Ethernet for three years before the introduction of Gigabit Ethernet. The acronym ''GE/FE'' is sometimes used for devices supporting both standards. Nomenclature The "100" in the media type designation refers to the transmission speed of 100 Mbit/s, while the "BASE" refers to baseband signaling. The letter following the dash ("T" or "F") refers to the physical medium that carries the signal (twisted pair or fiber, respectively), while the last character ("X", "4", etc.) refers to the line code method used. Fast Ethernet is sometimes referred to as 100BASE-X, where "X" is a placeholder for the FX and TX variants. General design Fast Ethernet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
100BASE-TX
In computer networking, Fast Ethernet physical layers carry traffic at the nominal rate of 100 Mbit/s. The prior Ethernet speed was 10 Mbit/s. Of the Fast Ethernet physical layers, 100BASE-TX is by far the most common. Fast Ethernet was introduced in 1995 as the IEEE 802.3u standard and remained the fastest version of Ethernet for three years before the introduction of Gigabit Ethernet. The acronym ''GE/FE'' is sometimes used for devices supporting both standards. Nomenclature The "100" in the media type designation refers to the transmission speed of 100 Mbit/s, while the "BASE" refers to baseband signaling. The letter following the dash ("T" or "F") refers to the physical medium that carries the signal (twisted pair or fiber, respectively), while the last character ("X", "4", etc.) refers to the line code method used. Fast Ethernet is sometimes referred to as 100BASE-X, where "X" is a placeholder for the FX and TX variants. General design Fast Ethernet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structured Cabling
In telecommunications, structured cabling is building or campus cabling infrastructure that consists of a number of standardized smaller elements (hence structured) called subsystems. Structured cabling components include twisted pair and optical cabling, patch panels and patch cables. Overview Structured cabling is the design and installation of a cabling system that will support multiple hardware uses and be suitable for today's needs and those of the future. With a correctly installed system, current and future requirements can be met, and hardware that is added in the future will be supported Structured cabling design and installation is governed by a set of standards that specify wiring data centers, offices, and apartment buildings for data or voice communications using various kinds of cable, most commonly category 5e (Cat 5e), category 6 (Cat 6), and fiber optic cabling and modular connectors. These standards define how to lay the cabling in various topologies in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
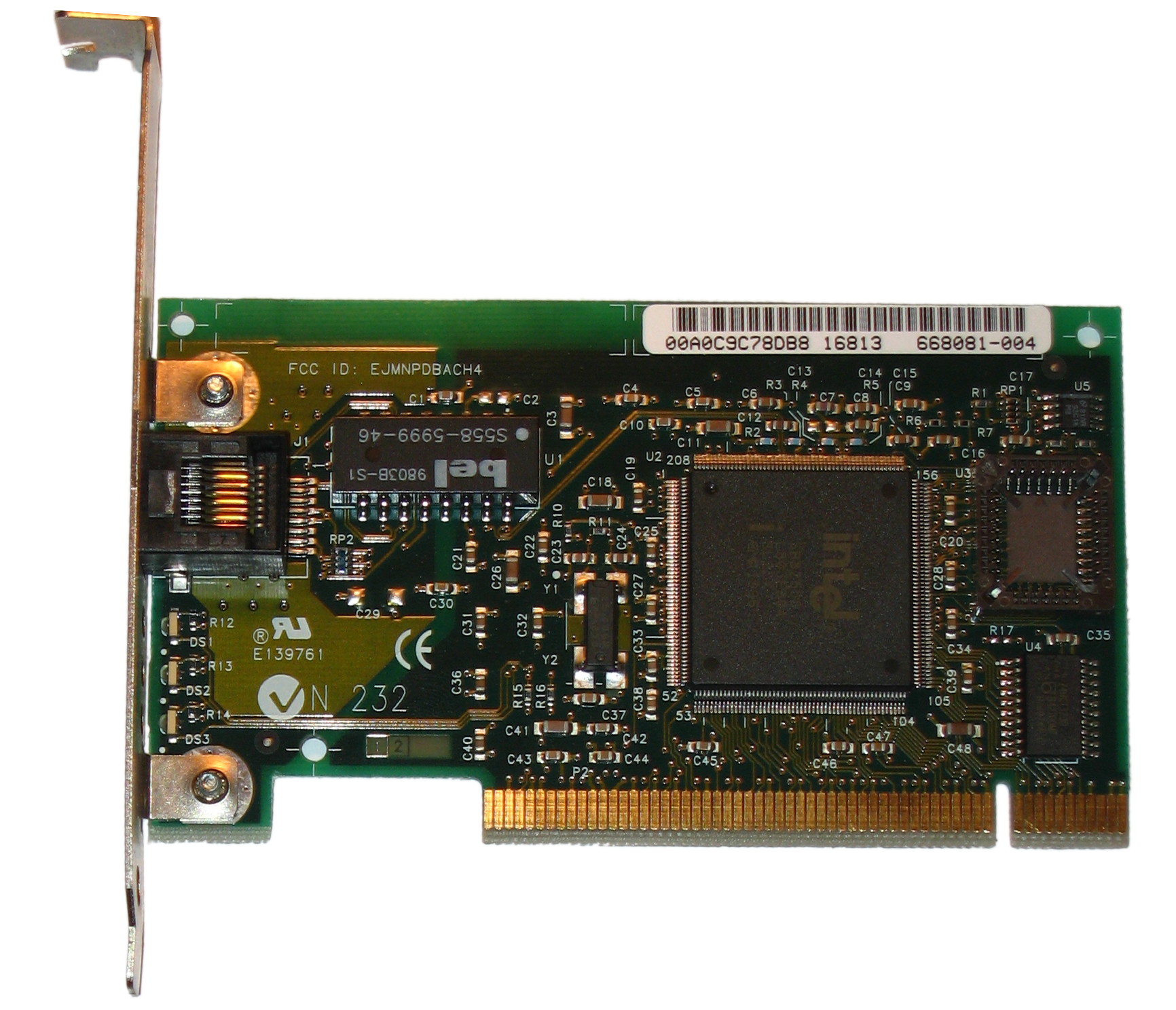
Network Interface Controller
A network interface controller (NIC, also known as a network interface card, network adapter, LAN adapter or physical network interface, and by similar terms) is a computer hardware component that connects a computer to a computer network. Early network interface controllers were commonly implemented on expansion cards that plugged into a computer bus. The low cost and ubiquity of the Ethernet standard means that most newer computers have a network interface built into the motherboard, or is contained into a USB-connected dongle. Modern network interface controllers offer advanced features such as interrupt and DMA interfaces to the host processors, support for multiple receive and transmit queues, partitioning into multiple logical interfaces, and on-controller network traffic processing such as the TCP offload engine. Purpose The network controller implements the electronic circuitry required to communicate using a specific physical layer and data link layer standard such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hewlett Packard Enterprise
The Hewlett Packard Enterprise Company (HPE) is an American multinational information technology company based in Spring, Texas, United States. HPE was founded on November 1, 2015, in Palo Alto, California, as part of the splitting of the Hewlett-Packard company. It is a business-focused organization which works in servers, storage, networking, containerization software and consulting and support. The split was structured so that the former Hewlett-Packard Company would change its name to HP Inc. and spin off Hewlett Packard Enterprise as a newly created company. HP Inc. retained the old HP's personal computer and printing business, as well as its stock-price history and original NYSE ticker symbol for Hewlett-Packard; Enterprise trades under its own ticker symbol: HPE. At the time of the spin-off, HPE's revenue was slightly less than that of HP Inc. In 2017, HPE spun off its Enterprise Services business and merged it with Computer Sciences Corporation to become DXC Technol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 series of instruction sets, the instruction sets found in most personal computers (PCs). Incorporated in Delaware, Intel ranked No. 45 in the 2020 ''Fortune'' 500 list of the largest United States corporations by total revenue for nearly a decade, from 2007 to 2016 fiscal years. Intel supplies microprocessors for computer system manufacturers such as Acer, Lenovo, HP, and Dell. Intel also manufactures motherboard chipsets, network interface controllers and integrated circuits, flash memory, graphics chips, embedded processors and other devices related to communications and computing. Intel (''int''egrated and ''el''ectronics) was founded on July 18, 1968, by semiconductor pioneers Gordon Moore (of Moore's law) and Robert Noyce ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3com
3Com Corporation was an American digital electronics manufacturer best known for its computer network products. The company was co-founded in 1979 by Robert Metcalfe, Howard Charney and others. Bill Krause joined as President in 1981. Metcalfe explained the name 3Com was a contraction of "Computer Communication Compatibility", with its focus on Ethernet technology that he had co-invented, which enabled the networking of computers. 3Com provided network interface controller and switches, routers, wireless access points and controllers, IP voice systems, and intrusion prevention systems. The company was based in Santa Clara, California. From its 2007 acquisition of 100 percent ownership of H3C Technologies Co., Limited (H3C) —initially a joint venture with China-based Huawei Technologies—3Com achieved a market presence in China, and a significant networking market share in Europe, Asia, and the Americas. 3Com products were sold under the brands 3Com, H3C, and TippingPoint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Over Ethernet
Power over Ethernet, or PoE, describes any of several standards or ad hoc systems that pass electric power along with data on twisted-pair Ethernet cabling. This allows a single cable to provide both data connection and electrical power to devices such as wireless access points (WAPs), Internet Protocol (IP) cameras, and voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) phones. There are several common techniques for transmitting power over Ethernet cabling. Three of them have been standardized by Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) standard IEEE 802.3 since 2003. These standards are known as ''alternative A'', ''alternative B'', and ''4PPoE''. For 10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX, only two of the four signal pairs in typical Cat 5 cable are used. Alternative B separates the data and the power conductors, making troubleshooting easier. It also makes full use of all four twisted pairs in a typical Cat 5 cable. The positive voltage is applied to pins 4 and 5, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Token Ring
Token Ring network IBM hermaphroditic connector with locking clip. Screen contacts are prominently visible, gold-plated signal contacts less so. Token Ring is a computer networking technology used to build local area networks. It was introduced by IBM in 1984, and standardized in 1989 as IEEE 802.5. It uses a special three-byte frame called a ''token'' that is passed around a logical ''ring'' of workstations or servers. This token passing is a channel access method providing fair access for all stations, and eliminating the collisions of contention-based access methods. Token Ring was a successful technology, particularly in corporate environments, but was gradually eclipsed by the later versions of Ethernet. History A wide range of different local area network technologies were developed in the early 1970s, of which one, the Cambridge Ring, had demonstrated the potential of a token passing ring topology, and many teams worldwide began working on their own implementations. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unshielded Twisted Pair
Twisted pair cabling is a type of wiring used for communications in which two conductors of a single circuit are twisted together for the purposes of improving electromagnetic compatibility. Compared to a single conductor or an untwisted balanced pair, a twisted pair reduces electromagnetic radiation from the pair and crosstalk between neighboring pairs and improves rejection of external electromagnetic interference. It was invented by Alexander Graham Bell. For additional noise immunity, twisted-pair cabling may be shielded. Cable with shielding is known as shielded twisted pair (STP) and without as unshielded twisted pair (UTP). Explanation A twisted pair can be used as a balanced line, which as part of a balanced circuit can greatly reduce the effect of noise currents induced on the line by coupling of electric or magnetic fields. The idea is that the currents induced in each of the two wires are very nearly equal. The twisting ensures that the two wires are on average ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10BASE-T
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |